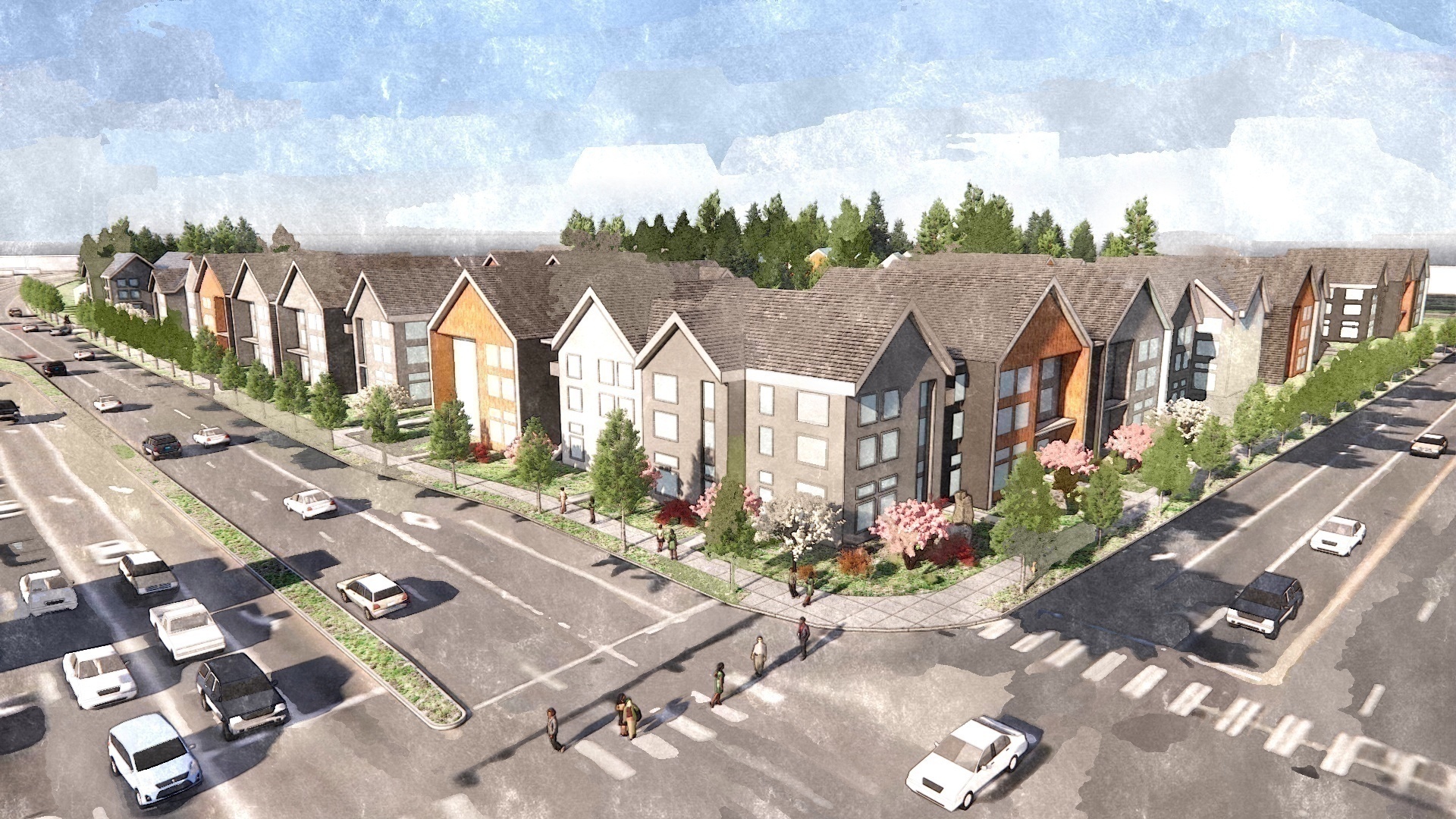
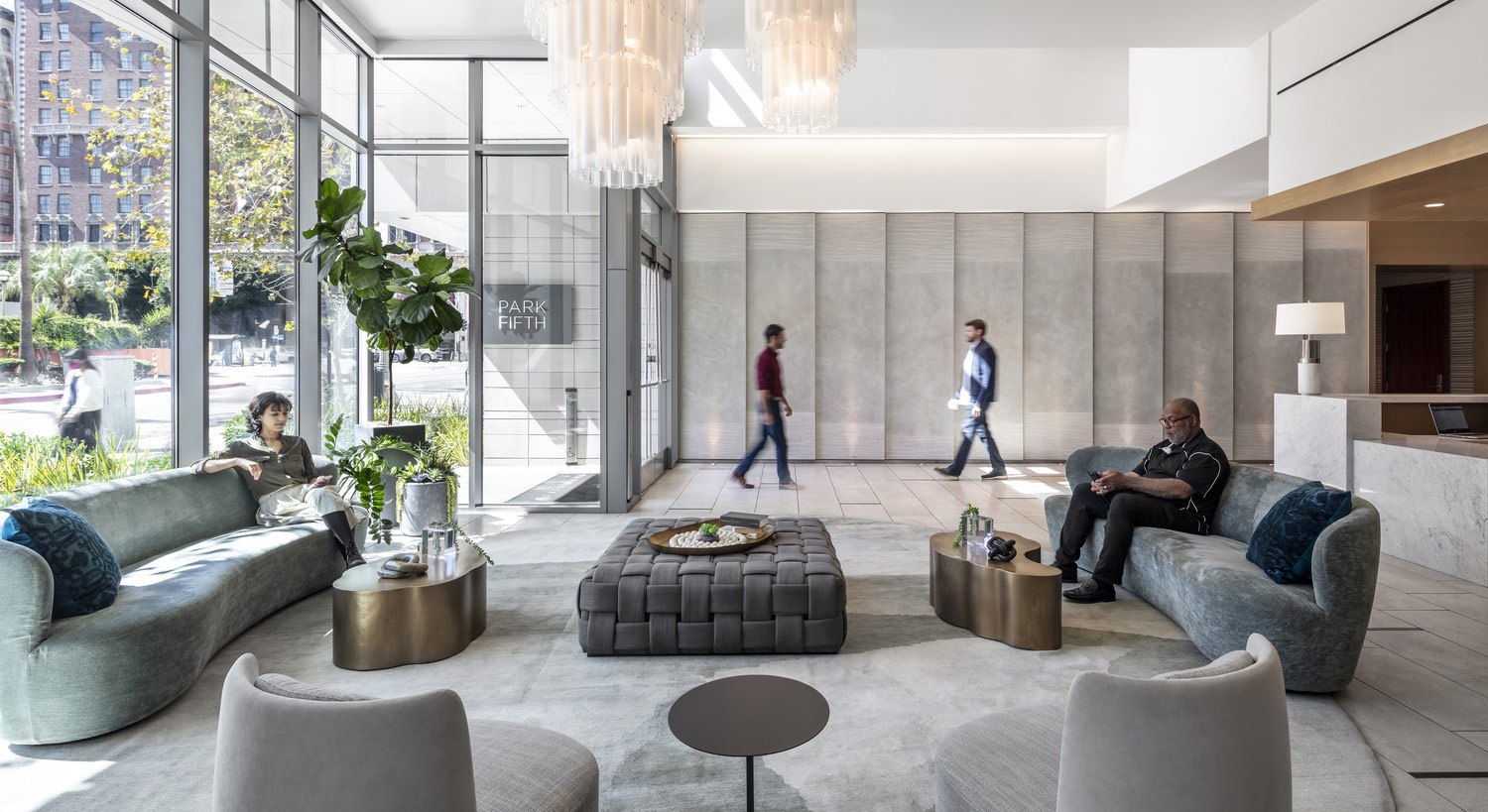
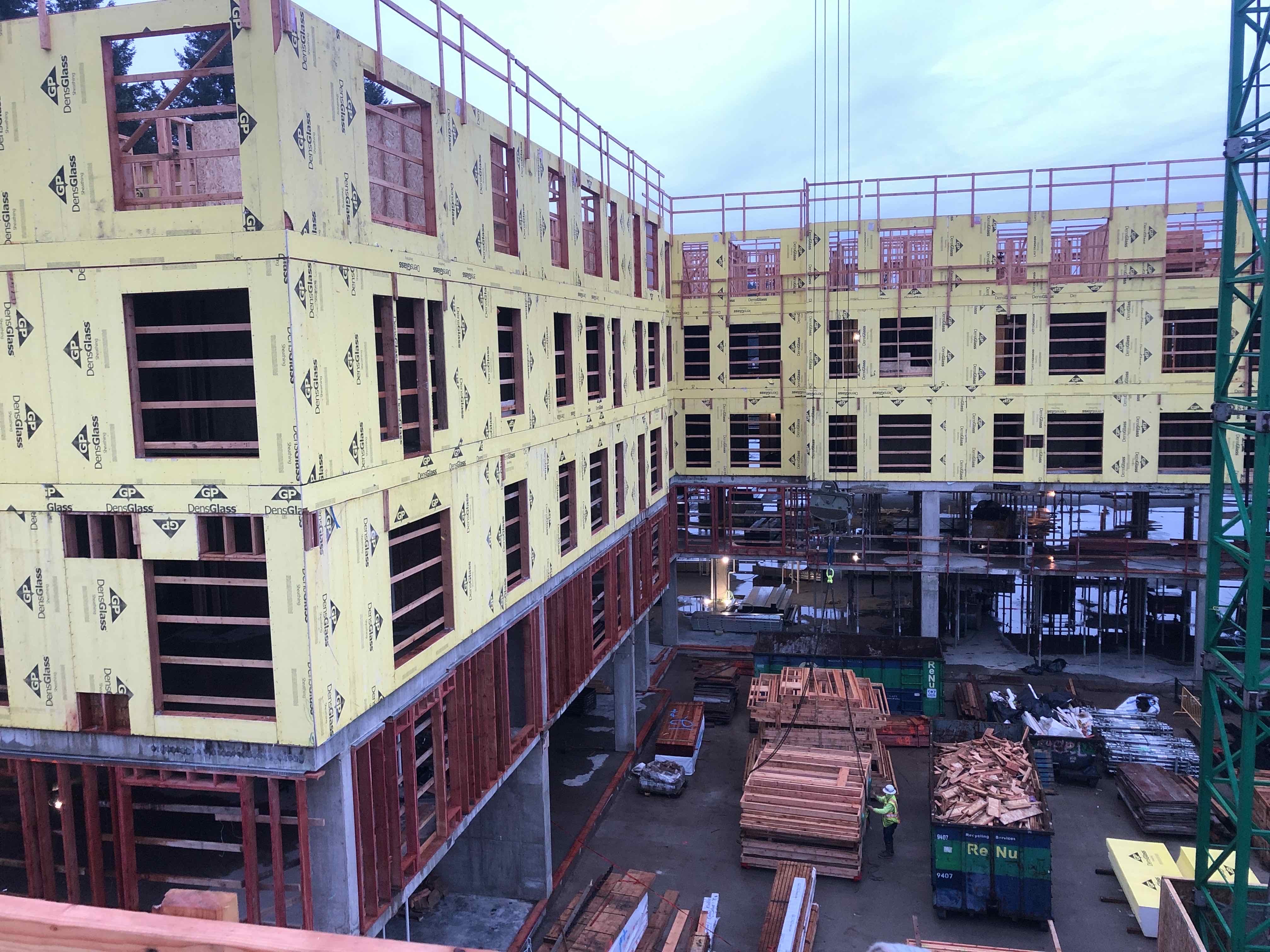
At Ankrom Moisan, our interior designers and architects bring both depth and breadth of experience to every project. That expertise allows us to support our clients throughout the full life of their buildings—from early programming and ground-up design through renovations and tenant improvements years later.
Because we know our buildings inside and out, we’re uniquely positioned to return as trusted partners when our clients’ needs evolve. Our architects often lead the initialground-up design, establishing the vision, systems, and structure. As the building matures and programs shift, our interior designers step forward to lead renovation work, ensuring the space continues to function beautifully for the people who use it.

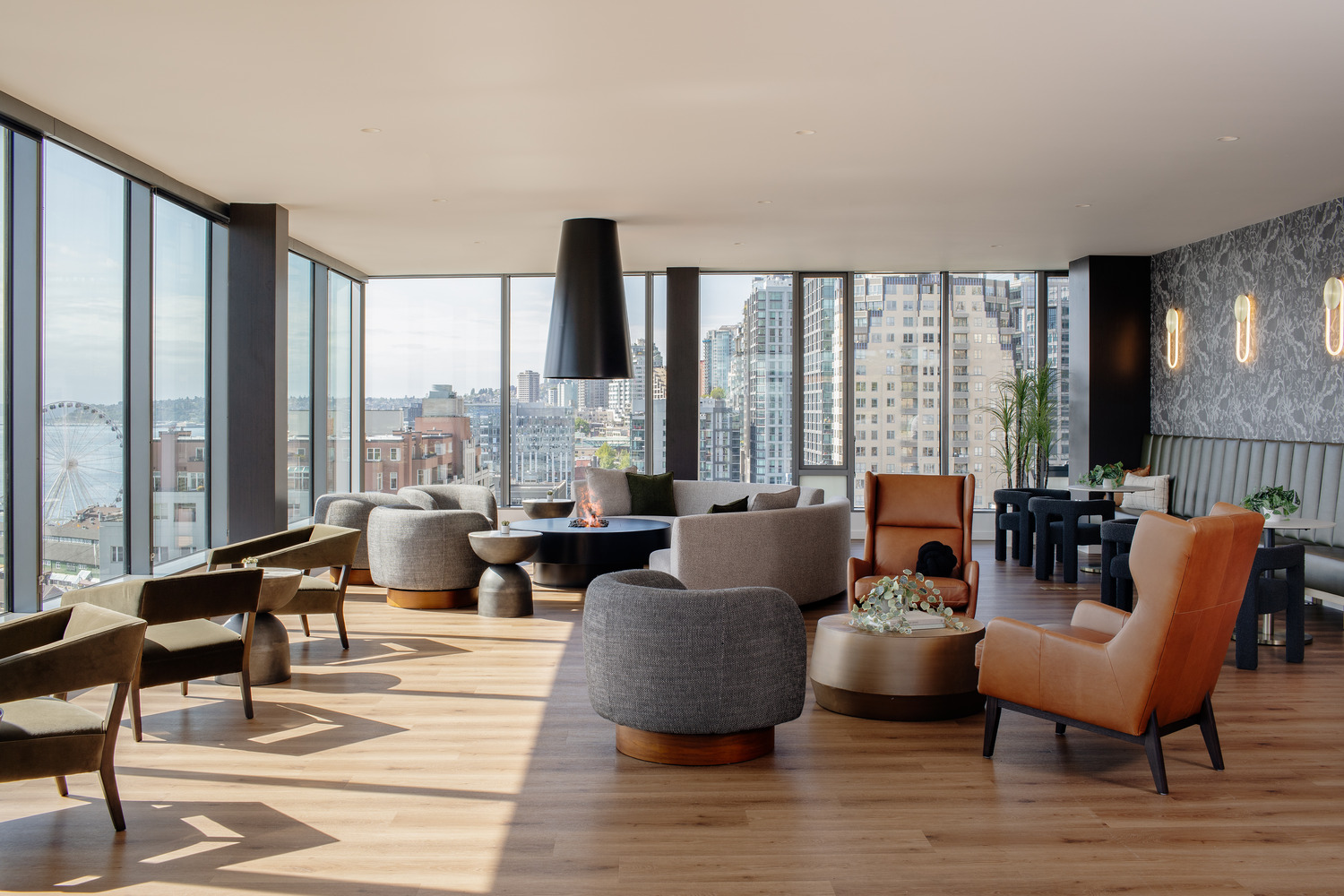
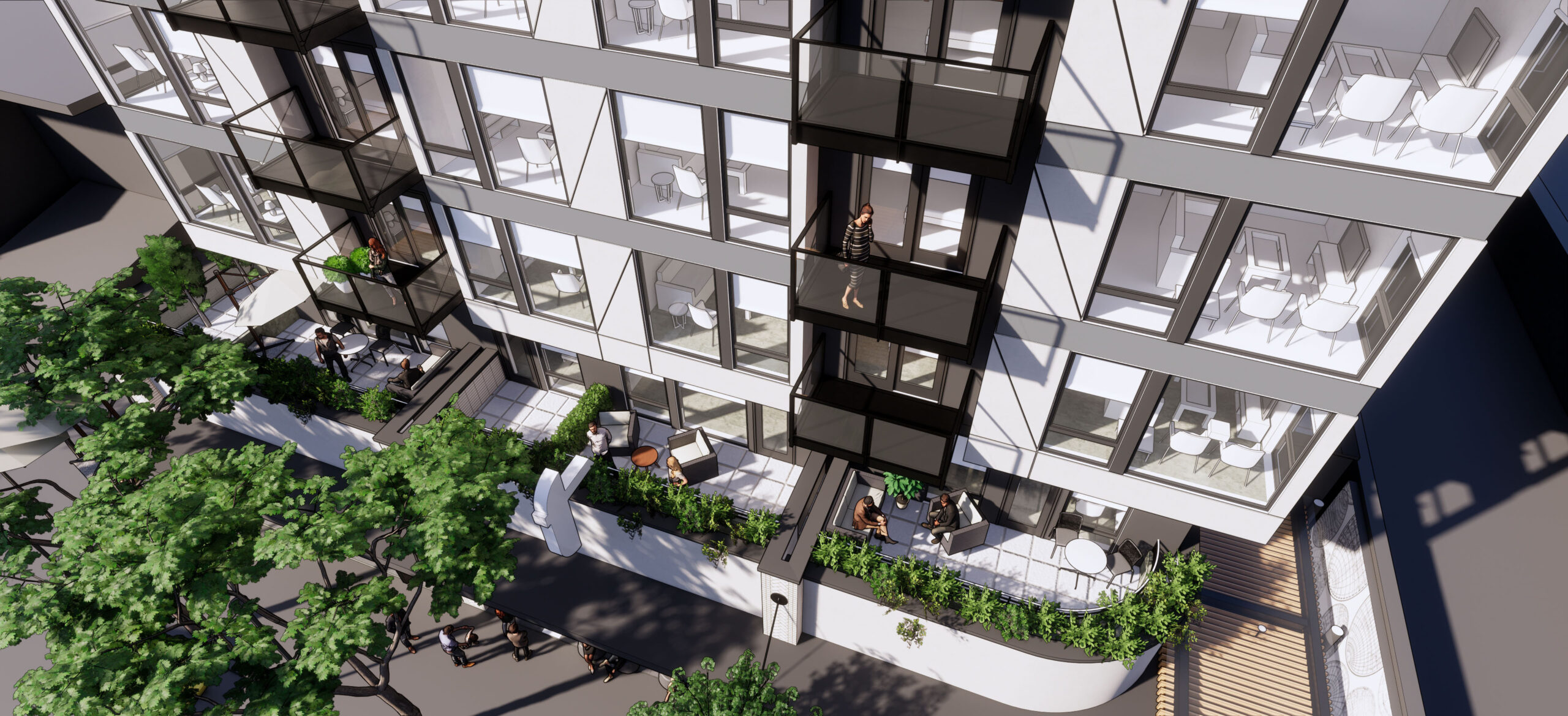
Griffis Seattle Waterfront
Across all studios, this collaborative model enables us to design not just buildings, but the entire lifespan of the environments our clients rely on.
In 2016, Ankrom Moisan partnered with Central City Concern to design the Blackburn Center, which opened in 2019. From the beginning, the team worked closely with CCC to create a welcoming, stigma-free entry experience that avoided the institutional feel common in healthcare settings.
About six months after opening, CCC reached out again — this time to explore adding a security room that could enhance safety while preserving the building’s warmth and approachability. Because we knew the building intimately and maintained strong relationships with CCC’s facilities team, we were able to respond quickly, re-engage original engineers and consultants, and deliver a coordinated tenant improvement solution within just a few months.
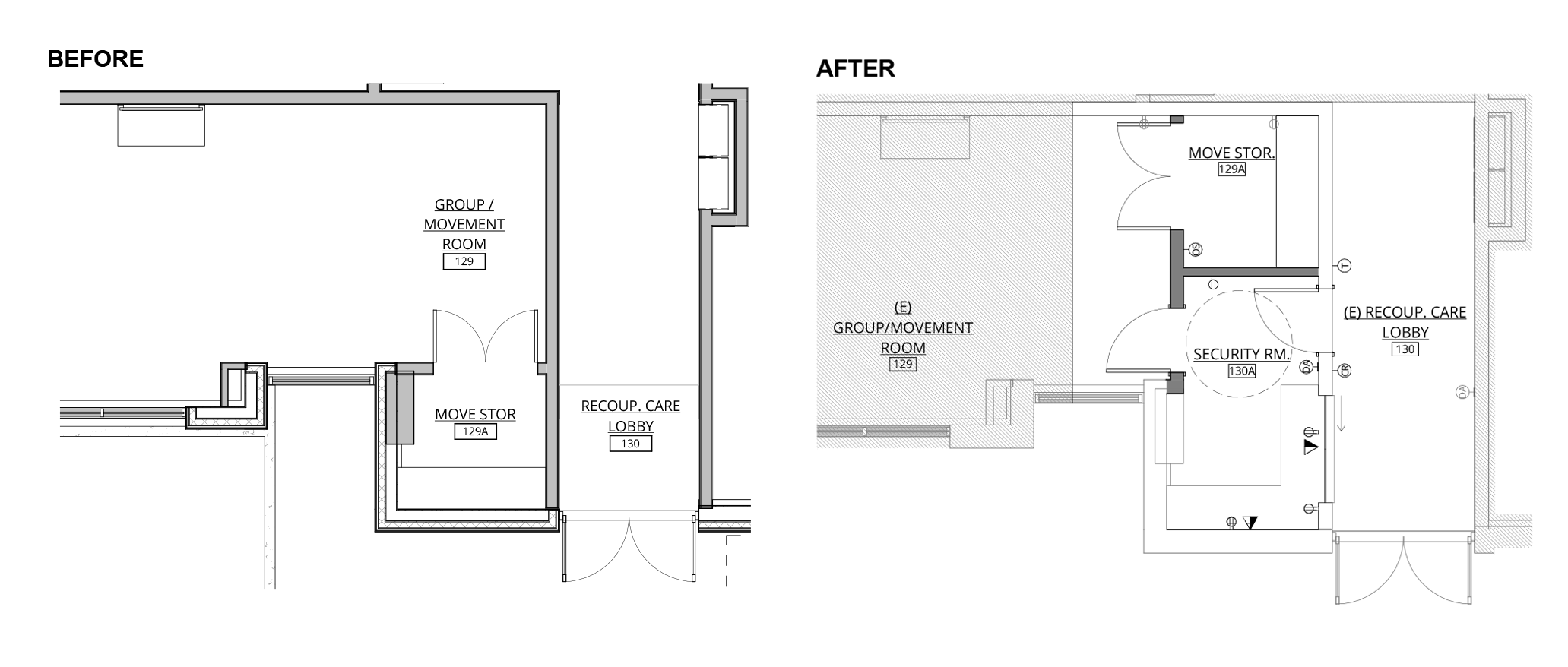
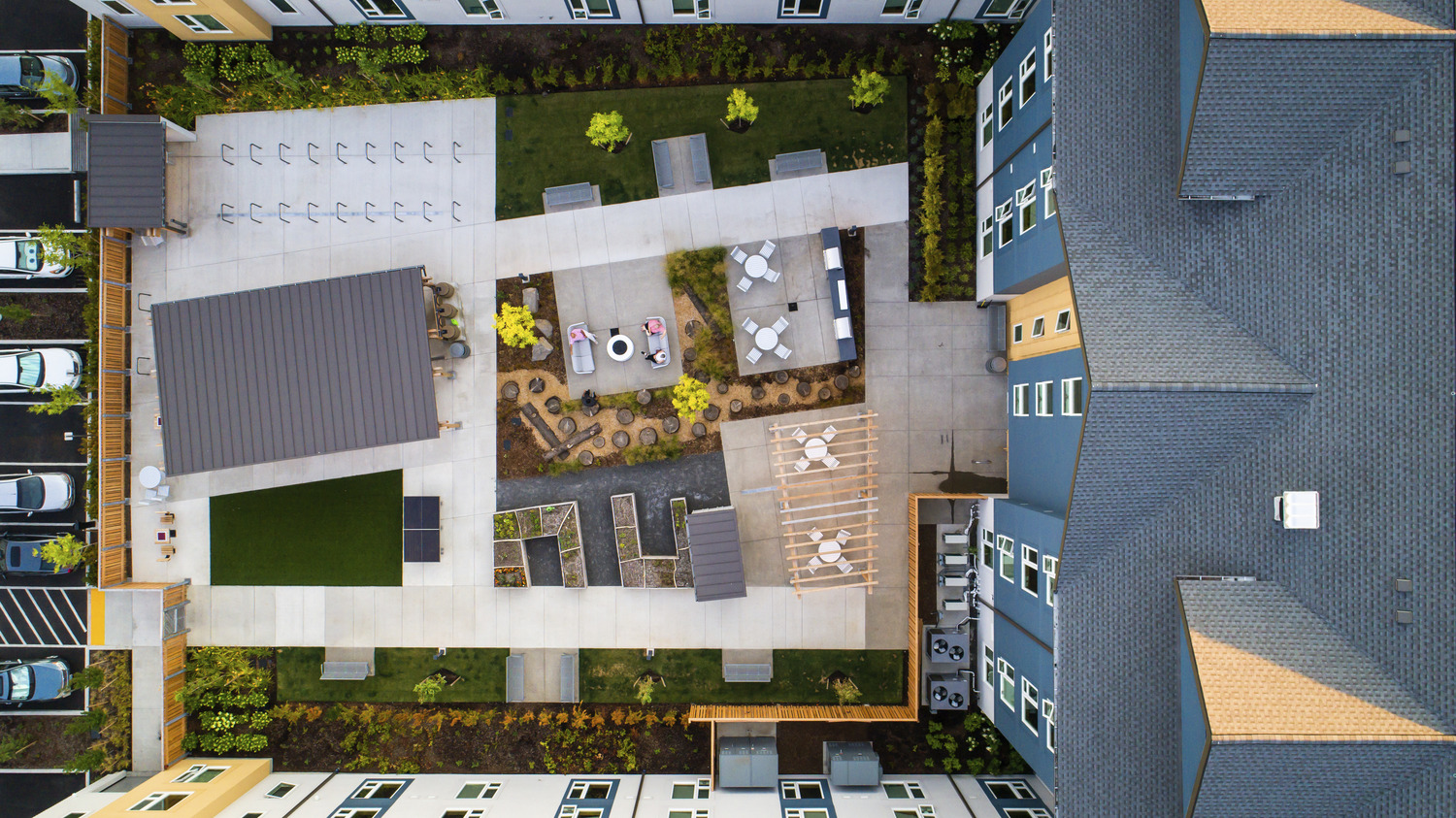
Site plans from before and after CCC Blackburn Center’s hallway renovation
This project is a clear example of designing for the life of a building. As needs, leadership, and programs evolve, we remain a trusted partner ready to adapt spaces that support our clients and the communities they serve.
Our relationship with Trinity Terrace campus began in 2003. We served as the stamping architect for the Phase 2 City Tower, which opened in 2007, and our studio later collaborated with Mariah Kiersey to design the Phase 3 River Tower—a full CCRC with Skilled Nursing, Memory Care, Assisted Living, Dining, and Independent Living.
After River Tower opened, the AM team was invited back to refresh the common spaces connecting the original Phase 1 Terrace Tower and Phase 2 City Tower, aligning them with the design language of the new Phase 3 tower. We also updated the existing kitchen, dining areas, several amenities, and continued our collaboration with the Healthcare studio on the skilled nursing renovation.

River Tower
Because we knew the building’s systems and structure, we were able to re-engage many of the original consultants and streamline the renovation process. That continuity led to a more efficient design schedule and a smoother experience for the client.
Great buildings don’t stand still—they evolve.
We believe the most successful workplaces are those that adapt over time, staying relevant as organizations grow, shift, and reimagine how they work.
In 2016, our Office Studio designed the Daimler Headquarters campus. Nearly a decade later, we continue to partner with Daimler on targeted tenant improvements and security enhancements that respond to evolving business needs.
Because we know this campus inside and out, our renovation work is faster, more strategic, and deeply rooted in the original design intent—delivering high-impact updates with minimal disruption.
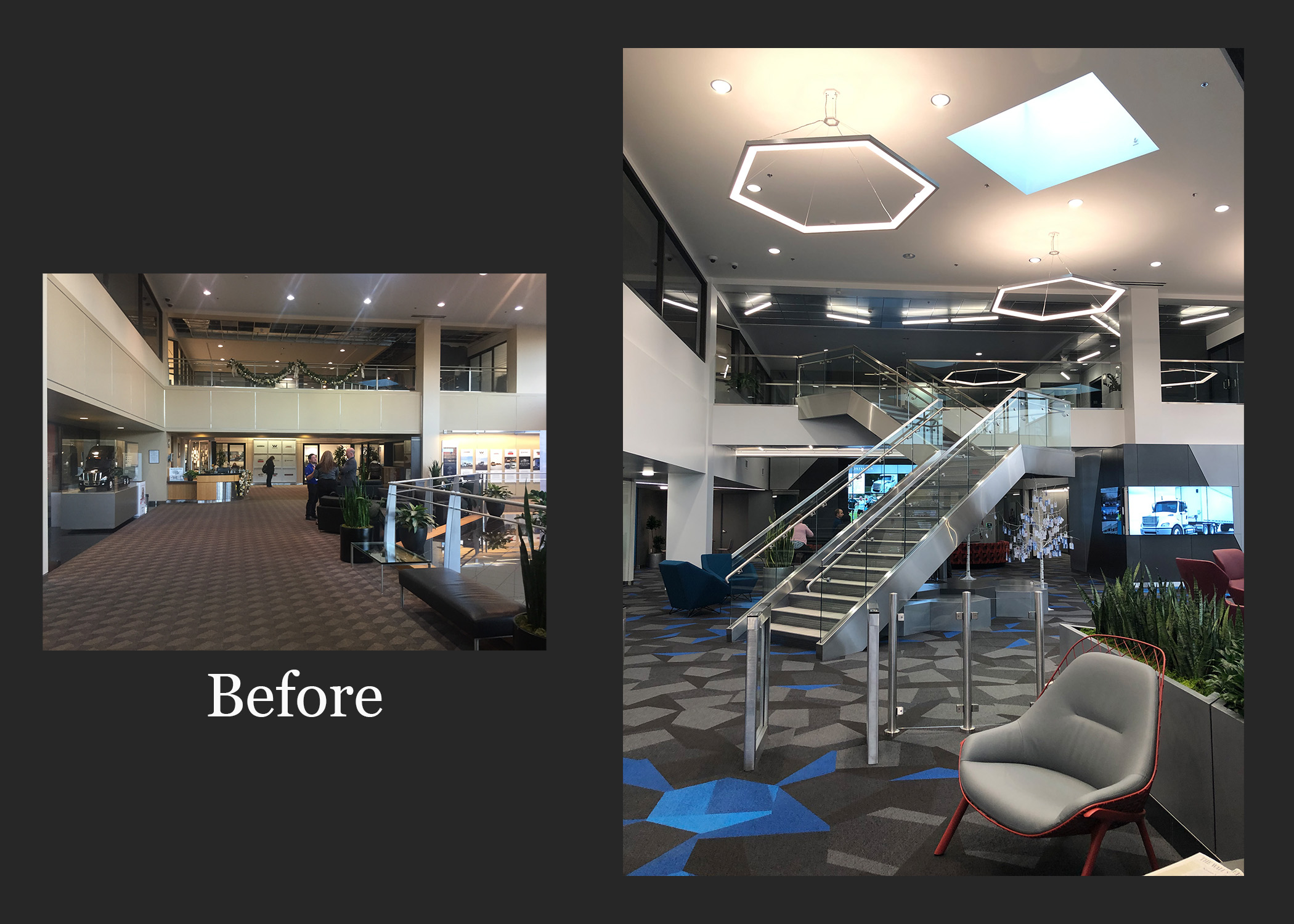

Daimler Headquarters
Our connection to the Peterkort Medical Office campus goes back to its beginning. Ankrom Moisan designed the original MOBs and parking garage, and that foundation has allowed us to stay closely involved as the campus has evolved over time. In partnership with Cushman & Wakefield, we’ve supported the full lifecycle of these facilities by expanding clinical services and enhancing the experience for patients, providers, and visitors.

Peterkort
From children’s clinics and internal medicine offices to outpatient care suites, elevator upgrades, lobby refreshes, and exterior canopy improvements, each project builds on the one before it. Because we know these buildings inside and out, our team can move quickly and deliver renovations that feel seamless, integrated, and forward-looking. It’s a partnership rooted in trust and long-term collaboration and a great example of how we design for the life of a building.
Renovation work is complex and requires close coordination with owners, the construction team, and consultants. At this campus it is also a cross-studio collaboration with Mariah Kiersey and Bethanne Mikkelsen working together to support these ongoing improvements over many decades.
Along Portland’s South Waterfront, Griffis South Waterfront was reimagined to meet the evolving expectations of today’s residents.
Following a change in ownership, Urban Living by Ankrom Moisan returned as the original design team, utilizing competitive research and demographic insight to shape a vision aligned with Griffis Residential’s diverse resident mix of young professionals, families, and older adults.
The amenity strategy focused on adaptable, enduring spaces. New amenities were intentionally introduced, including a dedicated co-working environment, enhanced mail and package spaces, and a reimagined fitness and activity room that now extends seamlessly outdoors – expanding wellness beyond interior walls and supporting both movement and social connection.
Rather than incremental upgrades, the strategy intentionally added missing amenities – identifying underutilized square footage to expand the program, anticipate evolving resident expectations, and position the building to compete with newer developments.
By aligning experience with strategy, the renovation reinforces the building’s identity and demonstrates how insight-driven design delivers both resident value and long-term performance.

Griffis South Waterfront
Through projects like the CCC Blackburn Center, Daimler Truck North America Headquarters, Griffis South Waterfront and others across our studios, we’ve seen firsthand how thoughtfully designed buildings stay resilient and successful long after opening. As technologies, trends, and community needs shift, our renovation work helps each space grow right along with them.
Now that residents have moved into Meridian Gardens, the building will naturally evolve as their needs and programs take shape. We hope to continue partnering with Central City Concern as new opportunities for design support emerge.
Visit our Renovations Expertise page to see how we are highlighting renovation stories from all our studios and to learn how we can help your community evolve, whether we’ve partnered before or are just getting started or just curious to see what we do!
Project Walkthrough: Plaza Los Amigos
Named after the large, multigenerational mutual aid society created by Mexican and Texan farmworkers who migrated to Cornelius in the 1950s, Plaza Los Amigos honors the traditions of the past while supporting the development of new relationships.
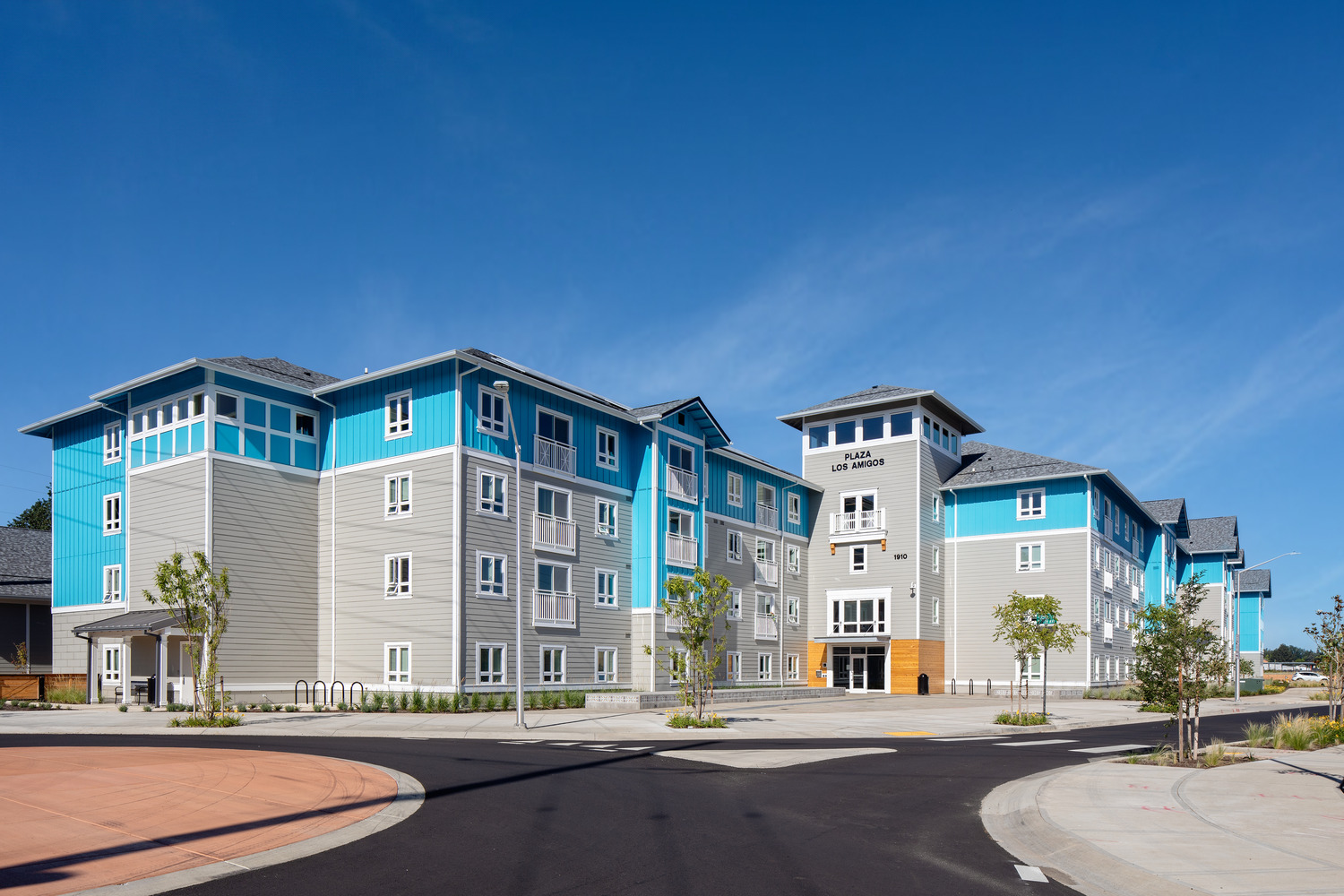

Opportunities to come together, celebrate, and support one another, much like the original Los Amigos group “Los Amigos Club” did, can be found throughout the property. Inside and out, community is emphasized through connected amenities and shared spaces, all designed with the traditions of the local Hispanic culture in mind.
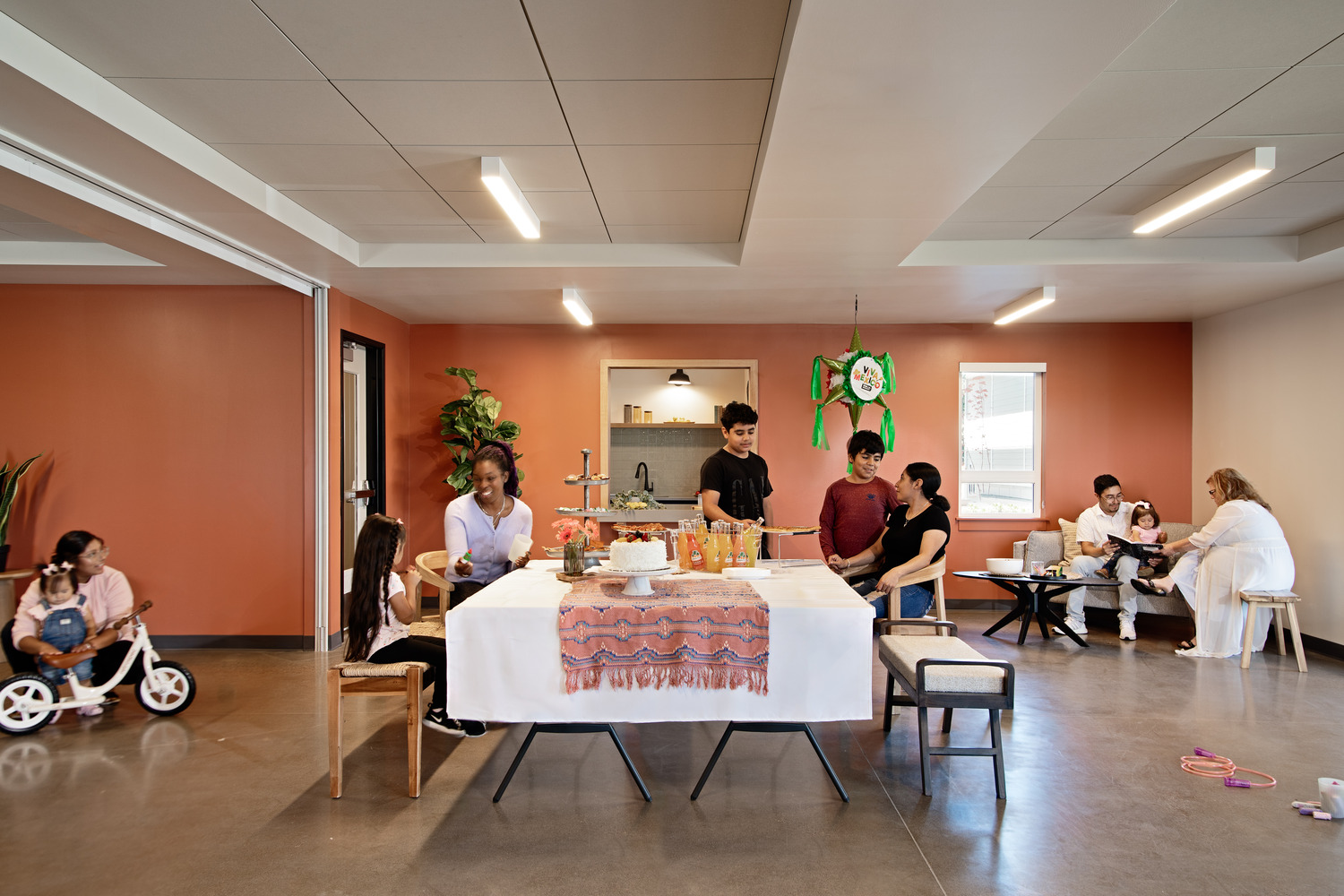

By embracing the heritage of Cornelius’ Hispanic demographic, the affordable, family-oriented housing complex seeks to strike a cohesive balance between reminders of home in Mexico and the aesthetics of the Pacific Northwest’s agricultural history.
Offering the promise of homemade food, a place to sleep, and a sense of belonging and support, the new Plaza Los Amigos is where strangers become friends, and friends become family.
Home on the Range
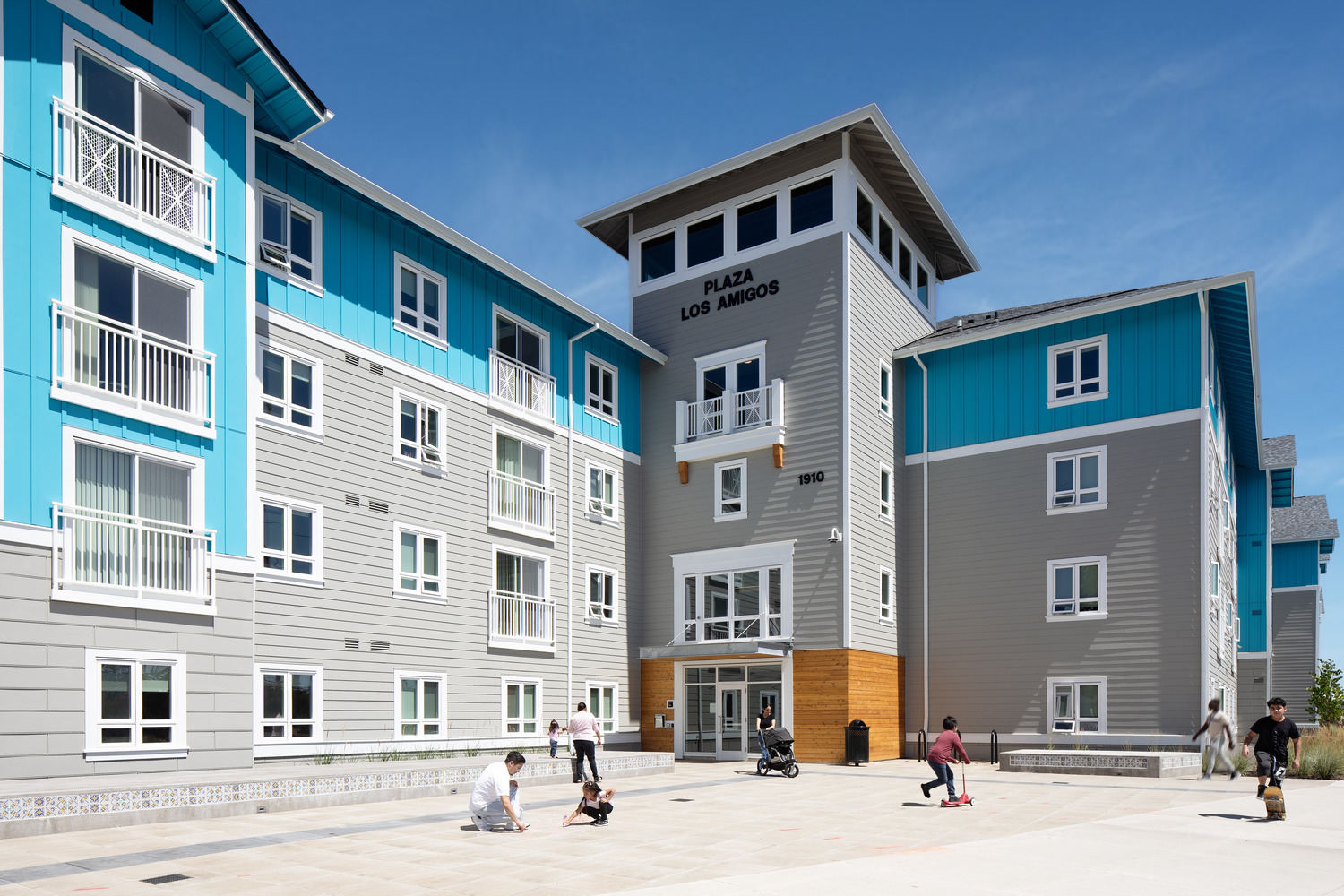

Inspired by the geographical location and the agricultural history of Cornelius, material choices traditionally tied to farmhouse aesthetics influence the design palette of Plaza Los Amigos, positioning the affordable housing complex as a spacious sanctuary of the new frontier.
Simple, yet hardy materials like lap and board and batten siding are paired with white trim and window frames, calling back to classical agricultural architecture and adding flashes of brilliance that stand apart from the rest of the structure’s grey-on-grey color scheme. The building is a zig-zag shape, permitting many connections between interior and exterior spaces and the residents that occupy them.
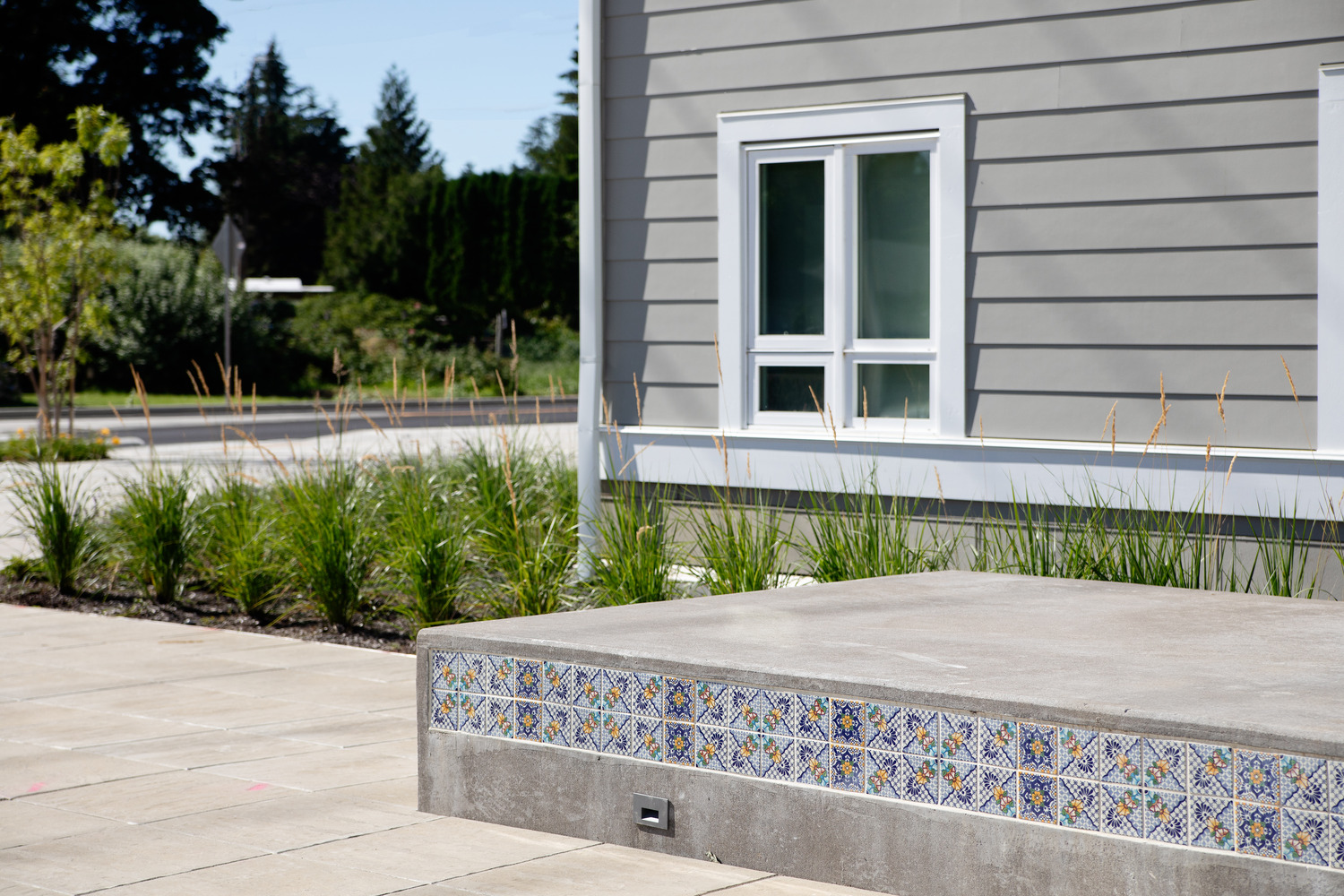

Saltillo tiles sourced from Mexico are used in planters and benches in the front courtyard of the site, bringing together the vibrant traditions of Hispanic culture and the regional, outdoorsy aesthetic of Oregon. The outdoor front plaza was a crucial element to the site, allowing residents to gather, host events, or enjoy the outdoors as they wait for a friend or rideshare to pick them up.
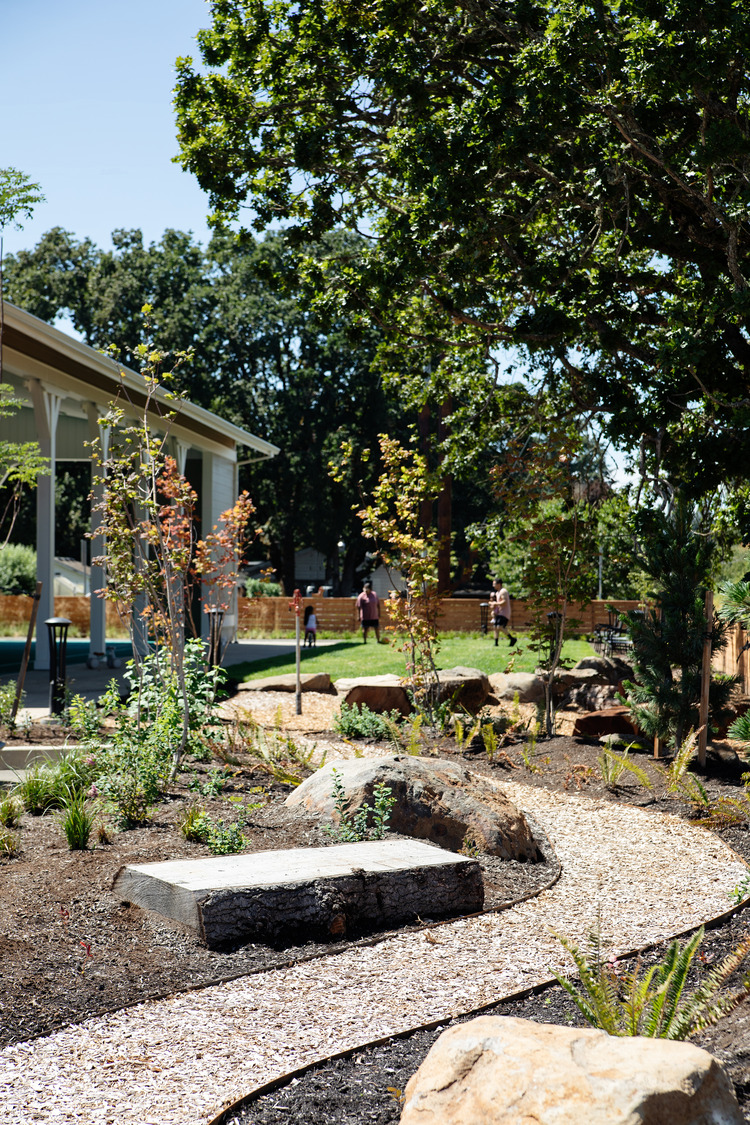

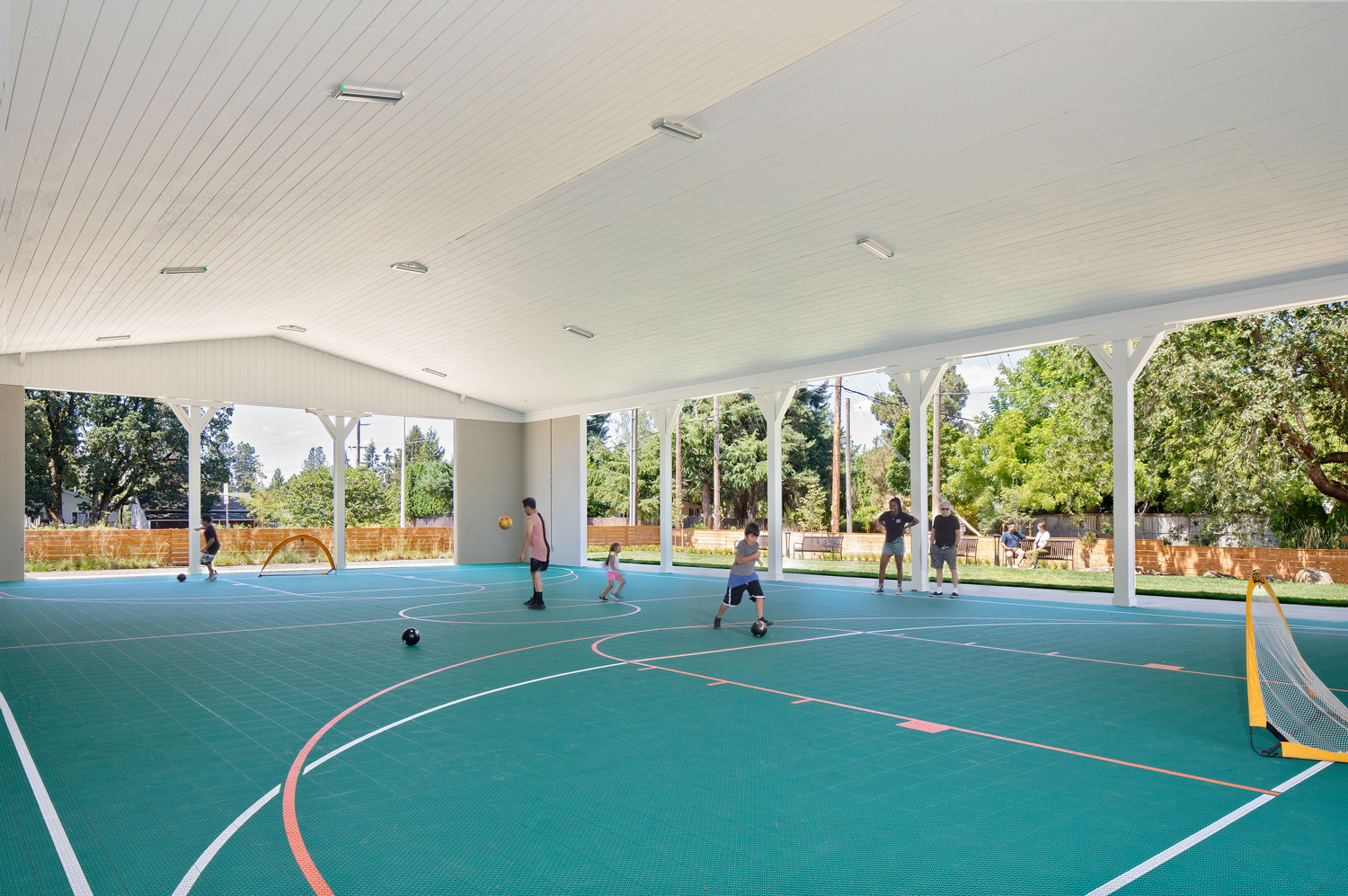
In the building’s back is an open space with a covered futsal court and greenery. Connecting to a park on the east of the site, both the front and back courtyards provide plenty of open space for use in get-togethers and other celebrations.

Where Families Flourish
Comprised of 113 affordable 2- and 3-bedroom units, Plaza Los Amigos is designed as a home for families to flourish. An understanding that these units would be the backdrop for multiple generations to grow up and grow old in led to an emphasis on family-oriented elements throughout the individual units and shared spaces.
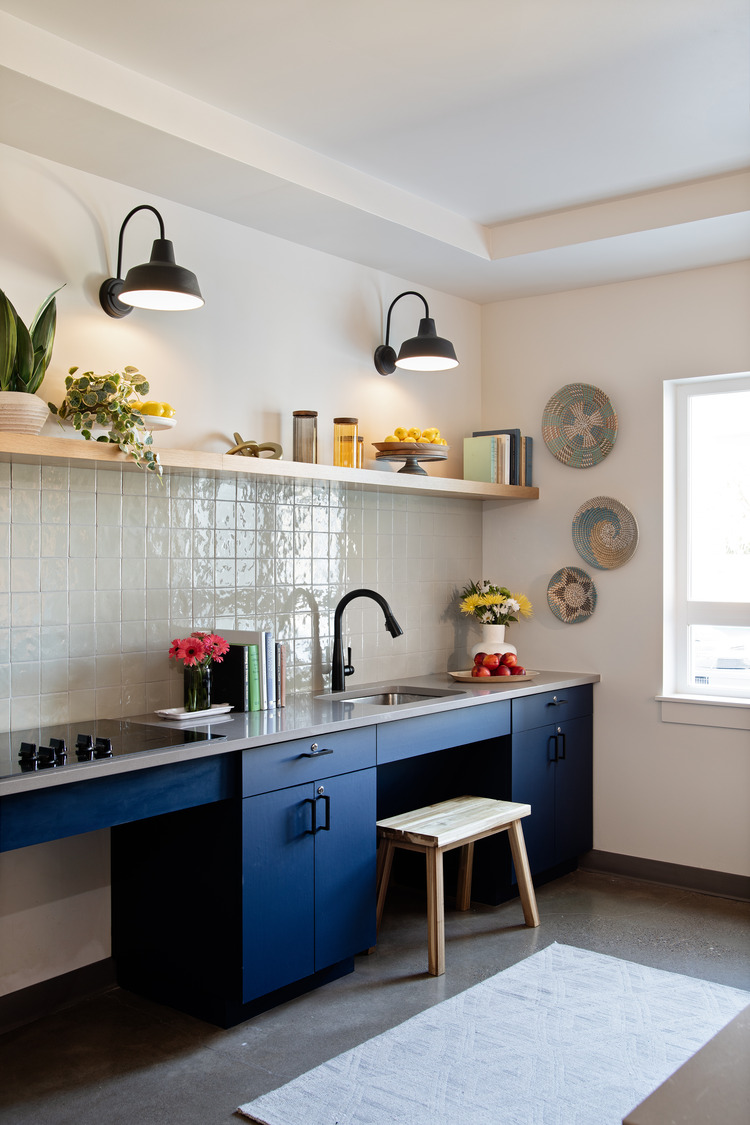

To support resident families through the challenges of raising kids, a unique decision was made to place residential kitchens along the exterior walls of units. This allows parents to keep an eye on their kids as they play outside in the plaza, while still being able to cook dinner or wash dishes.
Partnering with Sequoia Mental Health Services, the building offers culturally competent, accessible resources and support aimed at the safety, security, and well-being of residents. Sixteen individual residential units are designated to provide stability to unhoused community members.
Other forms of support are seen in the two lobby photo rails, which encourage residents to share and show off their accomplishments, whether they are good grades, a creative art project, a recent certification, or any other acknowledgement that they are proud of. A strong connection to the Dreamers resulted in this feature – Plaza Los Amigos wanted to highlight the dreams and achievements of its residents to encourage a more connected community.

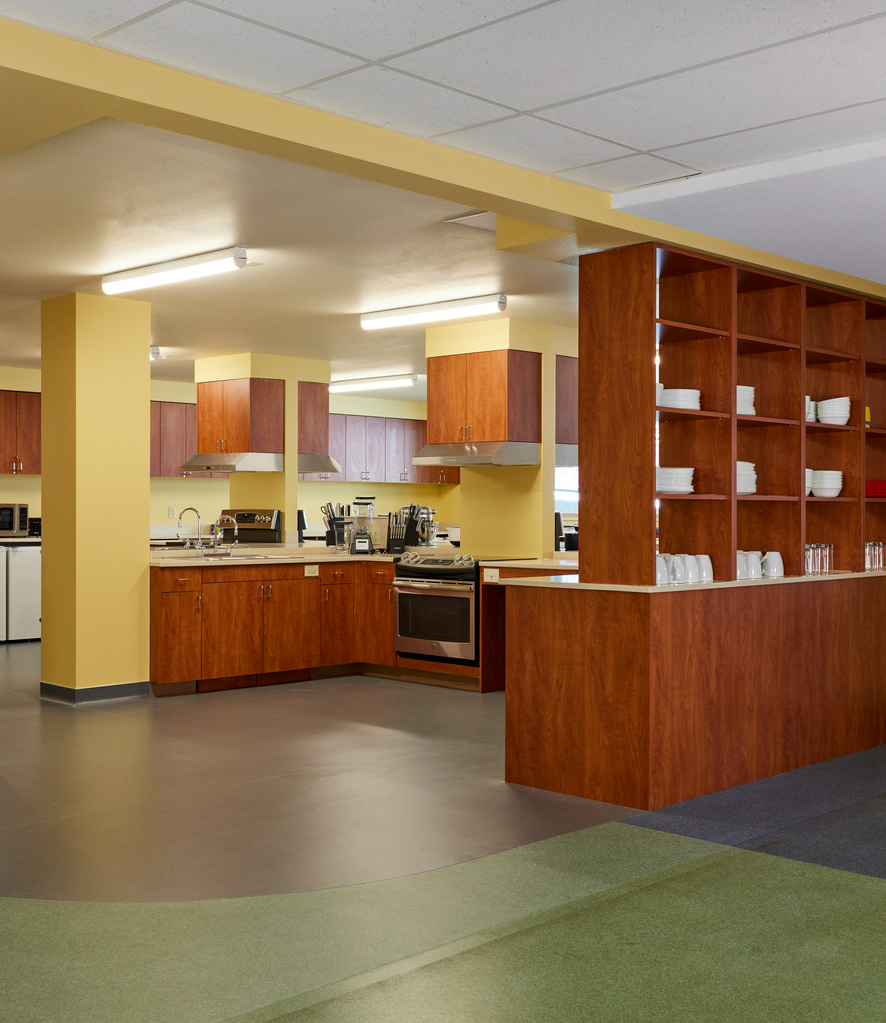
Spacious elevator lobbies on each floor – elevated by the patterns of colorful graphic tiles – serve as meeting points, overlooking the Plaza courtyard below and leading residents to shared amenities throughout the building. These amenities include laundry rooms on each floor, a community room and adjoining community kitchen, and an outdoor covered futsal court. The community kitchen includes a six-burner stoves, designed to help facilitate large celebrations and shared feasts that bring the community together as one.
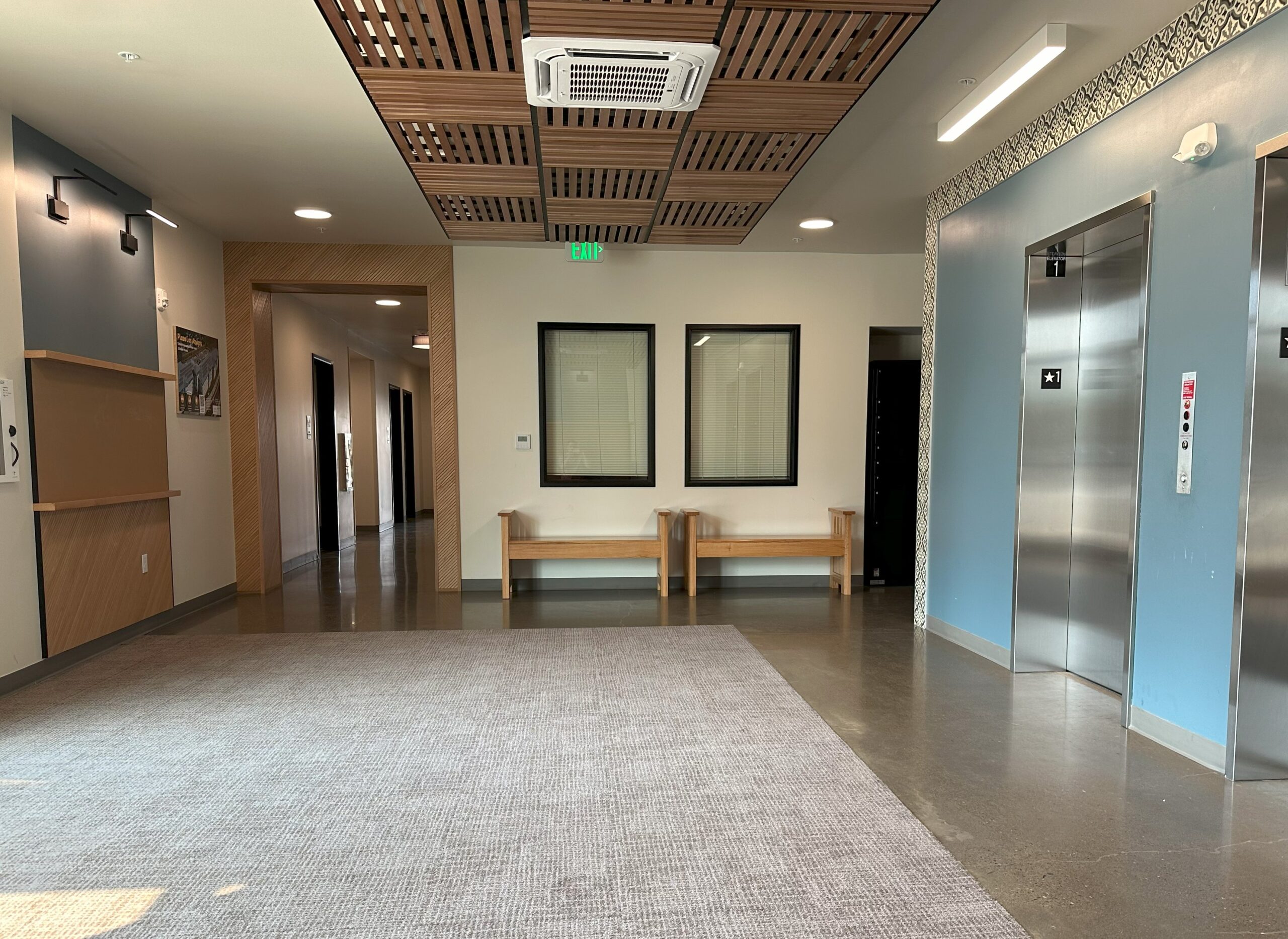

As a special gift to Bienestar, one of the key architects on the project spent their own personal time transforming lumber from a oak tree on a nearby Bienestar site into two custom benches, to be utilized in the elevator lobby at the heart of the community. Engraved with a note explaining the collaboration between LMC Construction and Ankrom Moisan, the benches recognize and celebrate the significant work that Bienestar and Plaza Los Amigos do to provide affordable housing to those who need it in Washington County.
The Ins and Outs of Adaptive Reuse
What is Adaptive Reuse?
Adaptive Reuse Residential Conversions are projects that repurpose existing buildings for uses other than what the space was originally designed for.
Adaptive reuse offers developers the unique opportunity to save their investment, create and unparalleled story for end users, and make money by converting a disused or underutilized project into a one-of-a-kind residential space.

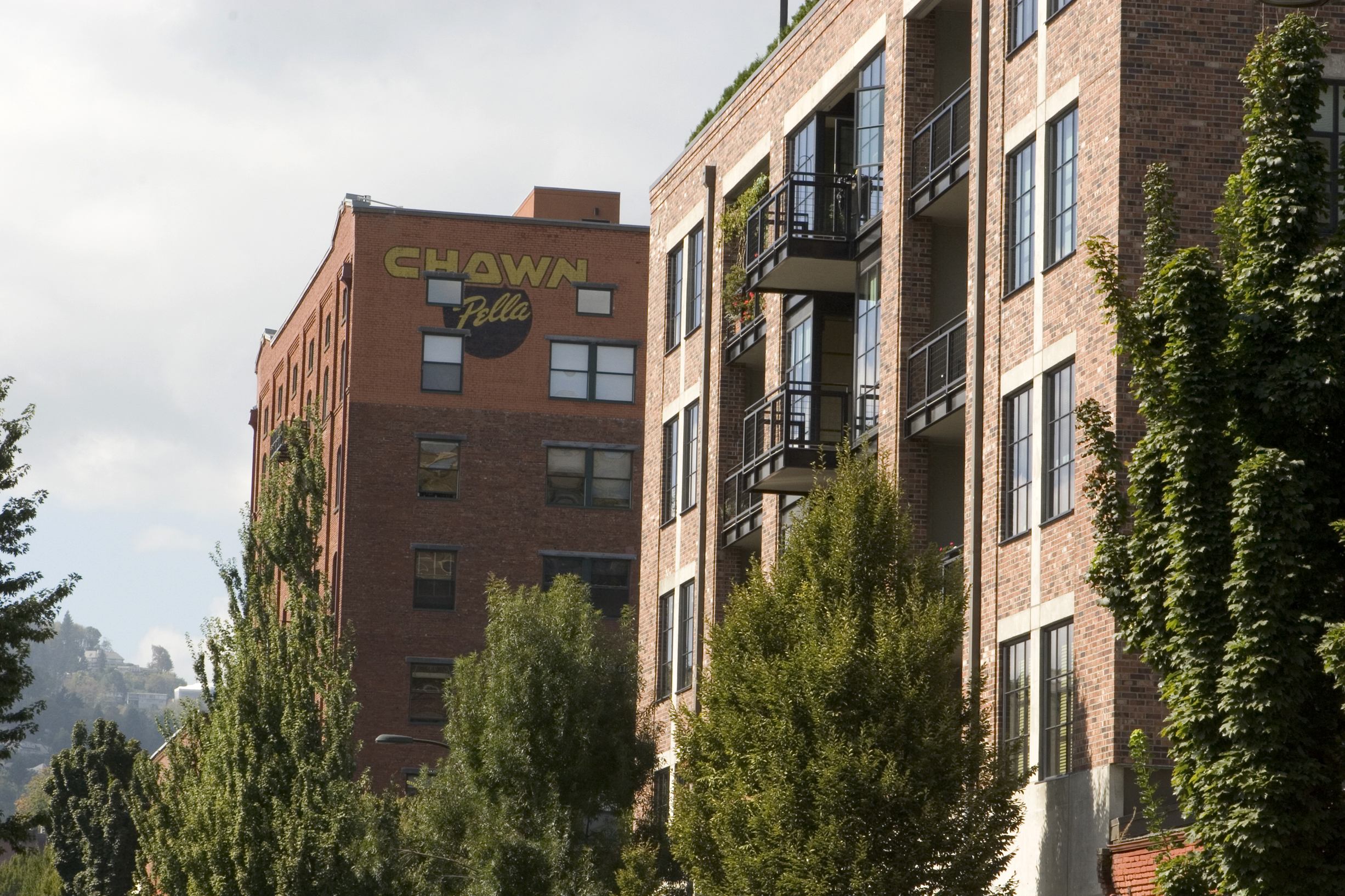
Chown Pella Lofts, an old factory warehouse converted into a multi-story residential condominium in Portland, OR’s Pearl District.
However, updating old buildings comes with layers of complexity.
Since 1994, Ankrom Moisan has been involved with adaptive reuse projects and housing conversions. The depth of our expertise means we have an intimate understanding of the limits and parameters of any given site – we know what it takes to transform an underperforming asset into a successful residential project.
Why Conversions?
There are many reasons to choose conversion over construction when considering how to revitalize old structures or adapt unused sites.
Rental Housing Demands
According to the National Association for Industrial and Office Parks (NAOIP), the United States needs to build 4.3 million more apartments by 2035 to meet the demand for rental housing. This includes 600,000 units (total) to fill the shortage from underbidding after the 2008 financial crisis. Adaptive reuse residential conversions are an affordable and effective way to create more housing and fulfill that need.
Desirable Neighborhoods
The way we see it, the success of our buildings, neighborhoods, and infrastructure is our legacy for decades to come. Areas with a diverse mix of older and newer buildings create neighborhoods with better economic performances than their more homogeneous counterparts. By preserving and protecting existing structures, conversions contribute positively to the health and desirability of the neighborhood, leading to a quicker tenant fill.
Being committed to the places we occupy, live in, and care about is another reason to embrace adaptive reuse residential conversion projects; they revive our cities. Reducing the number of buildings that sit empty in urban areas plays a major role in activating downtown districts.
Reduced Waste
Saving older, historic buildings also prevents materials from entering the waste stream and protects the tons of embodied carbon spent during the initial construction. AIA research has shown that building reuse avoids “50-75% of the embodied carbon emissions that would be generated by a new building.”
New Marketing Opportunities
Aside from these benefits to the community, adaptive reuse conversions present a way for developers to recover underutilized projects and break into top markets like affordable, market-rate, and student housing.
Construction Efficiencies
Compared to new buildings, residential conversion projects save time, money, and energy, since their designs are based on an existing structure. Adaptive reuse conversions also benefit from not having their percentage of glazing or amount of parking limited by current codes, since they’re already established.
One-of-a-Kind Design
We don’t believe in a magic formula or a linear “one-size-fits-all” approach to composition. Each site is a unique opportunity to establish a one-of-a-kind project identity that’s tied to its history and surroundings.
At the outset of any conversion, we analyze each individual site and tailor our process to align with the existing elements that make it unique. Working with what you have, our designs and deliverables – plans, units, systems narratives, pricing, and jurisdictional incentives – are custom-fit.
It’s our philosophy that you shouldn’t fight your existing structure to get a conversion made; if you can’t fix it, feature it.

Chown Pella Lofts.
Approaching each conversion opportunity with this mindset, we analyze the factors that set a site apart, and embrace those unique elements to ensure a residential conversion stands out. With this intricate and involved process, we’ve been able to get over 30 one-of-a-kind residential conversion projects under our belt.
Through these past experiences, we have identified six key characteristics that make a project a candidate for successful conversion, and six challenges that may crop up during the renovation process. To learn more about what attributes to look out for and what traits to be weary of when considering a residential conversion, read about our “Rule of Six” here.


By Jennifer Sobieraj Sanin, Design Director of Housing and Senior Principal, and Jack Cochran, Marketing Coordinator.
New Code Increases Accessibility
Background
At Ankrom Moisan, we work hard to ensure an equal experience for all users of the spaces we design. We explore how to push beyond the expected with accessibility features on projects like Wynne Watts Commons, and we welcome updated codes and standards to address the needs of our community. As the 2021 Building Code takes effect in each jurisdiction, the embedded 2017 A117.1 Standard for Accessible and Usable Buildings and Facilities also takes effect. The new 2017 A117.1 provides significant updates to accessibility clearances based on a study of wheelchair users. The A117.1 is developed by the International Code Council (same authors as the International Building Code). Their challenge is to find the best design criteria for a wide range of abilities, from wheelchair users to standing persons with back problems to persons with low vision or hearing challenges. Ankrom Moisan has participated in their process as an “interested party” in one issue, kitchen outlets, and can attest to the countless hours that go into just one requirement.
 At the Ronald McDonald House expansion we wanted to make all families staying for short or long stays be able to use all the amenities, including the common kitchens.
At the Ronald McDonald House expansion we wanted to make all families staying for short or long stays be able to use all the amenities, including the common kitchens.
Changes
Overall impacts to projects by this change are modest, resulting in a few rooms being enlarged by a few inches. While the changes are minimal to buildings, they provide much higher levels of accessibility for impacted users. The most impactful updates are changes to the following requirements:
- In most cases, clear floor spaces grow from 30-inch by 48-inch to 30-inch by 52-inch.
- The turning circle that was a 60-inch “wedding cake” with knee and toe clearance all around is now a 67-inch cylinder with minimal knee and toe clearance.
When looking at a typical privately funded apartment building, the changes are minimal as long as they are understood at the start of the project. There are no changes to Type B units (except new exceptions for kitchens outlets were added), and for the Type A units, the kitchen, bathroom, and walk-in closet may grow a few inches. The trash chute access room will see the biggest change, growing up to 7” in both directions. All these changes are minor when incorporated into the initial design of the building but could be very tricky late in the design process.
There are still some unknowns; If there are Accessible units in a project, they will now require windows to be fully accessible. While the height and clear floor space requirements are easy to meet, we are still searching for a window style and manufacturer that can meet the requirements that windows are operable without tight grasping and less than 5 pounds of pressure to open and lock/unlock.
Our work isn’t done; kitchen outlets were simplified in the corners where a range and refrigerator protrude past the counter with this code cycle, but we must wait for the next A117.1 cycle for kitchen outlets to no longer dictate kitchen design. Ankrom Moisan submitted code changes that are now in effect in the 2022 Oregon Structural Specialty Code and submitted a proposal for the next version of A117.1 and can report that kitchen outlets will no longer drive design or require any special design or construction features in the next code cycle.
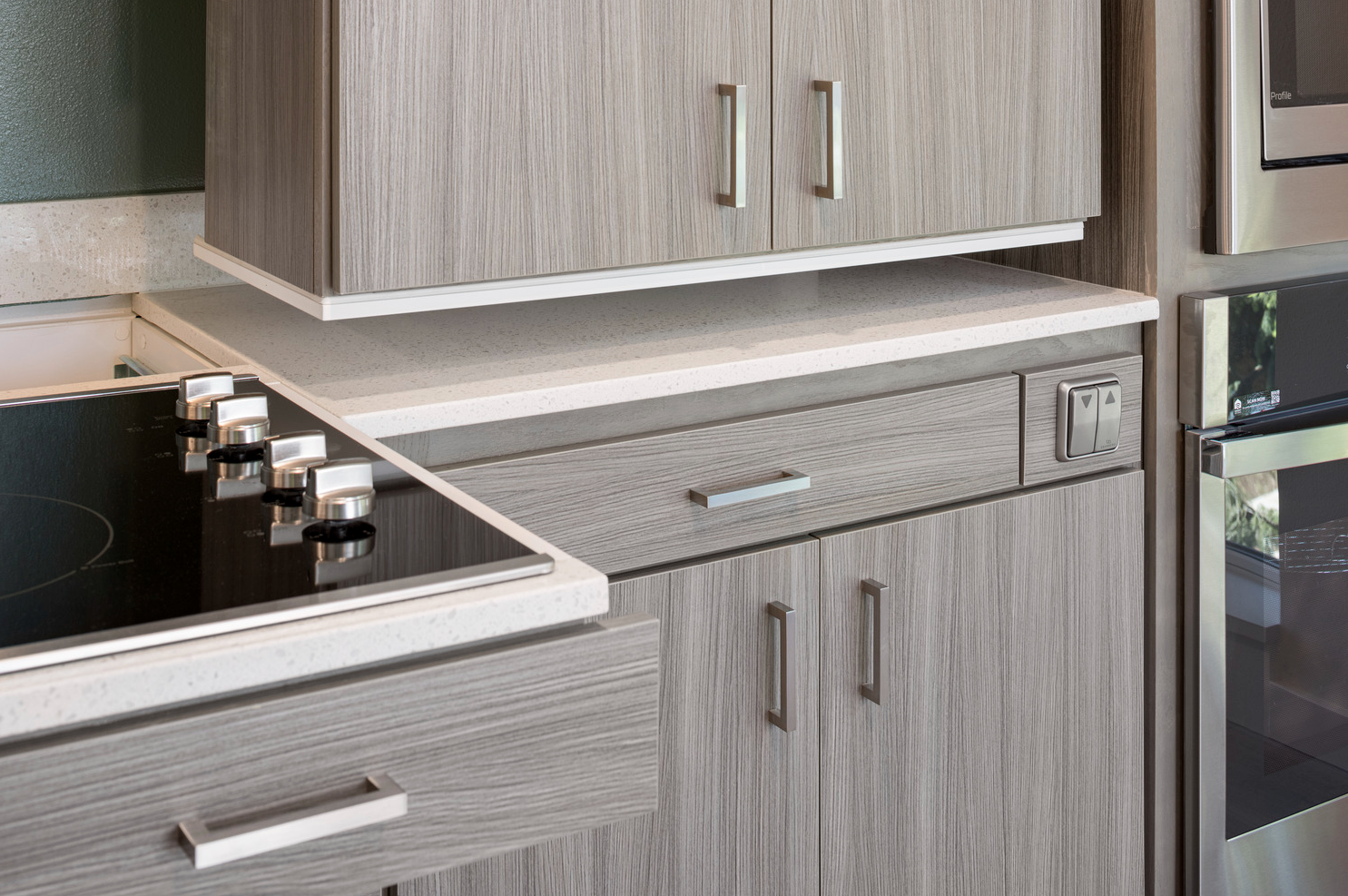 At the Wynne Watts Commons the team provided universal design residential units that included cooktops that pull out and upper cabinets lower with the controls shown in the cabinet front.
At the Wynne Watts Commons the team provided universal design residential units that included cooktops that pull out and upper cabinets lower with the controls shown in the cabinet front.
Added complexity with new code change
From a designer’s perspective, the requirements of accessibility have grown exceptionally complex. For example, under the new A117.1, there are now different size clearances for new and existing as well as Type A and Type B units, and the definition of “existing” in the A117.1 does not match the definition in the building code. This adds to the already confusing accessibility requirements that require us to reference multiple documents for any given item (building code with unique amendments by jurisdiction, Americans with Disabilities Act, Fair Housing Act, etc.). Coupled with different interpretations from different experts and code officials it is no wonder why accessibility requirements feel a bit daunting to us and our clients. As an example, California does not adopt the A117.1 but rather chooses to write its own Chapter 11 of the building code with its own unique scoping and technical criteria. And that is just accessibility, our Architects are juggling fire life safety, energy code, constructability, and our client’s budget all while creating great places where communities thrive.
As a firm, we had a challenge to overcome; the new accessibility requirements do not apply to all our projects at the same time. Depending on where they are in the permitting process and the jurisdiction they are in, every project must determine when, and if, they are required to flip to the new code. While most of our projects will be using the new code by early 2024, many will still be under the old code for years to come. We had to develop Revit resources for our project teams that could work for both codes at the same time. Our Accessibility experts partnered with our BIM team to develop a system meeting these goals and requirements:
- It had to be as simple and easy to use as possible for our project teams.
- It had to be blatantly obvious, by a quick glance within Revit, what codes were being shown on any given project.
- It had to provide all the options now allowed by the standards and guide teams to pick the applicable option.
Our solution to this challenge was rolled out to our project teams in September 2022 and provided over 500 updated Revit families.
Below is our graphic of the changes to the A117.1 that affect AM projects. The orange color helps all team members quickly identify the new families are being used.
We have found so many nuances in the accessibility codes that it can be hard to make generic statements. We would love to talk to you about your specific project or topic. Please reach out to Cara Godwin at carag@ankrommoisan.com to learn about accessibility for your project.
* Originally published October 6, 2022, updated 12/01/2023

by Cara Godwin, Senior Associate
New Seattle Development Design Review Exemptions
The City Council has amended the land use code to make two important changes to the design review program aimed at encouraging additional low-income housing. The first change permanently exempts low-income housing projects from the Design Review program. The second change provides a new Design Review exemption for projects that meet Mandatory Housing Affordability (MHA) requirements by providing units on site via the Performance Option under the Land Use Code. Projects that opt into the Performance Option can skip MUP and Design Review and proceed directly to Building Permit where land use code compliance will be evaluated concurrently with other review subjects.
Expediated Timelines:
Bypassing Design Review and MUP milestones could yield significant time and cost saving on project delivery.
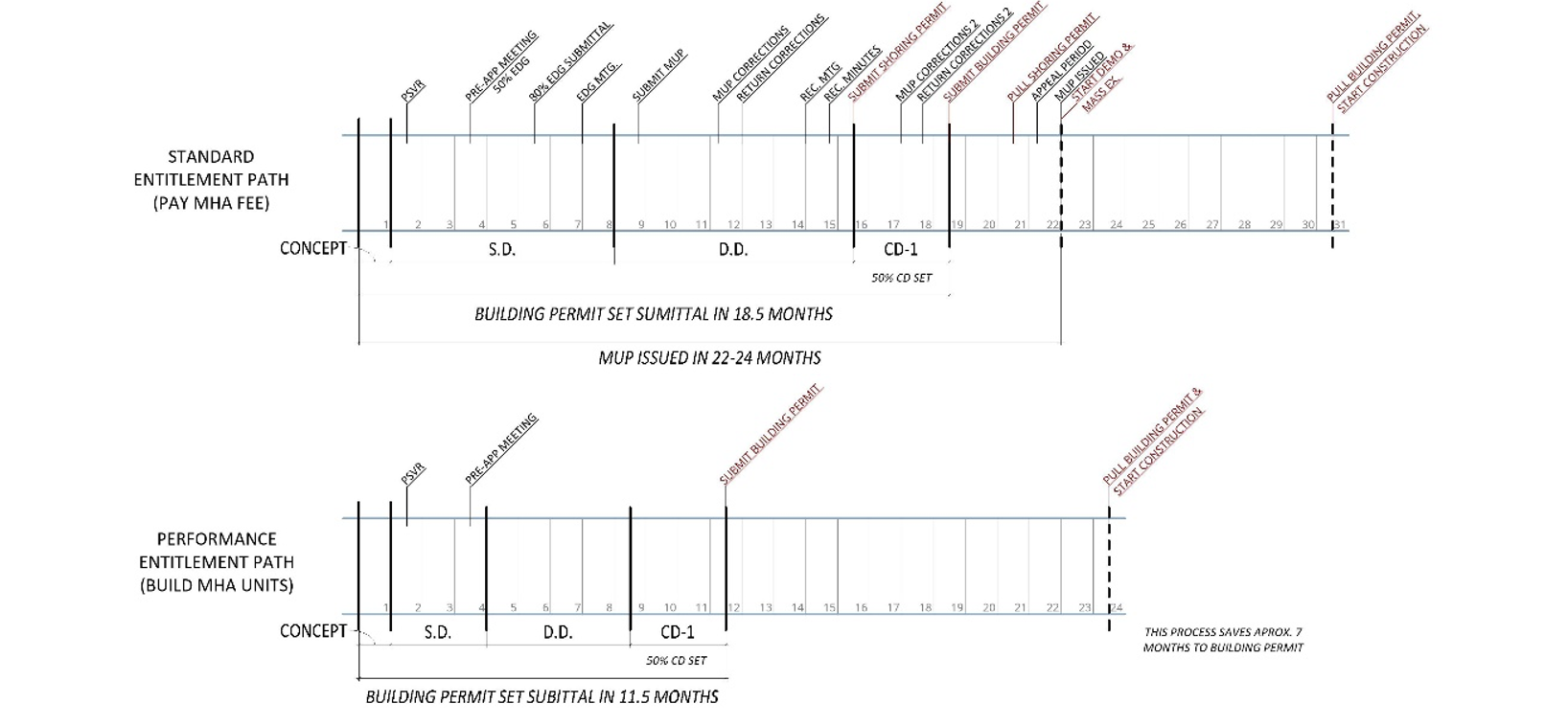
Schedule comparisons showing how fast the entitlements process can be if MHA units are provided instead of the ‘payment in lieu.’
Calculating the Number of Affordable Housing Units Required to avoid Design Review:
If a project contains commercial space, the area dedicated to affordable units required to satisfy the Performance Option is calculated as a percentage of the overall applicable area in commercial use. If a project contains residential space, the required number of affordable units is calculated as a percentage of the total number of dwelling units in the project. Developments that contain both commercial and residential space will use a combination of both calculation methods.
Performance Amount for Commercial Development:
The net unit area of affordable housing required to comply with Performance Option is outlined in Tables A&B for SMC 23.58B.050. The required square footage set-aside for affordable units varies respectively by zone, MHA suffix (M/M1/M2), and performance area intensity as noted in Map A for SMC 23.58C.050. For most zones, the area of affordable housing required ranges between 5-9% of the applicable commercial floor area.
Performance Amount for Residential Development:
The number of affordable housing units required to comply with Performance Option is outlined in Tables A&B for SMC 23.58C.050. The required percentage set-aside similarly varies respectively by zone, MHA suffix (M/M1/M2), and performance area intensity as noted in Map A for SMC 23.58C.050. For most zones, the number of affordable housing units required ranges between 5-11% of the total number of units to be developed in each structure.
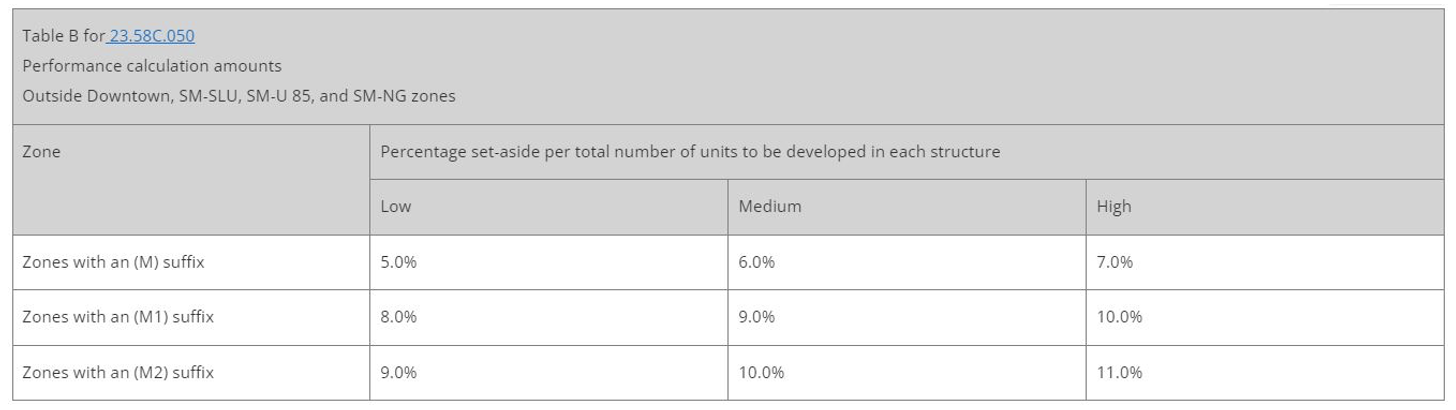
Table from the Seattle municipal code indicating how many units need to be affordable for a project to be exempt from development design review.
Performance Standards for Qualifying Affordable Units:
Duration: Units provided to comply with the Performance Option must remain affordable for 75 years from the date of certificate of occupancy.
Distribution & Comparability: Units provided to satisfy the Performance Option must be generally distributed throughout the structure and be comparable to other units in terms of: Type of dwelling unit such as live-work unit or congregate residence sleeping room; Number and size of bedrooms and bathrooms; Net unit area; Access to amenity areas; Functionality; and Lease term.
Eligibility: Household eligibility varies with unit size and rental date.
At initial occupancy (lease-up), units with a net area of 400 sf or less are eligible to households with incomes up to 40% of AMI. Units with a net area greater than 400 sf are eligible to households with incomes up to 60% of AMI.
Thereafter at annual certification, units with a net area of 400 sf or less are eligible to households with incomes up to 60% of AMI. Units with a net area greater than 400 sf are eligible to households with incomes up to 80% of AMI.
Public Subsidy: Affordable housing units provided to satisfy the requirements of the Performance Option may NOT be used to earn public subsidy such as through the Multifamily Housing Property Tax Exemption (MFTE Program).
Rent Levels: Monthly rents for units with a net area of 400 sf or less, shall not exceed 30% of 40% of AMI. Monthly rents for units with a net area greater than 400 sf, shall not exceed 30% of 60% of AMI. “Monthly rent” must include a utility allowance for heat, gas, electricity, water, sewer, and refuse collection, as well as any recurring fees that are required as a condition of tenancy.
Annual Certification, Third Party Verification: Every year an owner of the rental unit must obtain from each tenant a certification of household size and income. Owners of rental units shall attempt to obtain third party verification whenever possible to substantiate income at each certification, which shall include contacting the individual income source(s) supplied by the household. If written or oral third-party documentation is not available, the owner may accept original documents (pay stubs, W-2, etc.) At the discretion of the Director of Housing, the owner may accept tenant self-certifications after the initial income verification and first annual recertification. The owner shall maintain all certifications and documentation obtained on file for at least six years after they are obtained.
Reporting: Once a year the owner of the rental unit shall submit a written report to the Director of Housing, verified upon oath, demonstrating compliance with Chapter 23.58C. The written report shall state: the occupancy and vacancy of each rental unit, the monthly rent charged for the unit, and the income and size of the household occupying the unit. The Director of Housing may require other documentation to ensure compliance including documentation of rents, copies of tenant certifications, documentation supporting determinations of tenant income including employer’s verification or check stubs, and other documentation necessary to track program outcomes and the demographics of households served. The owner of the rental unit shall pay the Office of Housing an annual fee of $150 per rental unit for the purposes of monitoring compliance with the requirements.


By Jennifer Sobieraj Sanin, Managing Design Principal, and Michael Lama, Project Designer
The Art of Efficiency
Popularized because of their connection to nature and relative abundance of space, garden-style apartments are lower density, low-rise housing complexes that are typified by their green, garden-like surroundings. Through Ankrom Moisan’s experience designing high-quality low-density communities, we’ve found that successful garden-style design is all about striking a balance. There’s an art to creating a community that is highly livable and authentic, yet also efficient and economical. Based upon our expertise with this style of housing, here are our dos and don’ts for creating successful low-density garden-style communities.
Do capitalize on site assets.
Site plans are everything when it comes to designing unique low-density housing. Before any buildings are designed, take note of site features such as topography, open space, noteworthy views, and existing natural resources such as bodies of water or mature trees. Designing a site plan around these features elevates the design of a garden-style apartment community to be authentic to its location, setting the place apart as a destination with its own identity. For example, at Deveraux Glen the site plan intentionally takes advantage of the surrounding green space by orienting the buildings to maximize views. This is apparent in the irregular perimeter, shown below.
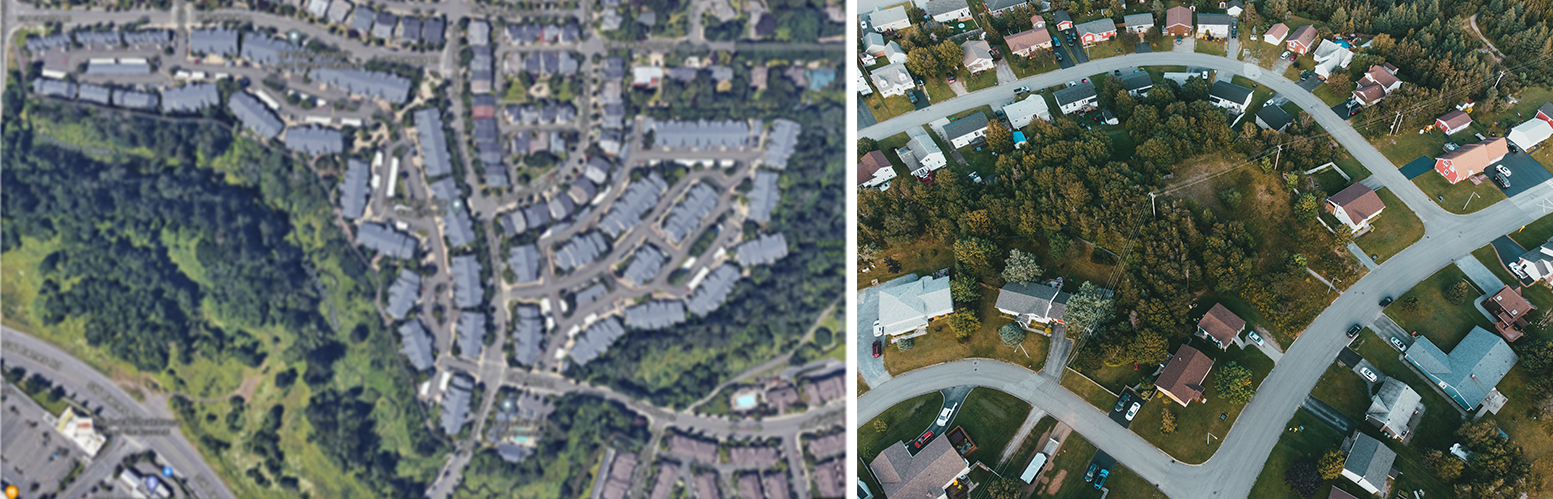

Deveraux Glen site plan | Aerial of a neighborhood by Erik Maclean
Do balance the parking.
While parking yield is important, preserving the character of the place is also essential for success. This requires finding a careful balance. Because available parking ratio ultimately determines home yield, and not allowable density, parking drives (pun intended) everything. Efficient footprints like parking must be designed first, with buildings fitting into the site afterwards and conforming to the lot’s parameters based on the home plan. However, that does not mean the parking lot has to be the focal point for a site’s layout. Remember: nobody wants to live in a parking lot. A certain degree of intentionality is required to design a desirable community that has a sense of place and doesn’t just feel like an asphalt lot.
North Ogden masterplan | Garden-style development photo by Maahid
Don’t neglect landscaping.
Use greenery to break up the humdrum of asphalt. Whenever possible, a space of 15 feet between parking and ground-level homes is ideal for garden-style, as it budgets 5 feet for the pedestrian sidewalk and 10 full feet for landscaping. There should also be landscaping between head-in parking stalls. 5 feet is the minimum amount of space recommended, but again, having more room for trees to be planted both screens the car park from above, and improves the quality of the space at ground level. Utilizing landscaping in this way improves the apartment’s sightlines and views for both the ground-floor homes that look towards the parking lot and the upper-story homes looking down on it. While covered parking may improve the visual landscape of a community, taking it a step further with green roofs or alternated landscaping does much more for both the environment and residents. The ultimate goal in garden-style design is to create a place that is as livable as possible to drive absorption, retention, and rent rates.

Club at the Park | Parking lot at The 206
Do consider walkability.
Since garden-style home doors are exterior-facing, the outdoor experience must be carefully considered. Distances between frequently visited areas need to take walkability into account. Remote parking may allow for an increase in home yield but result in a reduction in rent rate. Designers should be very intentional with how far residents will have to walk to get from their cars to their front door, and vice versa. Parking allocation studies need to be done to assign parking stalls to certain buildings and determine whether or not distances and available parking options realistically work. Trash enclosures, too, need to be within a reasonable distance from residential homes and located along a route accessible to trash collection vehicles for removal. By putting forethought into residents’ travel patterns, designers can create a highly livable place.

Meridian Gardens rendering | Kitts Corner rendering
Do enhance ground-level homes.
Ground level living is perhaps the most important design consideration for low density garden-style apartments. There are a handful of ways to enhance first-floor ground-level homes, the most effective being the inclusion of a stoop at the entrance. Stoops help create a sense of defensible space, and resident identity. Ground level homes also benefit from street elements. Streets are characterized by parallel parking and sidewalks, whereas parking lots are based on 90-degree parking, which means that light from cars in parking lots are angled directly into ground-level windows and the amount of land dedicated to the car is the greatest. Ground-level homes often receive the short end of the stick, so giving those homes extra thought can go a long way for improving the resident experience.

Stoops at The Villas at Amberglen West | Ground-level porches at The Arbory
Don’t underestimate the importance of identity.
Develop an encompassing identity for the entire community through a central amenity. As the heart of the place, the amenity building reinforces the character of the site. Surrounding spaces should support that identity through the quality and character of their architecture and interior design. Don’t shortchange design fees here; It’s better to spend up on the club house and economize elsewhere than to forgo the identity established by a central amenity.
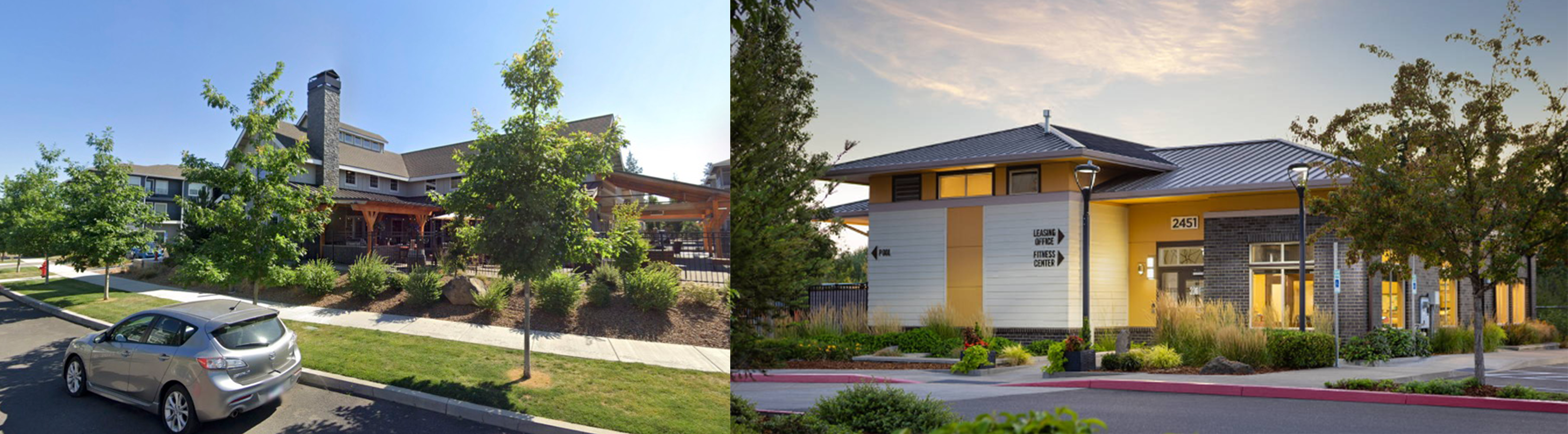

Clubhouse at Seasons Apartments and Farmington Reserve | Clubhouse at The 206
These guidelines are only a brief overview of some of the key principles to creating successful garden-style communities. There is a tremendous level of consideration of the specifics of a site when translating these principles into a successful design. What it all essentially comes down to is hiring an architect who understands these design principles and how to apply them to create efficient, high-quality communities. And of course, having beautifully maintained greenery doesn’t hurt, either.

By Don Sowieja, Principal-in-Charge
Being Well
While physical health and fitness have been an important aspect of residential design for many years, it’s only in the last 5-10 years that the language – and the thinking – has become more expansive.
Wellness is the new watchword. It’s not just a trend, but rather a powerful approach to residential planning, design, and programming that has the potential not only to improve your residents’ lives, but your bottom line, driving demand and tenant loyalty.
Wellness, approached thoughtfully and executed with purpose, is more than an amenity, it’s a business strategy.
Read on…
The Principles of Cost Cutting
Q. What’s your top piece of advice for clients and the entire project team regarding cost efficient design?
A. The most important thing when you’re taking a hard look at cost-efficient design is building a strong, committed team. The owner can really help drive the ship by building a team that will support the goals that they’re advocating for. So, when they bring on a design team or a general contractor, it should be with a clear instruction that this project is prioritizing cost containment and you’ve been selected to help lead us in that direction.
Q. What impact does site selection have on project costs?
A. It can be huge. Some sites are quite simple. They’re flat, they’re unencumbered, they don’t have any nasty soil conditions, they don’t have any onerous zoning requirements. They don’t have a complicated design overlay. And then there are sites that are just the opposite. Maybe they have a lot of topography and require a subgrade system to get a buildable foundation for the building.
They might have really contaminated soil that requires a lot of upfront costs. If it’s in a historic district, there’s historic design overlays. Other design overlay districts require extra jurisdictional review. Anything that takes extra time, extra effort, extra coordination just creates extra work and stretches out the design schedule, which is going to cost the project more money at no significant benefit to the end-user or the developer.

Q. Is it possible to have elevated design while also reducing costs?
A. I know it sounds like it could be an oxymoron, but YES! We know we need to approach the project from a cost containment standpoint, and we want to have design at the forefront of every decision we make. It’s not cost containment first, design second; they should be parallel goals. We can still do excellent design and use those constraints around cost containment as a driving force for our creativity. How we can be creative within the constraints of cost containment – and letting that be our design challenge.
Q. What have you learned about designing efficient units in a way that prioritizes cost containment?
A. One of the biggest things is to design the units with as few variations as possible. We would minimize the number of unit types and then design each of those unit types as efficiently as possible. We also start by asking the question, How small can we make the unit and still make it livable and dignified and usable? The simple truth is square-footage costs money.
On Wy’East Plaza, we built a full-size one-bedroom mockup and loaded it with furniture and people and cabinets and asked, Is this too small? Okay, let’s move the wall out by 12” or 24”. How about now?
Once we felt like we’d found the lowest comfortable size by reducing the square footage we worked to put the whole building on a 24-inch module. This works really well with the scale of building materials. Then we worked to minimize inside and outside corners within the unit, each little moved saved. We tried to minimize the number of doors to reduce purchase and install time. so that there’s a door into the bedroom, a door to the bathroom and that’s it.
Q. How do materials and components factor in to cost cutting?
A. It’s important to work around standard material sizing from the industry so there’s not a lot of material waste and not a lot of cutting and fitting for the folks forming the concrete, the framing contractor, the drywall contractor, etc.
If everything’s designed around those material modules there’s less waste so they’re not having to buy as much overage. Then, you can take it more to the procurement level like, Are we buying materials that are locally sourced? Is the brick coming from Oregon versus Ohio? We look for those kinds of efficiencies wherever we can get them.

Q. Can you talk about leveraging the expertise of subcontractors. And how can their knowledge and experience help ensure design efficiency?
A. This is hugely impactful. How to do that is a trick that falls on a quality established general contractor, who has a lot of existing relationships with quality subcontractors. Those relationships can be leveraged to get subs to participate in the early design work not yet knowing whether they’ve won the bid.
Once you get the subcontractors engaged in the design process, then you start asking them, What would a building look like that has the most efficient plumbing system? What would a building look like that has the most efficient HVAC distribution system? If you could put your electrical room anywhere in the building to be the most efficient to install, and purchase equipment for, where would that be? If we do the roof this way is it more complicated than if we do it this way? What if you were king or queen for the day? And then you just listen. Really, nobody knows more about how buildings go together than the people who are on the job site doing the work, so it’s great if you can harness all that practical experience.
Q. What have you learned about setting a project up for successful approval during the design review process?
A. Well, one way to look at it is that we have to be humble designers. What I mean by that is if we design something and hope to get approval for it because it doesn’t exactly match the zoning or the design overlay requirements, and we’re going to have to ask for special compensation for a design move that we think is important but doesn’t match what’s allowed, then we’ve put another encumbrance on the project that’s going to cost time and money to resolve. So, we try to leverage our creative design abilities to do the best building we can within the existing set of approved design criteria. If we’re in a zone that has a particular set of design overlays, then we need to just work within those constraints and not try to use this project to flex our most impressive design edginess.
Click to read and download the Seven Principles of Cost Efficient Design, assembled in partnership with Walsh Construction and Reach Community Development.

Michael Bonn, Principal
Bringing Bigger Buildings to Smaller Jurisdictions
Over the last several years, more demand in smaller markets has resulted in increased proposals for larger scale developments. These jurisdictions have not previously had to review projects that utilize code criteria that are unique to larger building types.
From the construction permitting point of view, bigger buildings have different codes, and those codes have different interpretations from city to city, and sometimes reviewer to reviewer.
Jurisdictions are experts at the familiar but can often be resistant to the new. Given the role that building officials play in safeguarding the health, safety, and welfare of their community, a conservative approach to new code criteria is a reasonably common practice.
Our experience in jurisdictions with more complex code usage can help clients understand the way others have successfully worked with designers to implement unfamiliar strategies in code compliance.
Our expertise in larger buildings in bigger markets can be valuable with code analysis and interpretation in smaller markets, both from the designer and reviewers’ points of view.
We have consistently seen that building official/fire marshal engagement prior to submittal is key. Meeting early and often minimizes unforeseen issues arising during plan check review. Our history of discussions/solutions from multiple jurisdictions allows for specific issues to be flagged and addressed with real-world applications that have been proven to be successful.
We have found that when discussing podium construction there are several key elements to consider within the wood-framed components that differ from applications that do not include a concrete podium. Here are a few key items to consider:
- Type III: A wood construction with two-hour rated exterior walls, from the inside and out.
When building height exceeds 70 ft., this construction type allows for building heights up to 85 ft., and requires non-combustible exterior wall construction, commonly achieved through the use of fire-retardant treated lumber. Cladding and its support elements must also be non-combustible above 40 ft. Critical considerations include close study of the highest occupiable floor level based on fire access set-up point. If the lowest point of fire access results in a dimension to the highest occupiable floor level that exceeds 75 ft., then high-rise criteria become applicable. Cost typically limits high-rise construction to projects which far exceed 75 ft. height. Designers must consider this cost impact, especially when contemplating occupied roof decks, which some jurisdictions will allow to exceed the 75 ft. height, while others will not.
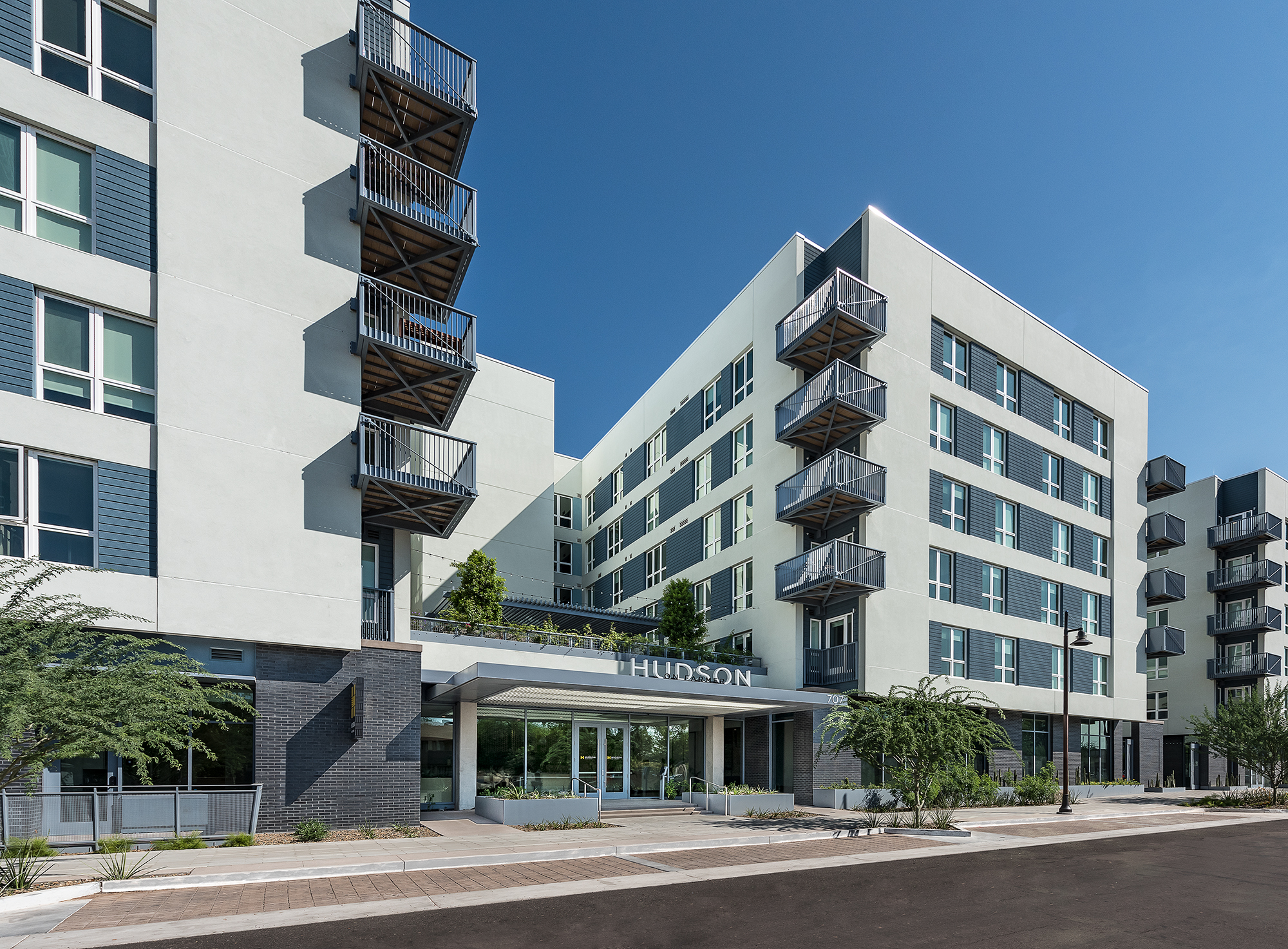
Project Example – Hudson on Farmer (Farmer Arts), Tempe, AZ (Framing construction, completed building)


- Type V: A wood construction with one-hour rated exterior walls from the outside.
When construction does not exceed 70 ft. this construction type allows for reduced costs and more easily managed fire resistivity criteria. Building area is limited, and in many cases fire walls within the building are required to compartmentalize the structure. For multifamily buildings, corridors penetrate these walls requiring rated opening protection. Although these walls add cost, they provide an opportunity to reduce the number of stairwells when used as horizontal exits between building compartments. Designers must consider how, and when, to use the horizontal exit tool, ensuring that no more than half of the required exits from a floor level are provided by horizontal exits. Additionally, these opening assemblies can be provided via several options, including manufactured assemblies, and custom specified components. Designers must consider the comparative costs of the different approaches and the capacity of the project’s general contractor to manage the installation of the selected approach.
Project Example – Modera Northgate, Seattle, WA. (Final rendering, floor plan compartment diagram)

- Type I: Podium/basement non-combustible construction of one, two, or three levels can be provided as a podium for multiple stories of wood construction above.
The ability to allow for the wood frame construction type of the building above to penetrate the podium reduces costs when stairs are able to be built of wood. Exterior wall framing must be built of non-combustible framing, however, when using metal studs, exterior insulation is often required to meet energy code insulation values. Using fire-retardant treated lumber can be an effective tool in allowing for exterior sheathing and cladding planes to align across the podium level.
Project Example – Canopy (Shea Aurora) Phase II, Shoreline, WA (podium construction photo, final rendering)


There is no one-size-fits-all solution. However, being able to work from multiple points of view allows for specific concerns to be addressed, while looking to past successes for location-specific solutions.

by Don Sowieja, Principal AIA, NCARB
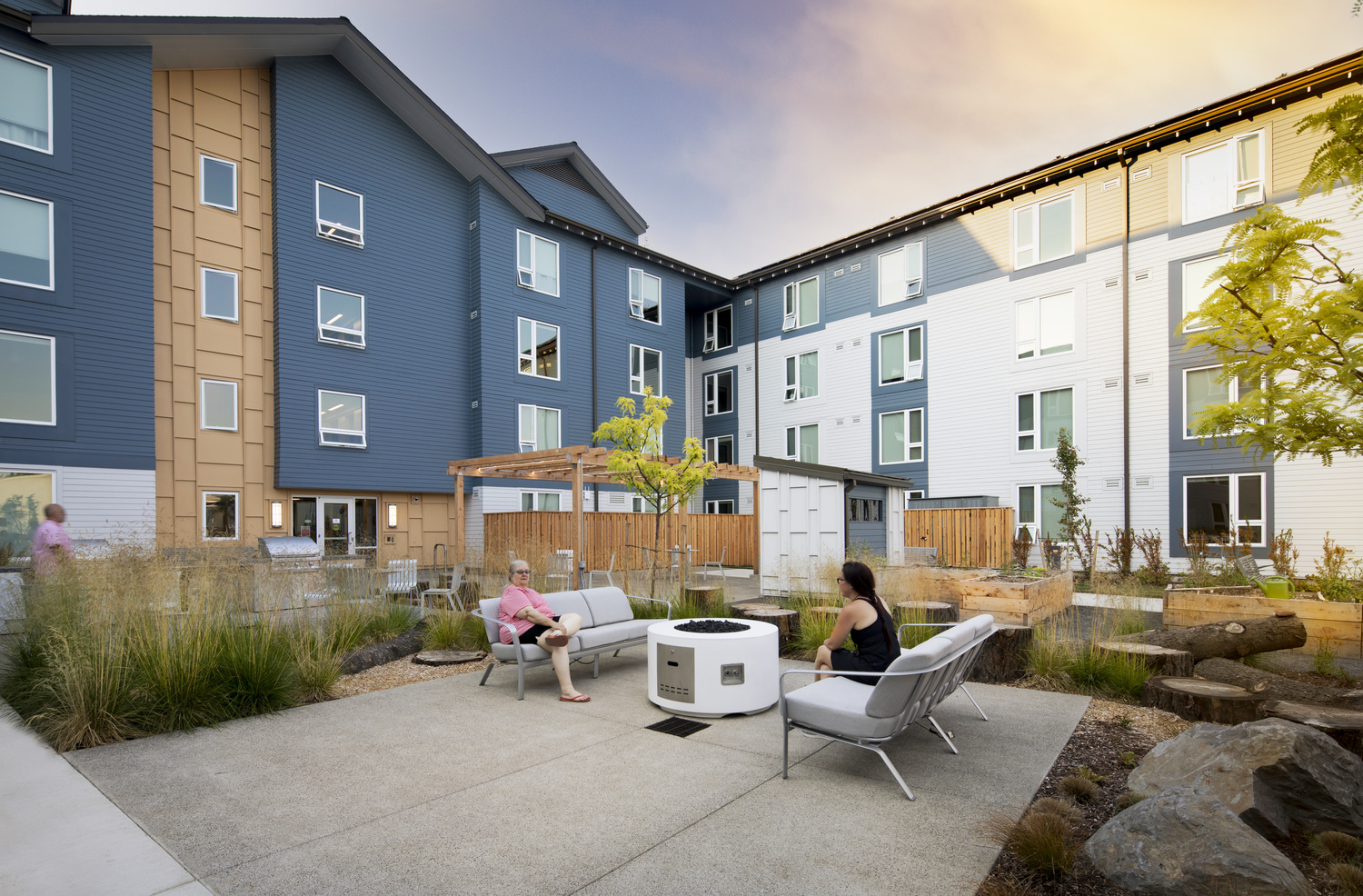
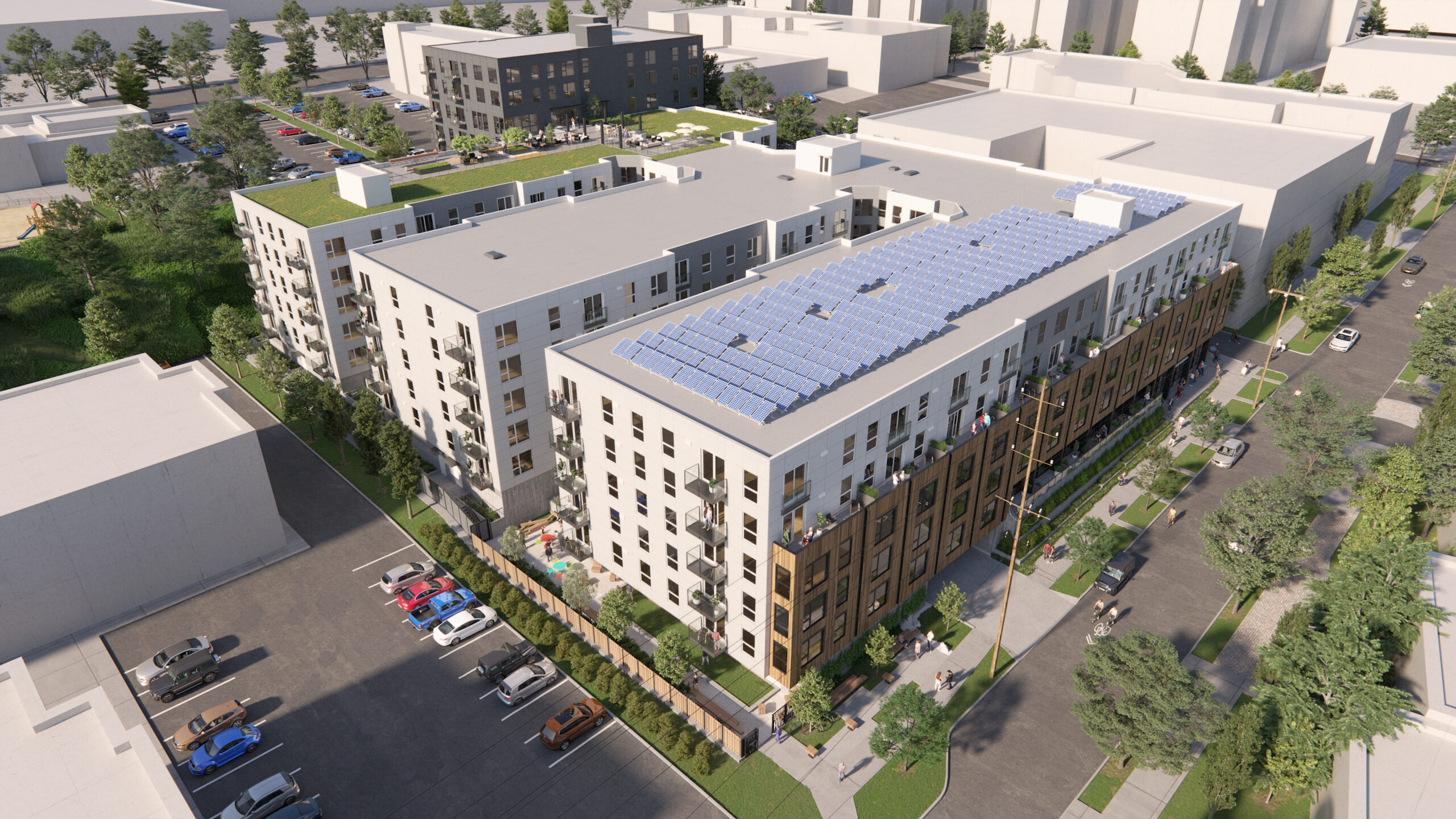
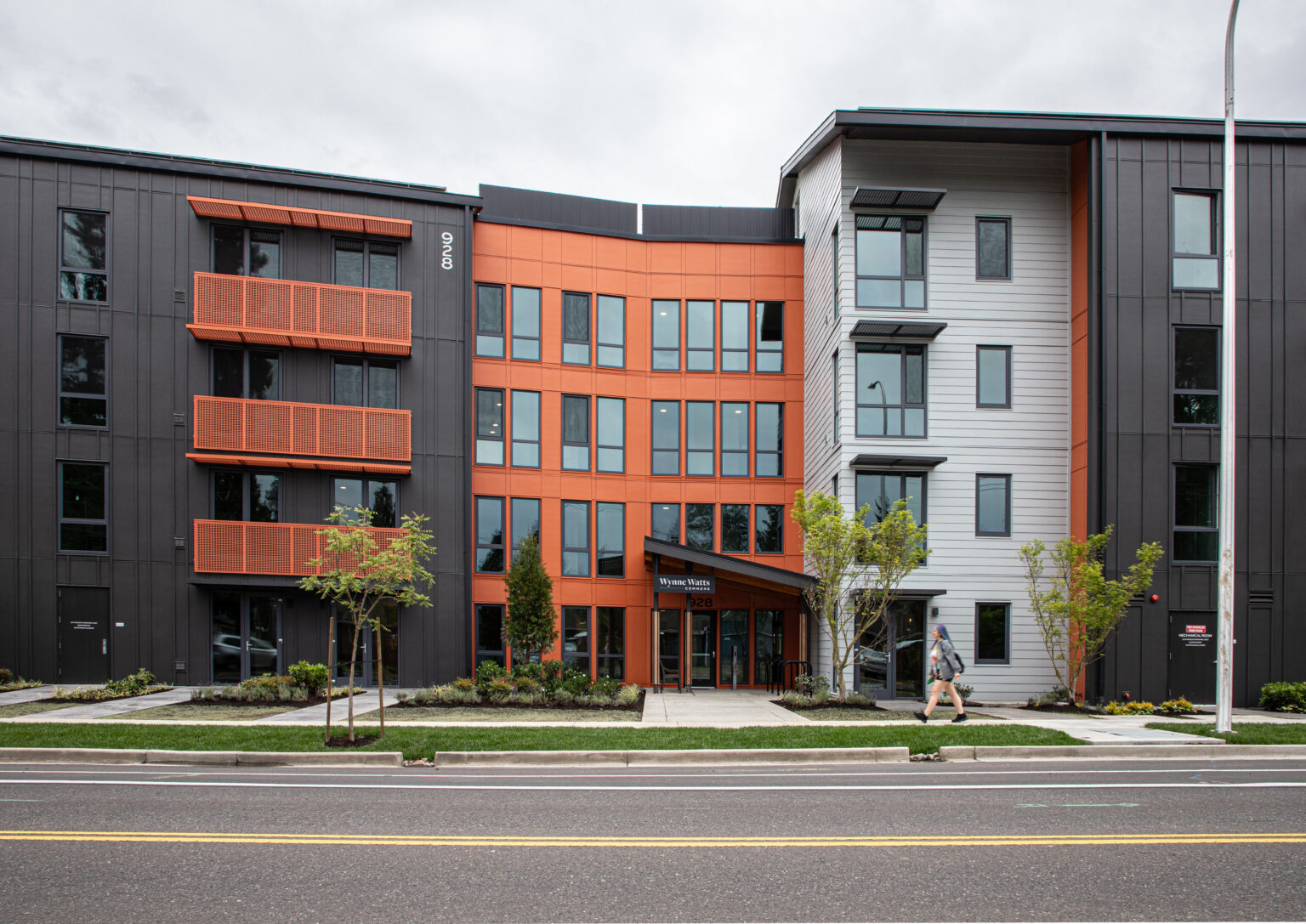
Wynne Watts Commons
It is undeniable that housing insecurity affects millions across the United States. Rents are up and homelessness is on the rise. There are many factors that lead to these crises, including high housing costs relative to income, poor housing quality, unstable neighborhoods, or even health concerns and peripheral medical challenges and costs. Add to that the encompassing environmental impacts of climate change and a driving need to design and build more sustainably; we are faced with the need to take a more holistic approach to housing and accessibility to address our growing concern for the wellbeing of our communities.
We partnered with Albertina Kerr, an organization dedicated to supporting people experiencing intellectual and developmental disabilities (I/DD), mental health challenges, and other social barriers, to design the largest affordable and accessible housing project in the PNW. This joint project became one of the largest Zero Energy affordable housing projects in the U.S.
This four-story, 150-unit complex features 30 accessible units designed to provide adults with intellectual and/or developmental disabilities, earning 30% or less than the average median income, a place to live independently. Three units are available to families needing temporary housing and the remaining units are reserved for low wage direct service providers. This project showcases innovative technologies and design features readily available today to achieve better health outcomes for residents, minimal overall carbon emissions, and significant savings on energy bills. Energy-efficient features include a 660 KWh PV Array that will produce 727 MW-hours of electricity annually, enough renewable energy to fully operate the building with no utility cost to residents.
Albertina Kerr’s in-house staff were consulted to help inform the direction of features that are most useful to the residents. Smart-home integrations enhance safety and useability, and pull-out cook tops and mechanized upper cabinets help residents manage daily tasks. Thoughtfully integrated accessibility features include room darkening shades, RGB controllable lighting for chromatherapy mood management, and acoustically enhanced wall, floor, and ceiling construction that gives residents control of their space to prevent overstimulation.
Wynne Watts Commons is a huge step forward for sustainable and inclusive quality housing for some of the most vulnerable in our community.

by Mackenzie Gilstrap, Sr. Marketing Coordinator















