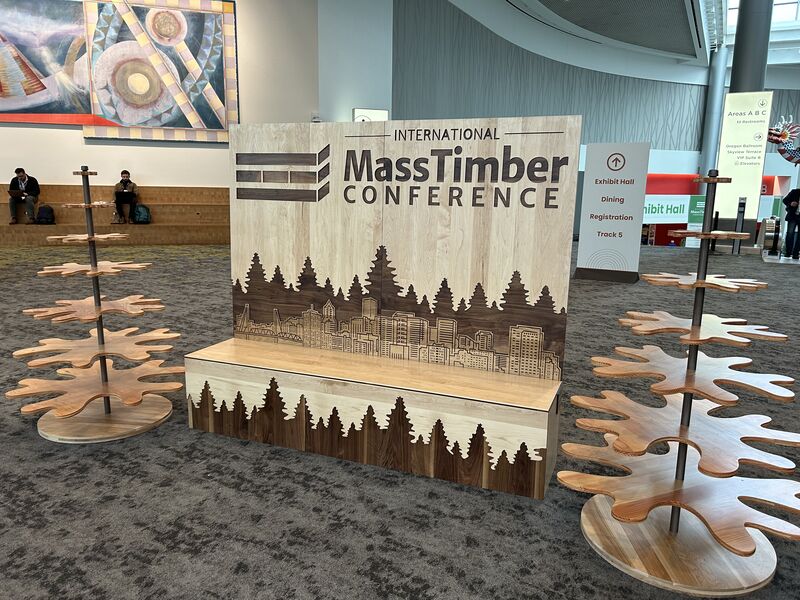
Our in-house sustainability expert, Amanda Lunger, participated in the 2025 International Mass Timber Conference this month.
Amanda attended several sessions to better understand the benefits of Mass Timber—beyond sustainability—for developers and building owners.
Here are four key insights.
Mass timber creates opportunities for rental premiums.
One developer shared that in their spec-built office building, there was a 20% upfront cost premium for mass timber over light gauge steel, but their building commanded a 40% rental premium when compared to other conventional structures in the area!
Mass timber results in cost-savings.
Although the base material cost of wood is currently high, savings from shorter project timelines, reduced onsite labor, lower import duties, and other operational efficiencies can offset the initial premium. Plus, mass timber performs better thermally, further enhancing its long-term cost-effectiveness.
Mass timber is a long-term investment.
Mass timber structures are valuable long-term investments thanks to their adaptability. CLT panels are easily cut into and filled in, making mass timber structures flexible to the changing needs of a building program and ideal for tenant improvement projects. Mass timber structures are also often inherently designed for disassembly, meaning they can likely be deconstructed and reconstructed in another place in the community when densification happens.
Mass timber requires design team expertise.
The first question an insurance company will ask is whether the design and construction team has any experience with this typology. It’s critical to have an architect who understands the specific moisture, fire, and building code concerns that come with wood buildings.
Mass Timber Case Study: Sandy Pine
As a firm, Ankrom Moisan has a robust experience with mass timber. We were early adopters of the technology, and our expertise exemplifies our commitment to both sustainability and innovation.
Initially, we carved out a niche in mass timber office buildings, completing several projects with technologies like CLT, NLT, and Mass Plywood systems.
As our expertise and relationships in the mass timber market grew, we decided to merge this knowledge with our core strength in multifamily housing. With over 33,000 residential units completed for developers over the past 40+ years, we have amassed a deep understanding of this typology.
Seeing an opportunity for technology to meet typology, we decided it was time to unify and evolve these two distinct areas of expertise.
Sandy Pine stands as a testament to this evolution – a towering high-rise of market-rate housing in Portland, Oregon’s vibrant east side. This project represents many of our best strategies for integrating modular CLT mass timber systems within multifamily buildings, offering a perfect case study for the future of mass timber in housing projects of various types.
Check out the case study here:
Project Walkthrough: Plaza Los Amigos
Named after the large, multigenerational mutual aid society created by Mexican and Texan farmworkers who migrated to Cornelius in the 1950s, Plaza Los Amigos honors the traditions of the past while supporting the development of new relationships.
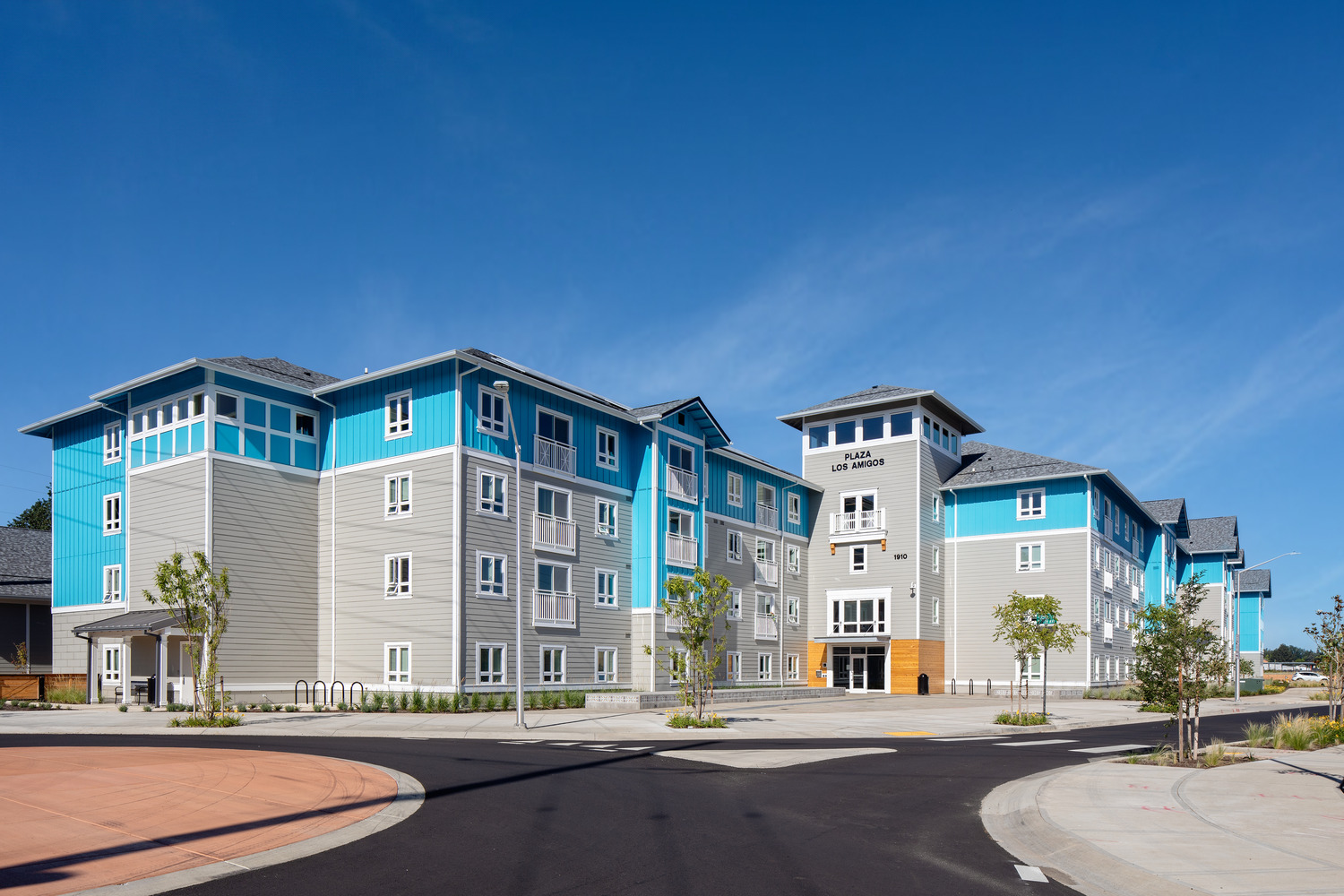

Opportunities to come together, celebrate, and support one another, much like the original Los Amigos group “Los Amigos Club” did, can be found throughout the property. Inside and out, community is emphasized through connected amenities and shared spaces, all designed with the traditions of the local Hispanic culture in mind.
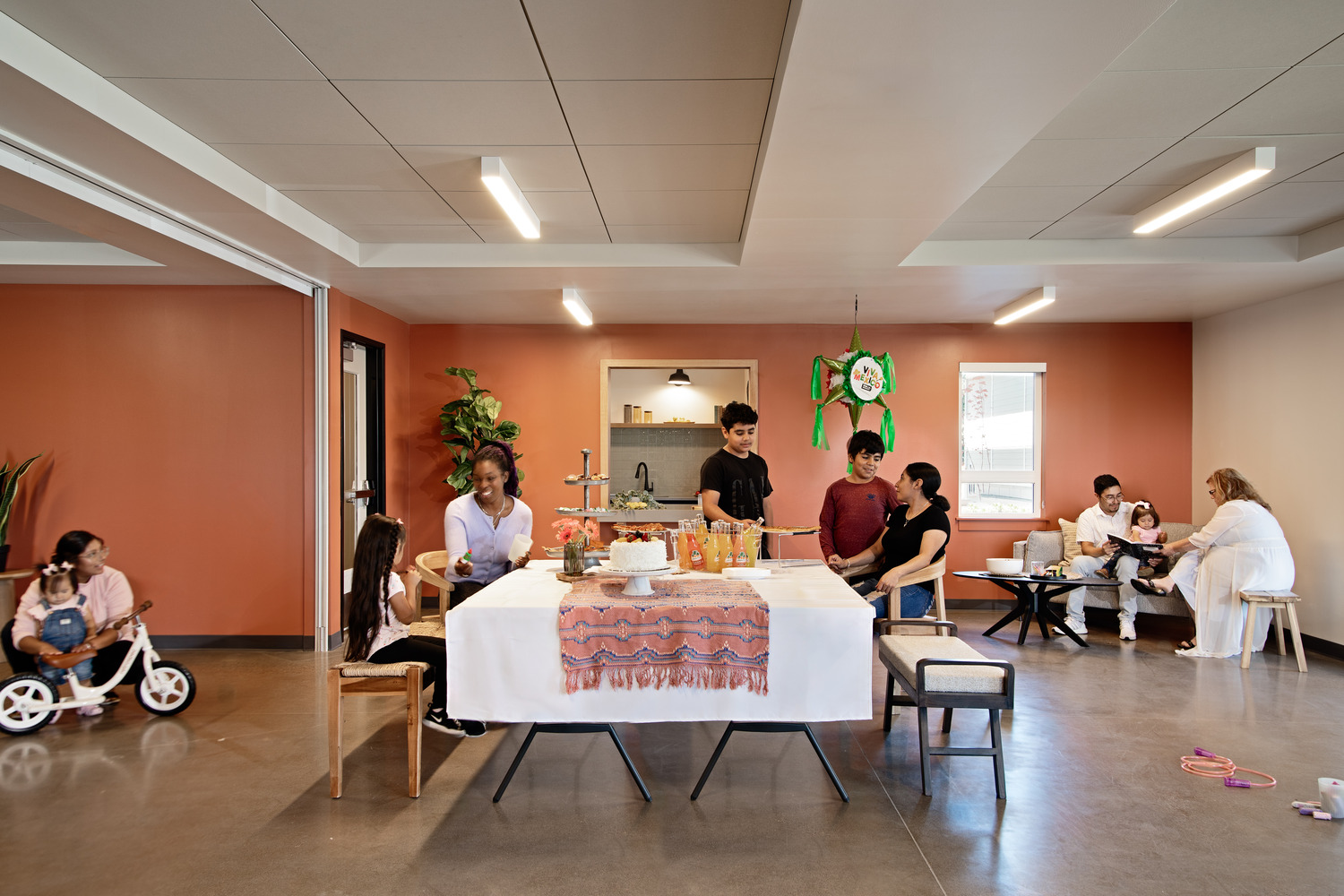

By embracing the heritage of Cornelius’ Hispanic demographic, the affordable, family-oriented housing complex seeks to strike a cohesive balance between reminders of home in Mexico and the aesthetics of the Pacific Northwest’s agricultural history.
Offering the promise of homemade food, a place to sleep, and a sense of belonging and support, the new Plaza Los Amigos is where strangers become friends, and friends become family.
Home on the Range
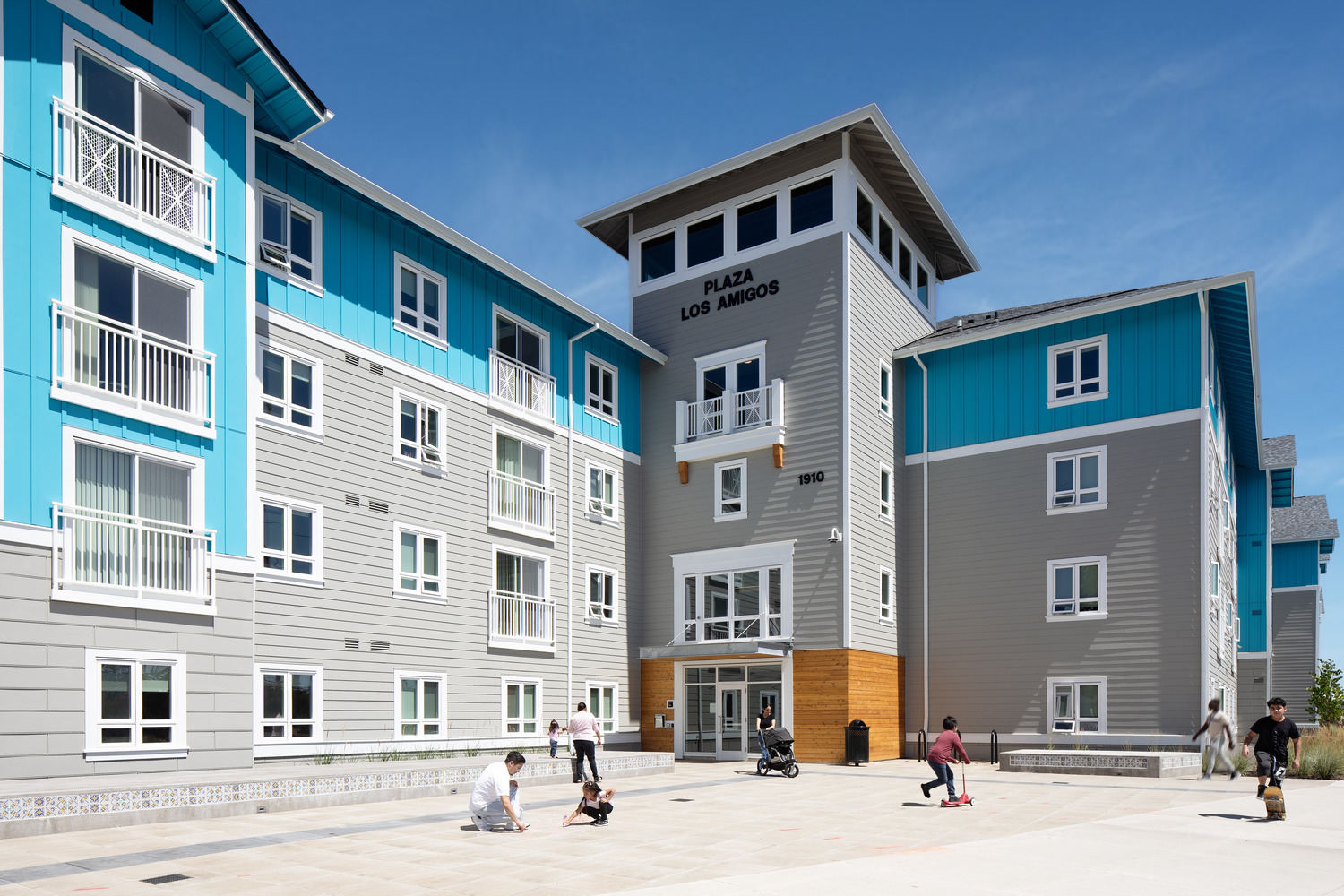

Inspired by the geographical location and the agricultural history of Cornelius, material choices traditionally tied to farmhouse aesthetics influence the design palette of Plaza Los Amigos, positioning the affordable housing complex as a spacious sanctuary of the new frontier.
Simple, yet hardy materials like lap and board and batten siding are paired with white trim and window frames, calling back to classical agricultural architecture and adding flashes of brilliance that stand apart from the rest of the structure’s grey-on-grey color scheme. The building is a zig-zag shape, permitting many connections between interior and exterior spaces and the residents that occupy them.
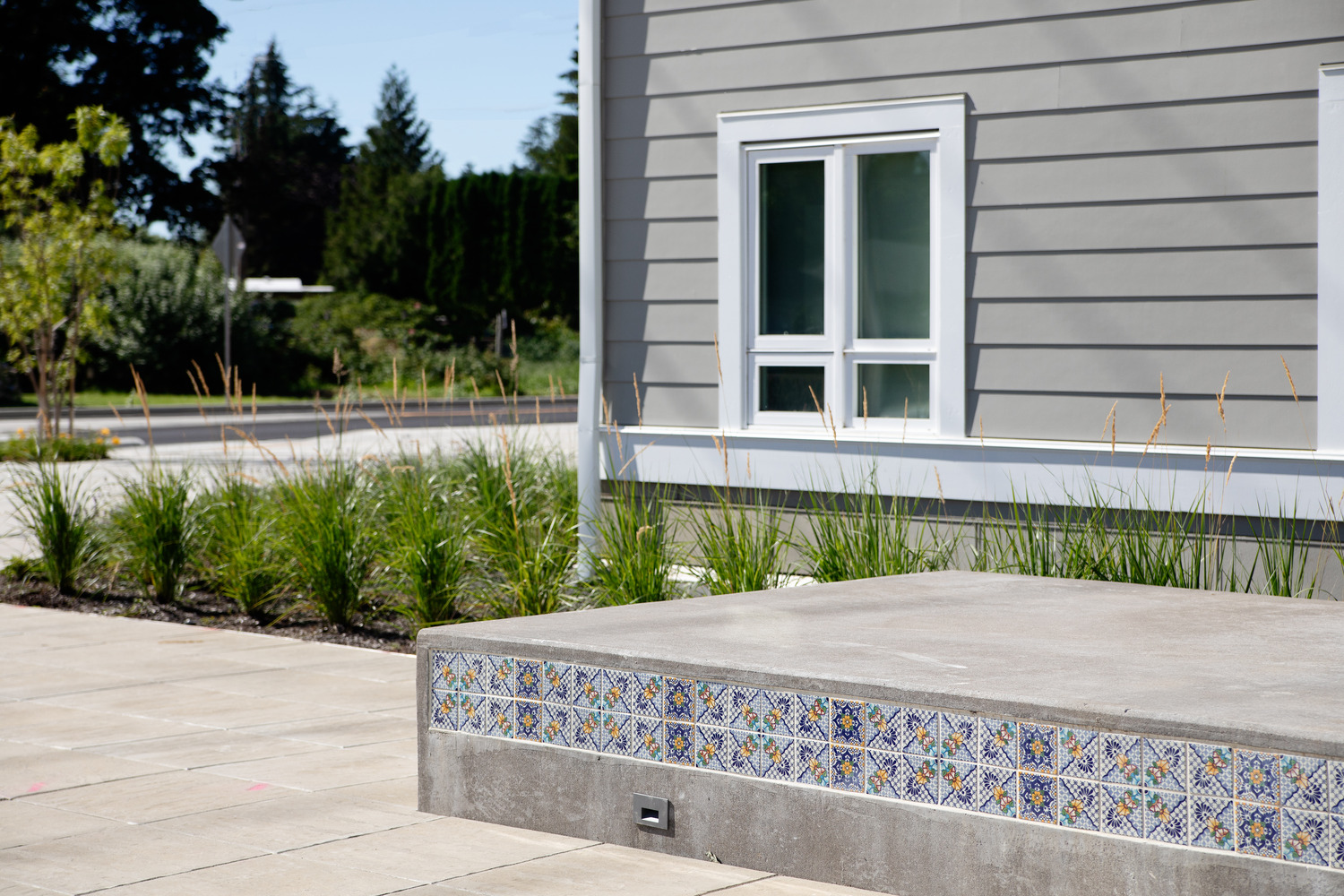

Saltillo tiles sourced from Mexico are used in planters and benches in the front courtyard of the site, bringing together the vibrant traditions of Hispanic culture and the regional, outdoorsy aesthetic of Oregon. The outdoor front plaza was a crucial element to the site, allowing residents to gather, host events, or enjoy the outdoors as they wait for a friend or rideshare to pick them up.
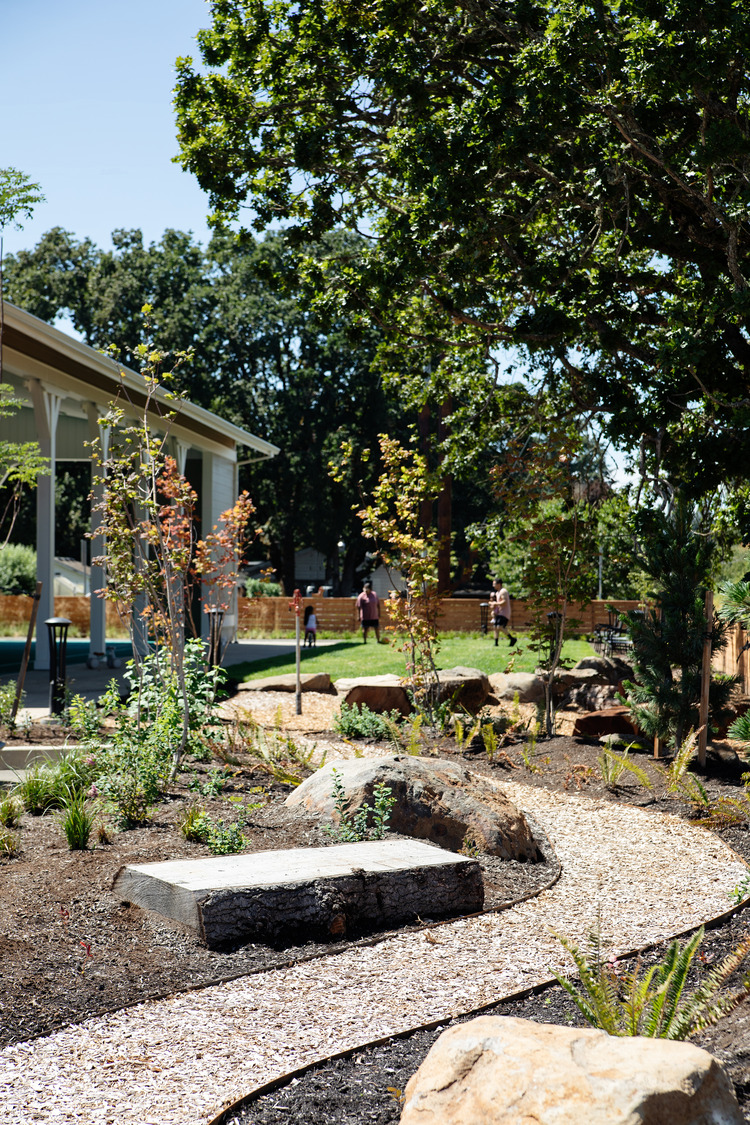

In the building’s back is an open space with a covered futsal court and greenery. Connecting to a park on the east of the site, both the front and back courtyards provide plenty of open space for use in get-togethers and other celebrations.
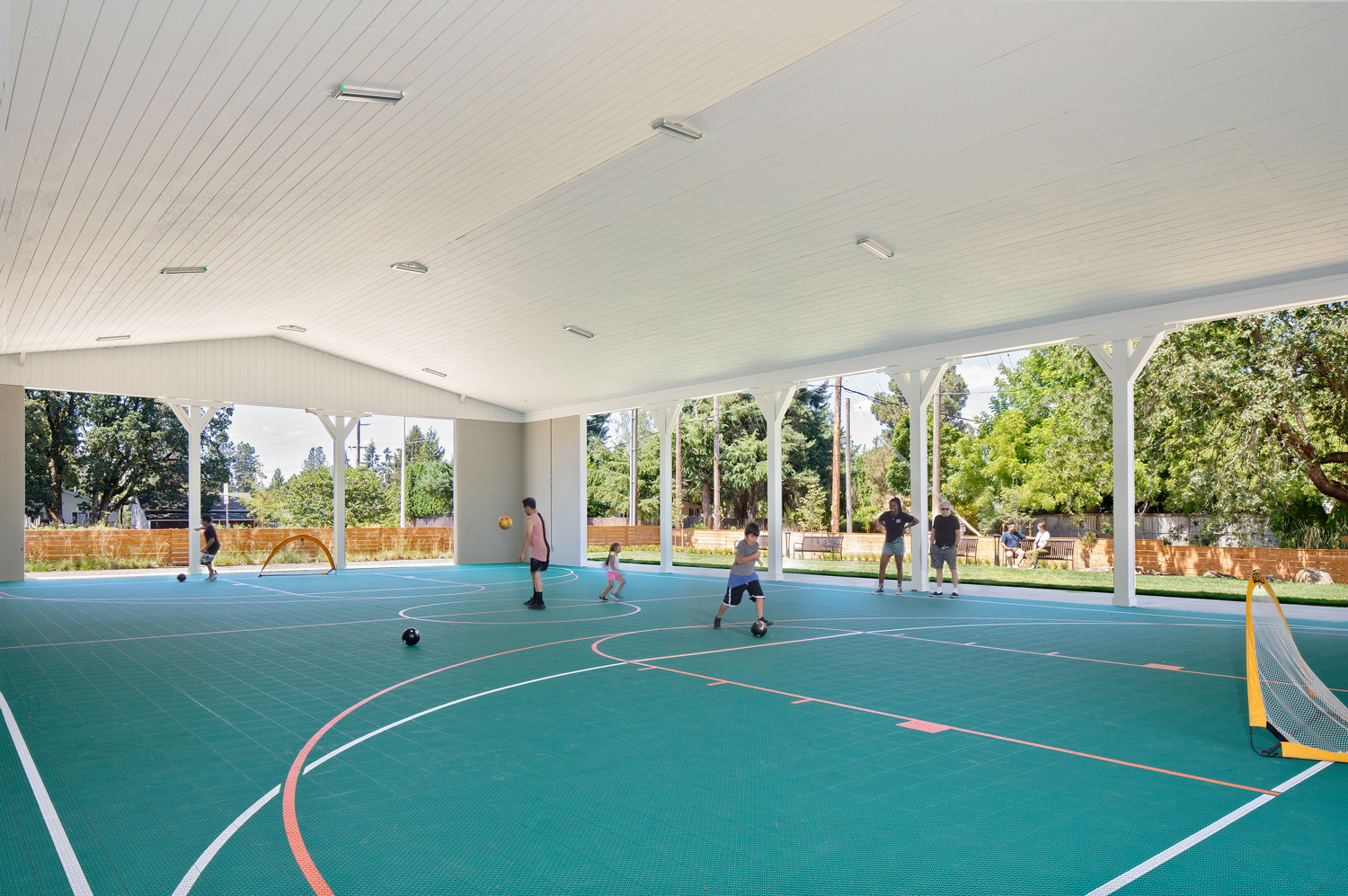

Where Families Flourish
Comprised of 113 affordable 2- and 3-bedroom units, Plaza Los Amigos is designed as a home for families to flourish. An understanding that these units would be the backdrop for multiple generations to grow up and grow old in led to an emphasis on family-oriented elements throughout the individual units and shared spaces.
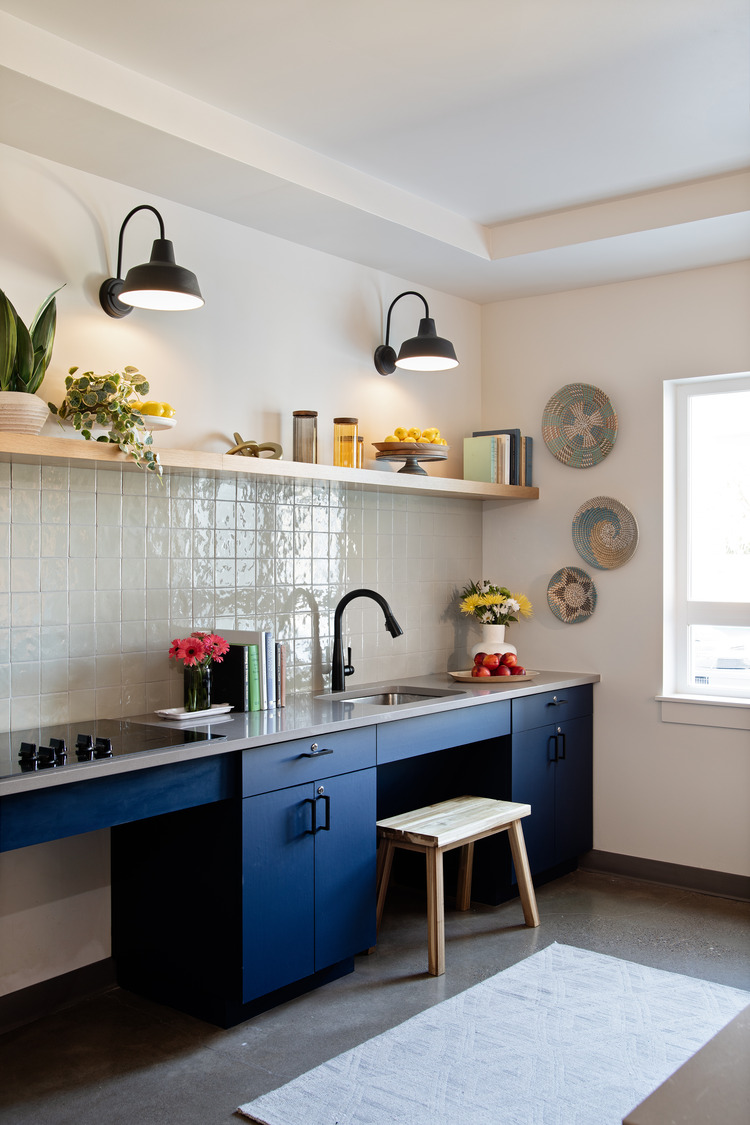

To support resident families through the challenges of raising kids, a unique decision was made to place residential kitchens along the exterior walls of units. This allows parents to keep an eye on their kids as they play outside in the plaza, while still being able to cook dinner or wash dishes.
Partnering with Sequoia Mental Health Services, the building offers culturally competent, accessible resources and support aimed at the safety, security, and well-being of residents. Sixteen individual residential units are designated to provide stability to unhoused community members.
Other forms of support are seen in the two lobby photo rails, which encourage residents to share and show off their accomplishments, whether they are good grades, a creative art project, a recent certification, or any other acknowledgement that they are proud of. A strong connection to the Dreamers resulted in this feature – Plaza Los Amigos wanted to highlight the dreams and achievements of its residents to encourage a more connected community.

Spacious elevator lobbies on each floor – elevated by the patterns of colorful graphic tiles – serve as meeting points, overlooking the Plaza courtyard below and leading residents to shared amenities throughout the building. These amenities include laundry rooms on each floor, a community room and adjoining community kitchen, and an outdoor covered futsal court. The community kitchen includes a six-burner stoves, designed to help facilitate large celebrations and shared feasts that bring the community together as one.
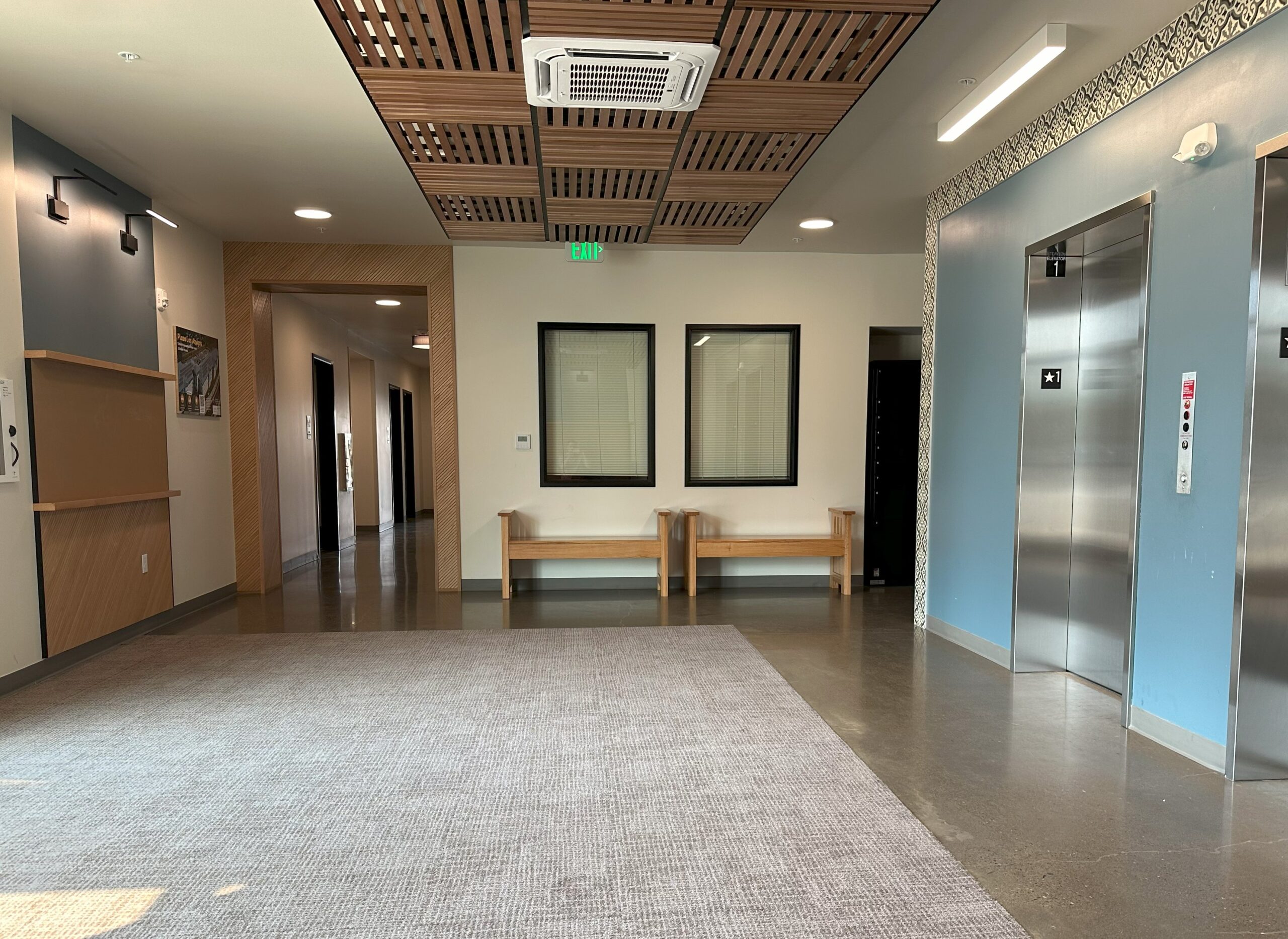

As a special gift to Bienestar, one of the key architects on the project spent their own personal time transforming lumber from a oak tree on a nearby Bienestar site into two custom benches, to be utilized in the elevator lobby at the heart of the community. Engraved with a note explaining the collaboration between LMC Construction and Ankrom Moisan, the benches recognize and celebrate the significant work that Bienestar and Plaza Los Amigos do to provide affordable housing to those who need it in Washington County.
Dave Heater Receives the 2023 Vistage Lifetime Achievement Award
Dave Heater has been a member of Vistage, an executive coaching organization for CEOs and key executives, since 2016—the same year he became President of Ankrom Moisan.
This year he was selected as the winner of the Lifetime Achievement Award, an award celebrating visionary leaders who embody Vistage values.
Dave’s achievement lies in having fostered very high client retention and employee satisfaction rates. His 100% ownership ESOP plan fosters team morale and prosperity, and he aspires to double the company’s size in four west coast offices. Leveraging diverse industries like housing, hospitality, senior, office, and healthcare, Dave ensures steady clientele and abundant design prospects.
“One of the things I am most proud of is establishing a vision for our company. A vision that includes our driving purpose, where we are going and how we all need to work together as a team to achieve that vision.”
Learn more about our vision here.
Dave with AM founders, Tom Moisan and Stewart Ankrom | Dave at the 2022 AM Holiday Party
Watch Dave’s acceptance video here.
More about the 2023 Vistage Awards here.
Making the Future Feasible
Ankrom Moisan has offered feasibility studies as a service to existing and potential clients for decades. For those who are unfamiliar, a feasibility study helps assess the viability of a potential development on a particular property. It aims to help a real estate investor understand the future amount of revenue-generating area on a piece of land, and what a reasonable sales prices might be for that land.
Typically, the feasibility study process begins when a client, landowner, or broker reaches out to us. We usually start with a site analysis, to get an idea of the average unit size and parking ratio, and then conduct a ‘fit test.’ That fit test quickly and efficiently diagrams potential development outcomes that could be realized on the land parcel. When conducting a fit test, we look at the site’s zoning code, relevant building code, physical site characteristics, visible utilities, site context, and building typology constraints. These constraints are often related to building uses, building type, height and size, or the amount of parking required. For example, a housing-use structure has much different parameters than an office-use one. Further, a ‘Stick-Frame Wood’ building typology will yield something quite different than Cross Laminated Timber or Concrete.
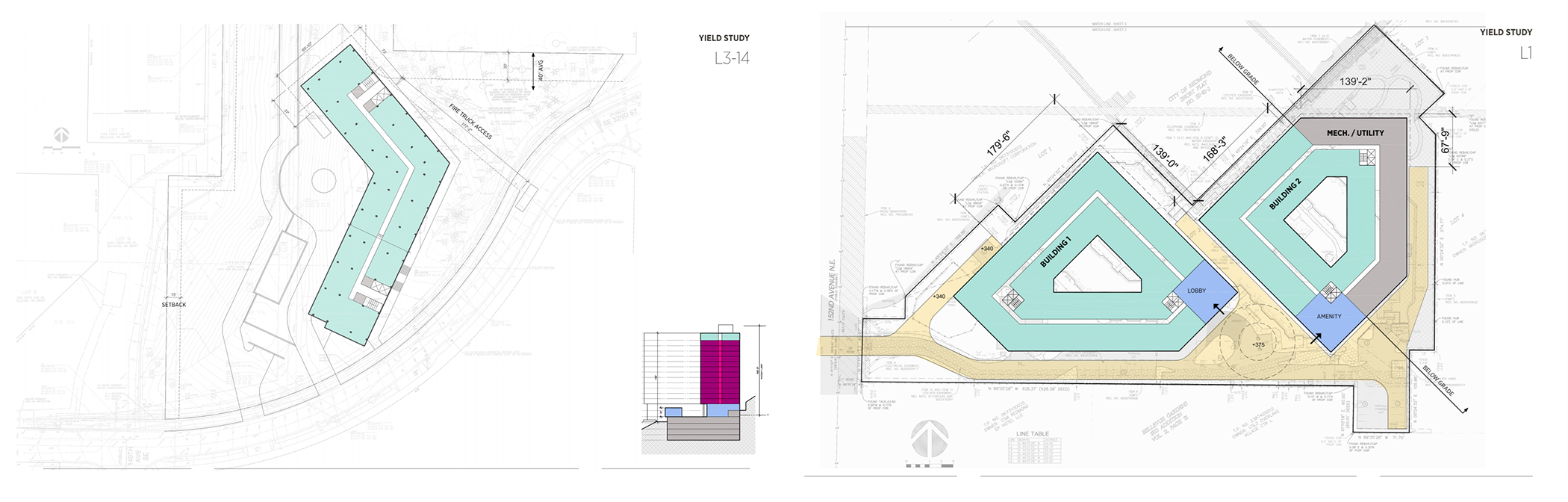
Examples of a feasibility yield study.
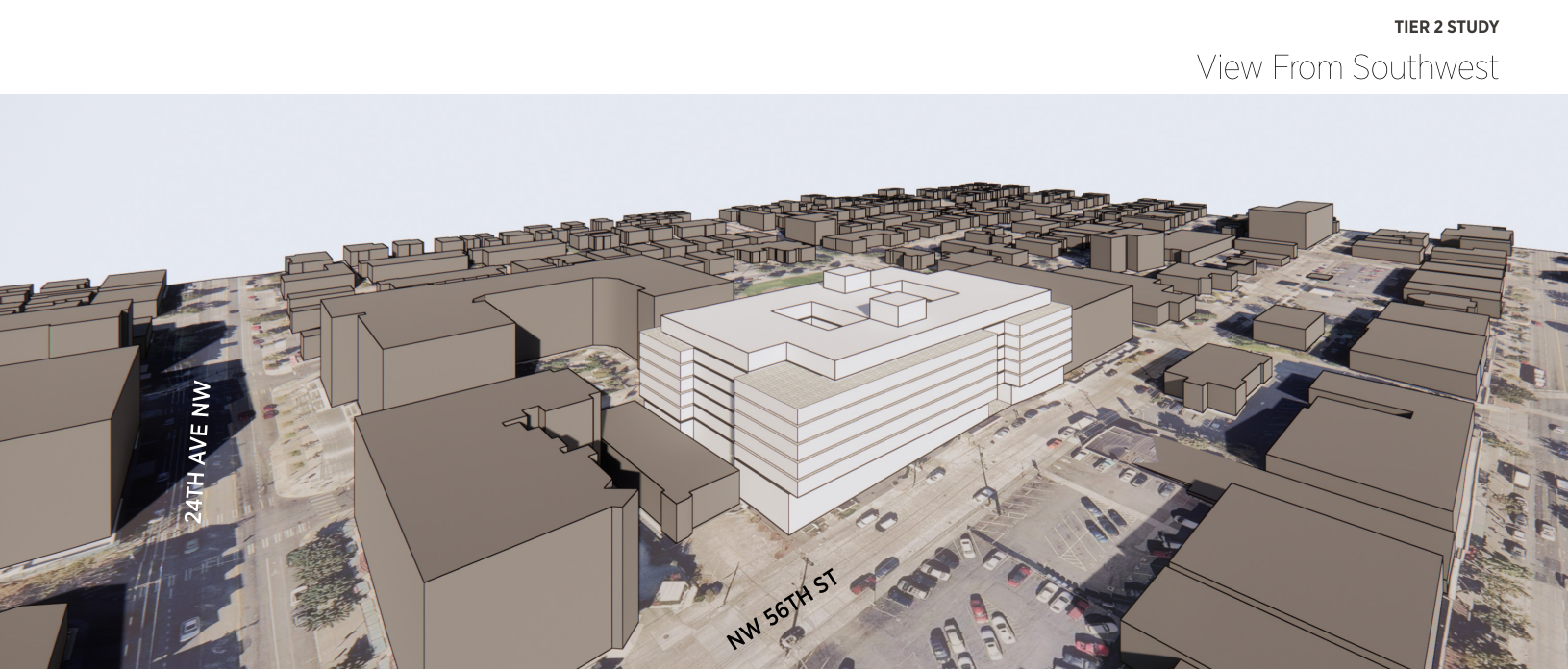
If desired, we can go further and analyze architectural outcomes that consider preliminary ideas about building design and character. Sometimes, a client will provide their own constraints or parameters, like a more detailed unit type and amenity program. Renderings of varied detail may be added to this process to help visualize a proposed project idea; they are useful to illustrate the early-stage potential of development ideas to a wider audience.
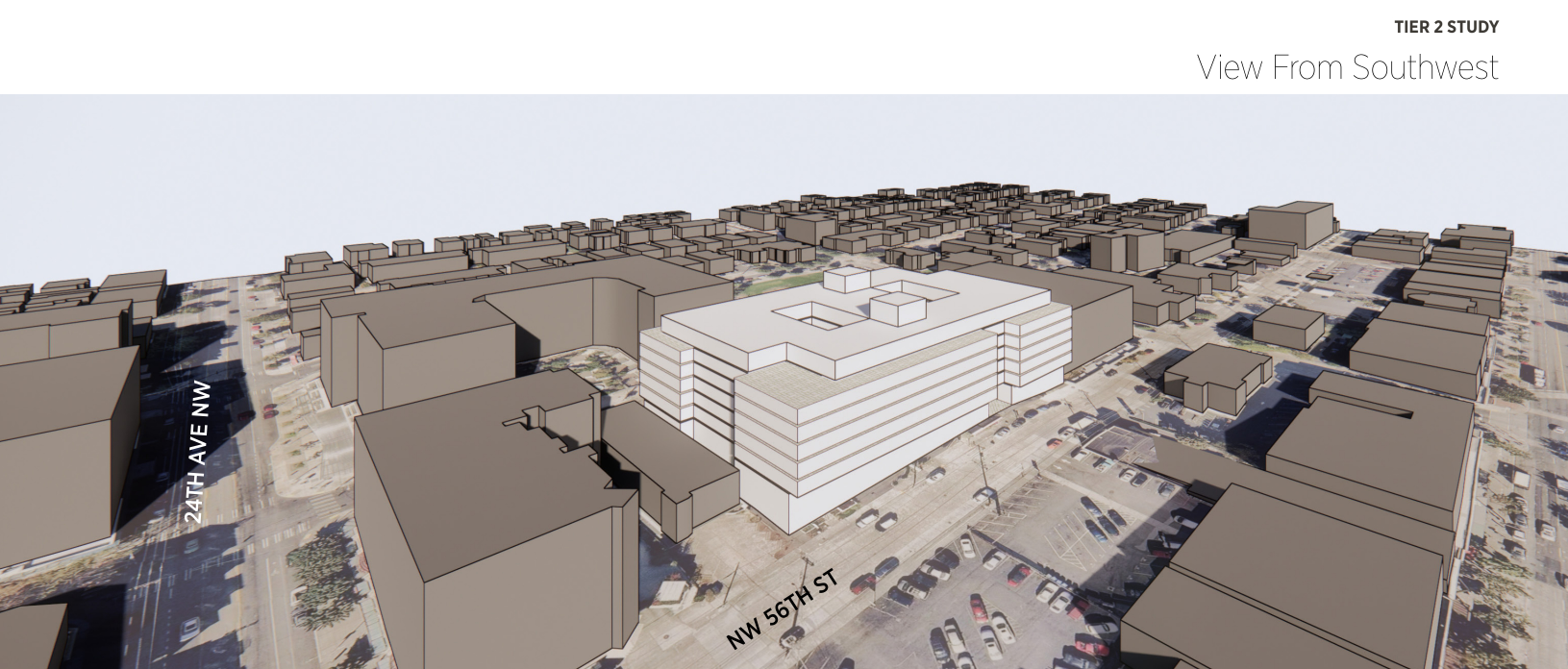

Example of a Tier 2 Feasibility Study Perspective View.
We often provide our clients with multiple (and sometimes contrasting) design ideas. By discussing the advantages and drawbacks of each idea, we reach a point of mutual understanding with our clients and can begin to fine-tune their vision.
Animated early visioning sketch for a multifamily housing urban land parcel assessment.
It is all about leveraging future architectural solutions to effectively utilize what a site has to offer. We are constantly seeking improvement in this process and are regularly evaluating methods to do so. From a basic ‘back-of-the-napkin and a calculator’ approach to a deeper architectural examination informed by years of design experience, or even the use of Artificial Intelligence software that can automate metric evaluation of a site, we consider all possibilities and methods of maximizing a project’s design according to client desires and site parameters.

3D Massing Views and renderings conducted for a Tier Three feasibility study.
Through this process, we give clients, landowners, and brokers meaningful guidance towards the value of their land parcel. This process is especially helpful for people interested in working with Ankrom Moisan for the first time, as a feasibility study is an uncomplicated way for prospective clients to get to know us and learn how we work. It is a great opportunity to see if we work well together.
We have a vast resumé of work and pull from a wide range of past experiences with different building types – everything from tall to small, across a variety of uses (retail, hotel, office, hospitality, housing, etc.). We enjoy this work as it is an essential part of our process. We enjoy offering feasibility study services that share our expertise with longtime and prospective clients, landowners, and brokers alike, showing exactly why Ankrom Moisan is a valued design partner.



By Jason Roberts, Managing Design Principal, Bronson Graff, Associate Principal, and Jack Cochran, Marketing Coordinator.
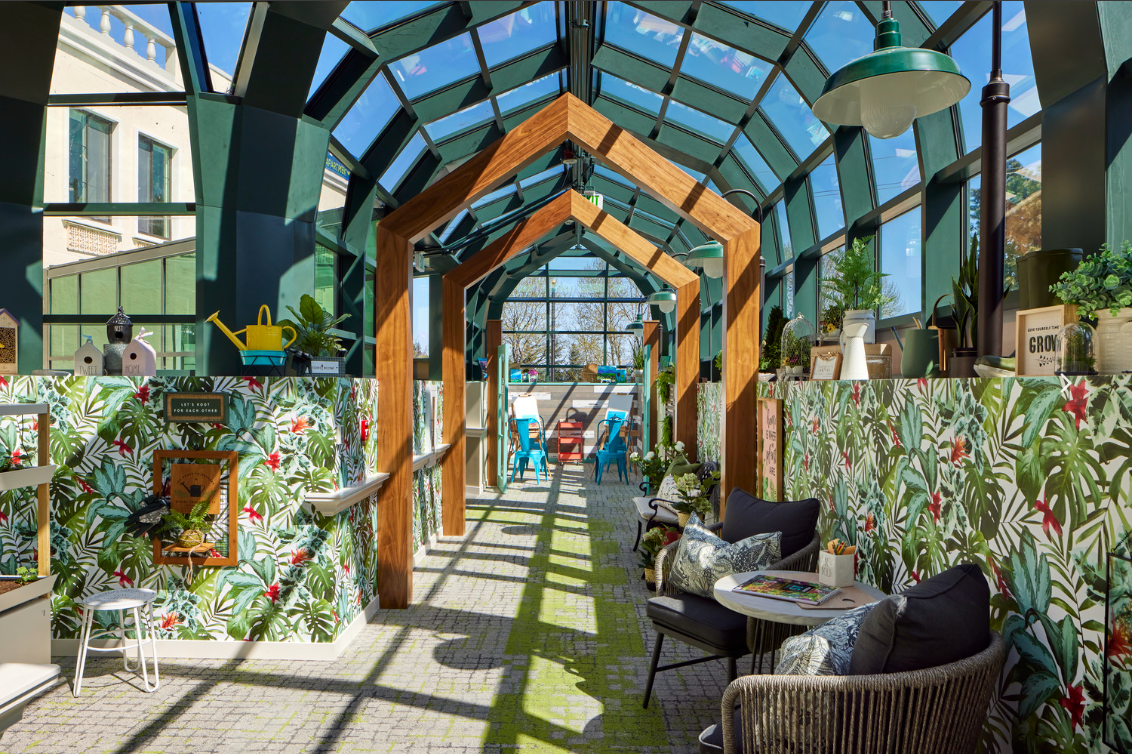
Get to Know (More of) Our Student Housing Leaders
Two of our Student Housing studio leaders, Jason Jones and Cindy Schaumberg, give us insight into what’s next for student housing (goodbye amenity wars!) and why they’re excited about it. They also share what makes each of them uniquely suited for this work; from college-aged kids to past careers.

Cindy Schaumberg, Principal, Market Studio Lead
10 years of experience in student housing
Q: What do you like best about designing student housing?
A: I enjoy working on student housing because it allows me to contribute to the well-being and success of students. Providing a comfortable and safe living environment for students is incredibly rewarding. I love that thoughtful interior design can create a sense of community that will support students during their educational journey and make their time away from home enjoyable.
Q: What has excited you about future work in this studio?
A: There is a focus on creating inclusive and diverse communities within student housing. This involves designing spaces that foster a sense of belonging and respect for different cultures, backgrounds, and identities. By prioritizing diversity and inclusion, student housing can become a place where students feel supported, comfortable, and valued.
Additionally, with increasing awareness of environmental issues, sustainable design practices have become a top priority in student housing. Incorporating energy-efficient systems, using eco-friendly materials, and implementing recycling programs are some ways to promote sustainability in student housing.
Q: What’s uniquely challenging about designing student housing?
A: Students come from various backgrounds and have different needs and preferences when it comes to their living arrangements. Designing student housing that can cater to a wide range of preferences, from quiet study spaces to communal gathering areas, can be a challenge, but a challenge we feel is important to embrace.
Q: What inspires you?
A: My daughters! As a parent of two college-age daughters, I understand the delicate balance between providing support and fostering independence. This has made me more aware of the importance of fostering a sense of community and support within student housing. My daughters have given me firsthand experience and knowledge of their needs and preferences. I also have a better understanding of the amenities and features that are essential for a comfortable, productive and healthy living environment.

Theory U District
Jason Jones, Associate Principal
18 years of experience in student housing
Q: What do you like best about designing student housing?
A: For me, it’s all about the students and collaborating with like-minded individuals who share a passion for raising the bar in living and learning environments. I take great pride in knowing that I can contribute to positive change in students’ lives and their impact on society on our planet.
Q: What trends are you seeing in student housing?
A: I am excited to see a shift in our industry that is supporting affordable housing solutions that focus on mental, social, and physical wellness. Biophilia is an overused term these days, but it has a powerful impact on a human’s well-being.
Q: Is there anything that makes you uniquely suited to working in this studio?
A: My journey in this studio has been a unique blend of two professional lives—one as an architectural professional and the other as a development manager in student housing. These distinct roles have enriched my expertise and vision, allowing me to craft architectural concepts that seamlessly align with financial objectives while upholding the utmost quality. Quality and innovation are at the heart of my work, and I’m excited to keep pushing boundaries in this ever-evolving field.
Q: What’s a memorable career moment?
A: One of my first student housing projects was remodeling an old dining hall in a student housing complex. We had the opportunity to do some fun design work that we thought the students would love. The day it opened, I snuck in before the students came in and acted like I was going to school there so I could see what they had to say firsthand. Their expressions and the incredible praise of the design still inspire me today.
Q: What changes have you seen in this studio over the years?
A: Watching the amenity race die. Instead, projects are becoming statements of well-being and sustainability.

Cornish Commons
Want to get to know more of the Student Housing Team? Learn about Alissa Brandt and Matt Janssen here.
HCAI Made Easy(er)
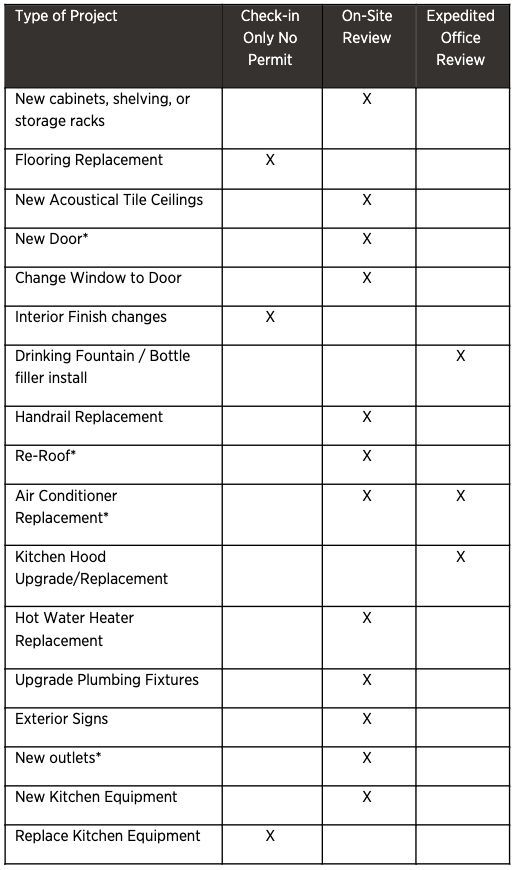
HCAI can be an intimidating organization to work with. But it doesn’t need to be. Many simple projects can even be done without a building permit.
What building changes can I make without HCAI involvement?
The simplest answer to this question is probably that you shouldn’t make any changes without at least some HCAI involvement. That said, for many types of projects the amount of involvement is limited, and is more a matter of building relationships than building approvals.
An example of this type of project is recarpeting and repainting your lobby. This type of project would likely not require HCAI approval or a building permit. The Freer manual only asks that the Area Compliance Officer (ACO) be notified prior to the start of the project. The ACO will want to confirm that the products you are proposing and the process of getting the work done will not put your residents at risk. They will check that products are not a fire hazard and that you have a plan in place to maintain a safe exit through the area while the work is taking place.
Even if a building permit is not required, design professionals that understand how HCAI works can save you time and money. In the example above experienced designers will know not only which products will meet the fire safety requirements, they will know how to find and package the certifications and other product information HCAI looks for, for easy approval. And while a permitted drawing isn’t needed, a diagram or narrative using industry terminology explaining how the exiting will work can greatly simplify the discussion and avoid unnecessary delays.
Did you know that not all HCAI projects require a full building permit review?
Some projects qualify for expedited office review, while others may only require an on-site conversation with your Area Compliance Officer (ACO) and no permit at all. This list gives an idea of when permits may be required, and when a faster process may be available. We identify which process is right for your project and help make sure it qualifies for the simplest path possible.
Why does HCAI have a difficult reputation?
HCAI (formerly the Office of Statewide Health and Planning, or OSHPD) came into existence in part in response to the 1971 Sylmar earthquake which caused the collapse of the Olive View Hospital in Sylmar, and Veterans Administration Hospital in San Fernando. They are responsible for overseeing all healthcare construction in the state of California, with a special emphasis on seismic safety and disaster preparedness. The 1994 Northridge earthquake proved the effectiveness of the requirements. In that earthquake 11 hospitals collapsed, and others had to be evacuated, but newer hospitals, built in accordance with updated standards suffered only minimal structural damage.
Most buildings are designed for safe exiting for the public, and structural stability for first responders. They are not designed to remain in service after a disaster, or to function while damaged. In hospitals, and to a lesser extent in skilled nursing facilities, the building infrastructure provides life sustaining care which needs to continue to be available in the immediate aftermath of a major seismic event.
Additionally, the needs of hospitals and skilled nursing occupants are very different from most other buildings: many occupants cannot self-evacuate, are not mobile or confined to beds, and the corridors are unfamiliar, these factors and others complicate building life safety planning. The services these buildings provide are needed immediately after, or even during, a major seismic or other disaster event. All these factors demand a higher level of life safety in design.
This higher level of safety means that many products and methods common in the construction industry cannot be used. And many of those that can require much more intensive verification, quality control, and inspection. Contractors and designers that are not familiar with the requirements are often taken by surprise when products or processes they’ve used on other projects are not allowed, leading to expensive revisions, late projects, and cost overruns.
Careful planning with design professionals and contractors familiar with these constraints can help to mitigate many of these risks. Knowledgeable designers can identify products and processes that have been pre-approved by HCAI. This frees up design time and fees to focus on items not pre-approved, or to develop custom solutions and work with HCAI for approval before construction schedules are impacted.
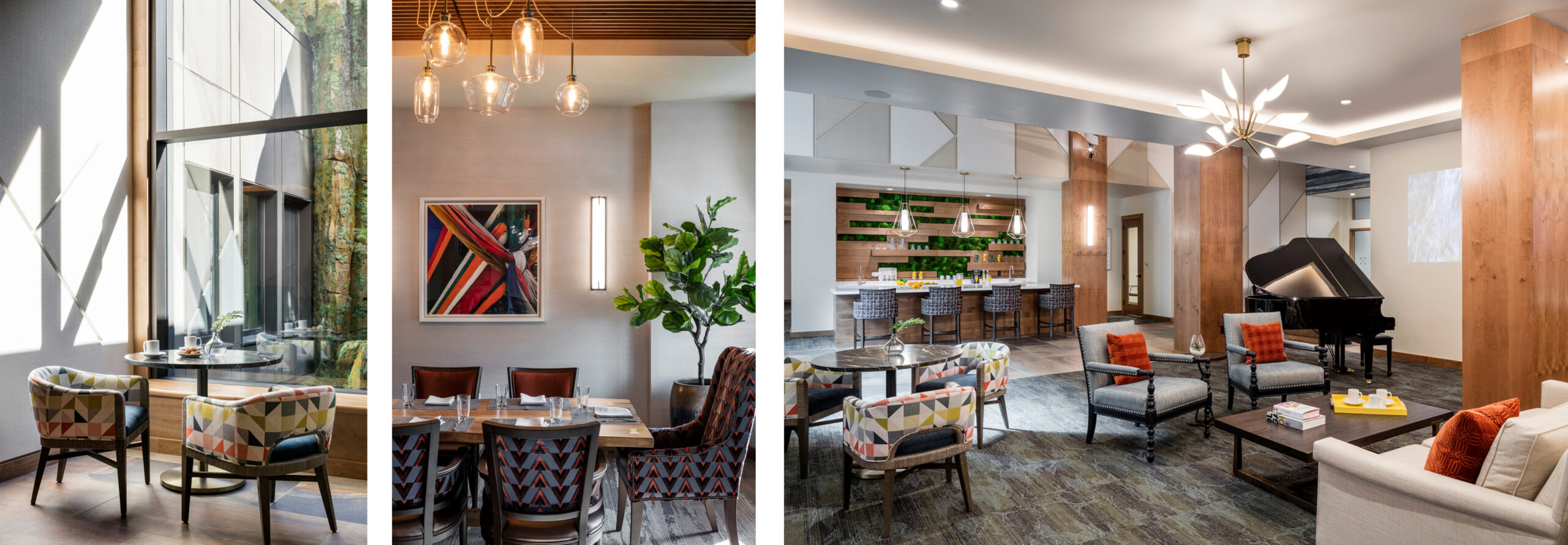
Developers Are Setting Their Sights on Redmond, WA
Developers are setting their sights on Redmond, WA, and for good reason; the area is experiencing a rapid transformation resulting in unique development opportunities. Thanks to a comprehensive growth plan from the city, a strong employment base, increasing transportation options, and excellent recreational amenities, Redmond is a highly desirable location.
However, the opportunities in Redmond are not without obstacles. The challenging regulatory environment makes development in Redmond unpredictable for teams without prior experience. Complicated review processes and new zoning rules make familiarity with the proposed code changes essential to success.

Avalon Esterra Park
The draw of Redmond.
Strong employment base. Home to campuses for Microsoft, Meta, and Nintendo, Redmond has strong employment in the tech sector and a high Average Median Income (AMI). As a result, rents are high (almost equivalent to Bellevue and Seattle) but the market is still less developed, and many low-density central sites remain.
Increased transportation and connectivity. With the East Link Light Rail stations nearing completion (expected to open in 2025), Redmond will soon be well connected to the rest of the region, making it a more desirable community to commute to and from.
High livability. Another draw to the area is the large—and growing—collection of urban amenities, including public parks and trails. Redmond is one of a small number of cities designated as a Bicycle Friendly Community—thanks to an extensive network of on-street bike lanes and off-street trails providing easy access to downtown, neighborhoods, and even to other cities. Nearing completion is the already-popular Redmond Central Connector Trail, a 3.9-mile trail corridor linking Redmond neighborhoods. Redmond is proving to be a highly livable location and is an increasingly popular alternative for Seattleites looking to escape the urban blight issues common in Seattle. There is currently a 3% lower vacancy rate in Redmond than in downtown Seattle or Tacoma: Redmond vacancy is on par with strong submarkets like Bellevue and Ballard.

Aloft & Element Hotels
Opportunities to keep an eye on.
Upzones. Redmond is currently working on updates to their comprehensive plan and is showing considerable upzones in the Overlake area and Downtown. Redmond’s growth targets are significant, and the city is actively creating opportunities for a substantial number of new households to be added to the area in the coming years.
Increased FAR. We are already seeing much higher height limits and Floor Area Ratio (FAR) proposed in Downtown and Overlake. Now is a good time to start studying sites in these upzoned areas.
Available land. Existing landowners are studying and planning for development with the upzones and some will be looking to sell entitlements and available land.
How our Redmond expertise can help.
Navigating incentives. The new code has many possible incentives for development, many add substantial costs or have implementation challenges that have not been resolved, and the tiered structure is difficult to understand. We can help you select incentives that are right for your needs.
Relationships. We have personal contacts with Redmond City staff and an established rapport. We are also connected with Geotech consultants, cultural resource consultants, land use attorneys, and various specialty consultants required to get a project approved in Redmond.
Experience with new code. We have studied the implications of new code, attending meetings, following the code changes, and providing comments on behalf of owners.
Our Redmond experience.
Entitlements:
We have significant recent experience in entitling sites throughout the city. A few examples:
- Avalon Esterra Park Blocks 4 and 7: 482 units: built
- Dual Brand Hotel Aloft/Element Hotel, 150/131 keys: built
- Avalon AVA, 386 units: built
- KGIP 16701 Cleveland, 125 units: in design
- Vega, 350 units: under construction
- Overlake East, 798 units: in design
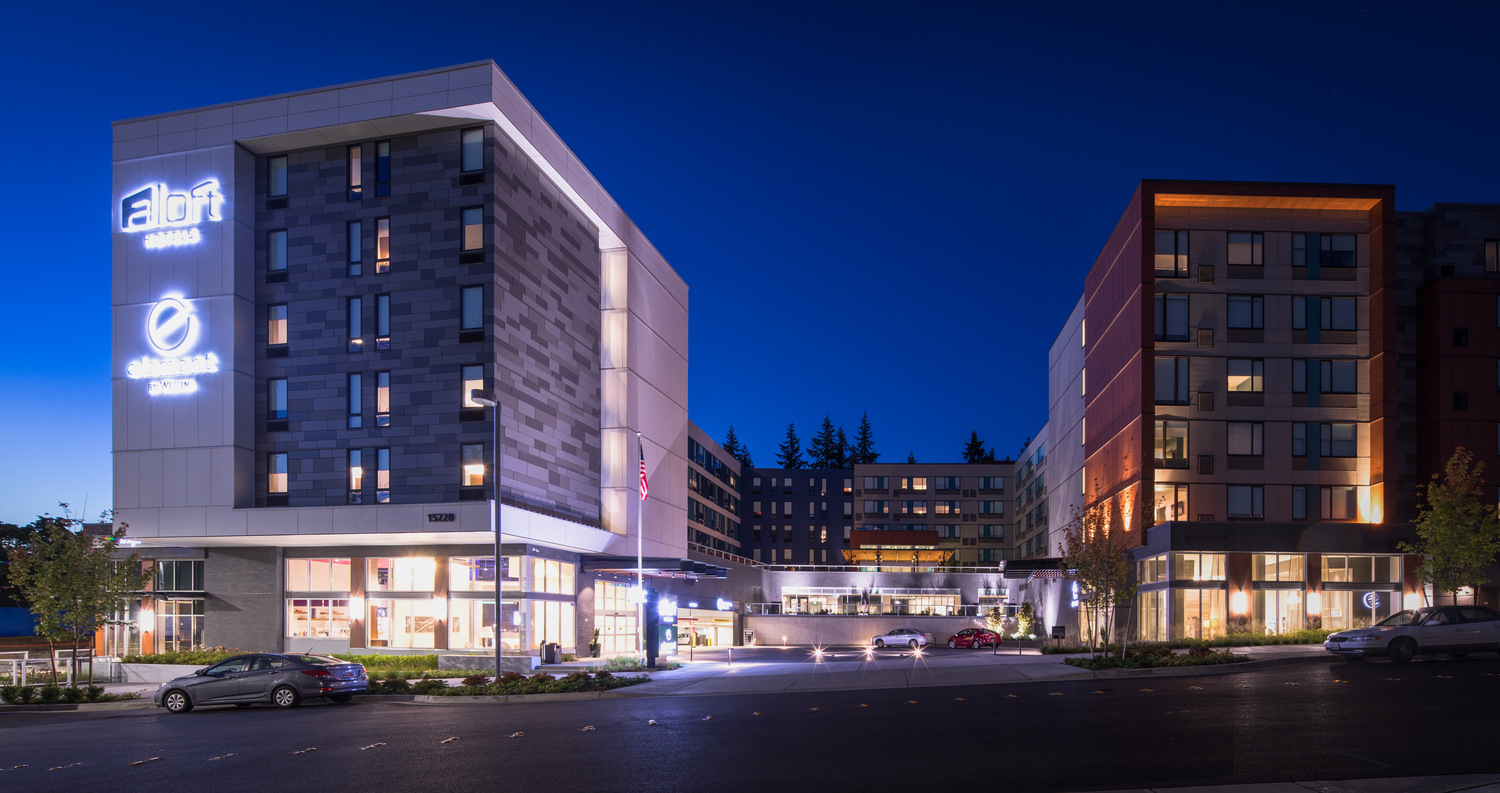

Aloft & Element Hotels
Modifying entitlements:
We have recent experience modifying existing entitlements to suit new owners—troubled development properties are great opportunities.
Vega. This 350-unit development was modified from a prior SPE approval. Our client Alliance took over a previously entitled site that was not well designed for the market. We redesigned the development and modified the entitlement, cutting a year out of schedule from an entitlement that would have started from scratch.
Avalon Esterra Park. In 2011, as the current wave of development was just beginning, we were brought in to design Blocks 4 and 7 of what is now known as Esterra Park. Adjacent to the upcoming light rail station, this site is prominent, and our design work there became the precedent for an entirely new neighborhood. Our expertise helped inform the master developer and allowed them to successfully respond to market realities. We pivoted from a roughly equal mix of office and residential uses in the originally approved Esterra Park master plan to one that heavily favored residential development in the built Esterra Park. Our work on Esterra Park also helped set a materials precedent that has proved beneficial for the developer and the city. We worked closely with the owner, contractor, and suppliers to educate the city staff about the current cladding performance of fiber cement siding to give the city quality buildings at a price point that the developers could afford.
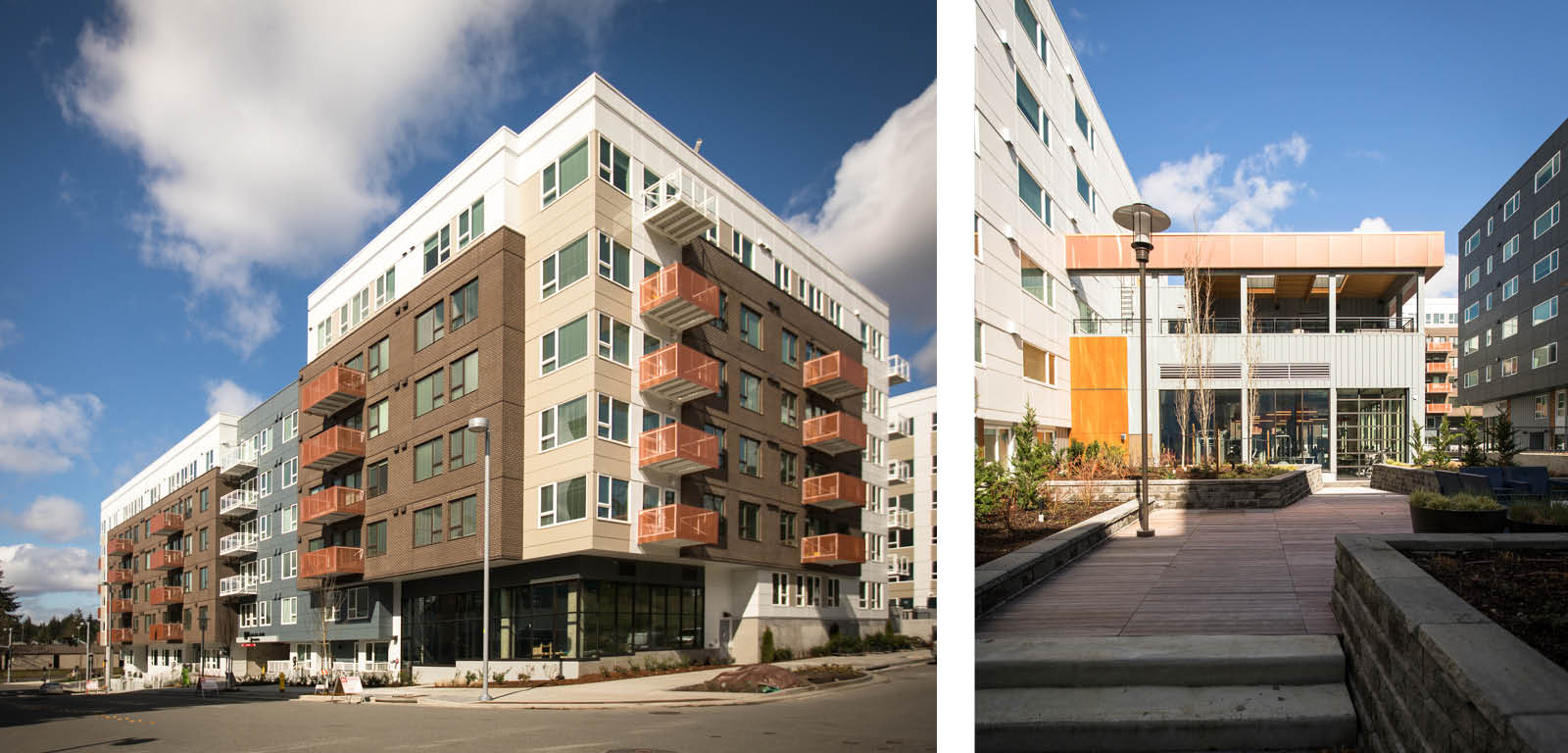

Esterra Park
Ground-up multifamily:
We have recent experience building multifamily in Redmond for multiple developers. A few examples:
- Vega, currently under construction
- Overlake East, Phase 1 and 2, projected start of construction, Q1 2025
- Three projects that are built with AvalonBay Communities

Overlake East
Feasibility studies:
We are familiar with the proposed upcoming upzones and have studied sites in detail with the new land use code which is not yet in effect and have had conversations with the city about adopting these standards early if applicable.
Master planning:
We have experience with the master-planning process required for large multi-building sites, which there are many opportunities for in the Redmond Overlake area. Our projects with AvalonBay were the first to test the newly adopted master plan for the Overlake Hospital site. Overlake East is three phase project with first two phases mixed use multifamily, third phase optional multifamily or office building, 798 units in total.
Want to know more? Get in touch with us:

David Kelley, Executive Vice President, AIA, NCARB, LEED AP

JP Emery, Principal, NCARB, MBA

Joe Tucker, Principal, AIA, NCARB
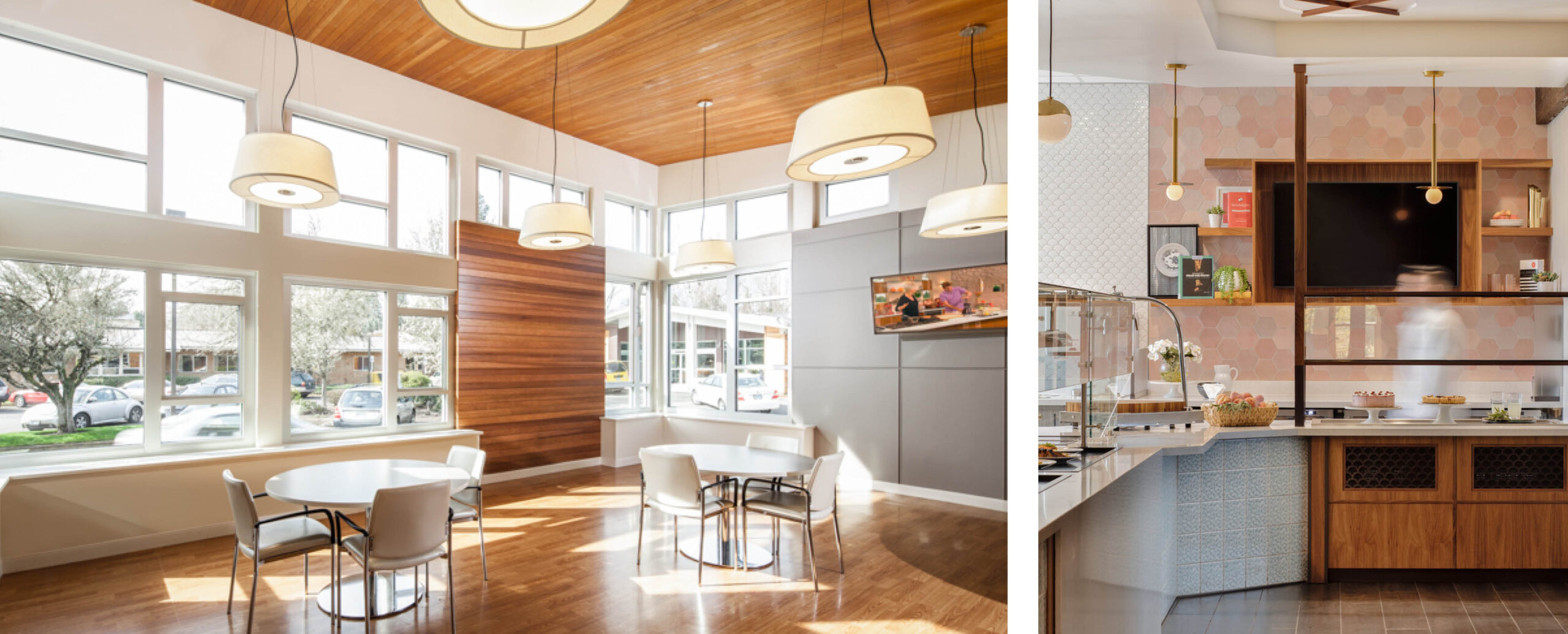
Repositioning Skilled Nursing Facilities to Adapt to a New Market
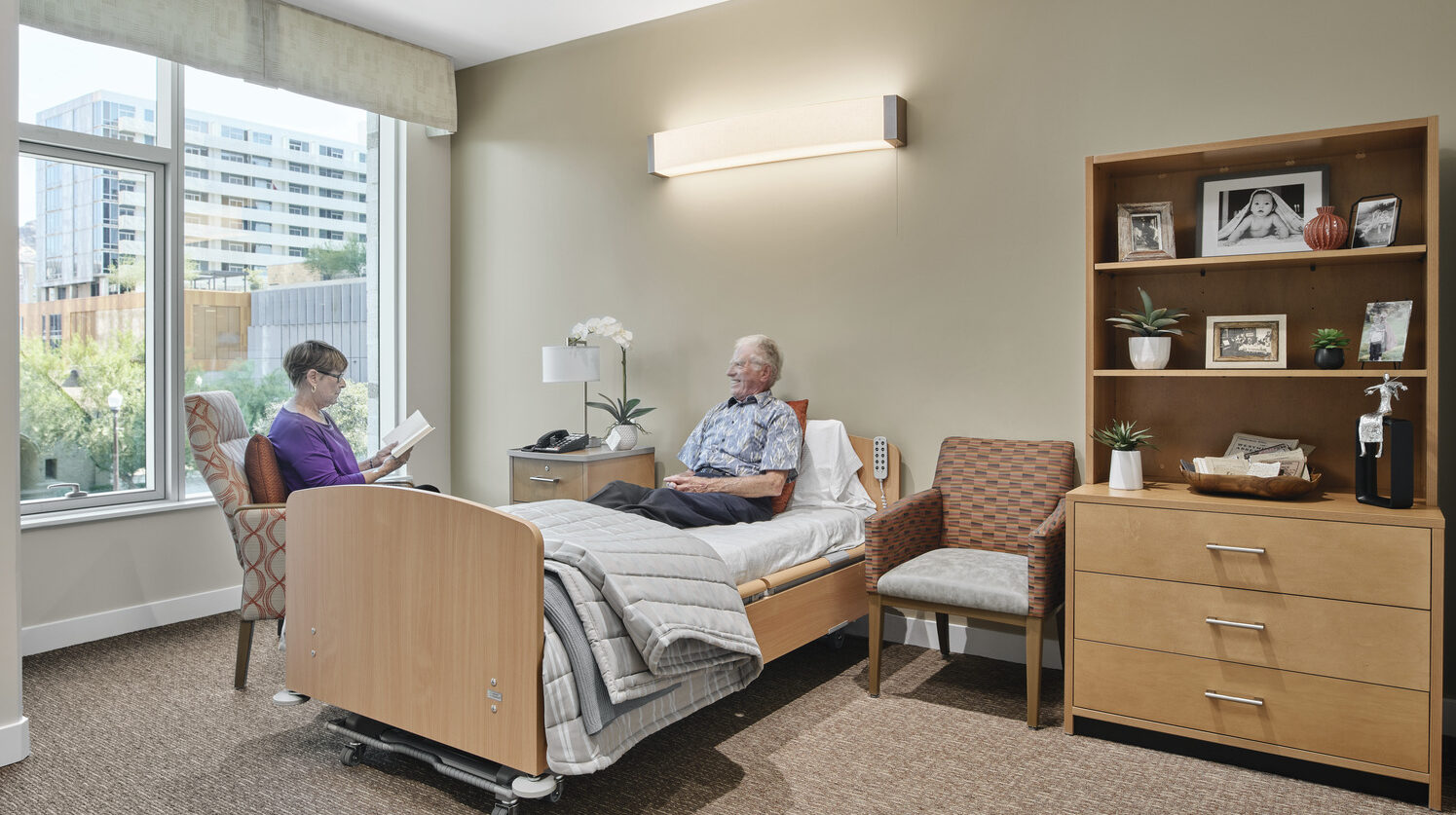
Skilled Nursing Facilities face numerous challenges in today’s evolving healthcare landscape with low occupancy levels and high operational costs not fully covered by reimbursements. By repositioning resident rooms, amenities, and caregiver operations, facilities can successfully adapt to the changing market and improve quality of life for all. Here are a few ways this can be done.
Adapt care spaces for an evolving market.
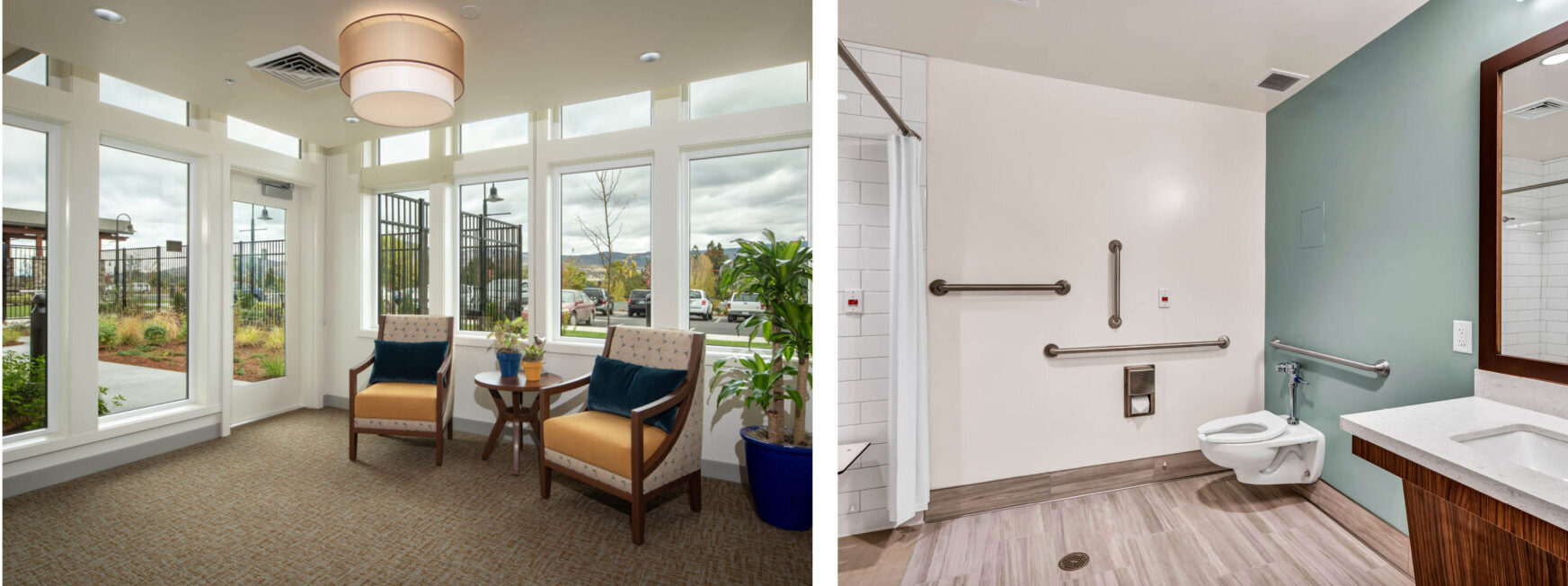
Eliminate semi-private rooms. Providing larger, private, more comfortable accommodations promotes better individualized care as well as infection control, thereby reducing required staffing levels.
Create tailored environments for care. Convert some skilled nursing units and down license into specialized areas for memory care and assisted living. This helps cater to residents with different needs and creates a tailored and supportive environment outside of the skilled nursing facility.
Introduce modern amenities to care suites. Adding amenities to care suites such as showers and built in furniture elevates the overall living experience, promotes independence, and supports caregiver tasks at the point of care. Built-in furniture provides the resident with more storage and display space and also provides staff storage for supplies and equipment.
Convert some rooms into specialized care suites. Renovating skilled units into specialized care suites for bariatric or specialized memory care provides increased marketability and flexible, efficient operations.
Adapting to transitional care services. Reposition long term care operations in whole or part to provide transitional care to residents recovering from medical procedures or injuries. Upgrade amenities and rooms to increase marketability to healthcare systems.

Mirabella ASU

Rogue Valley Manor, Meadows of Napa
Reimagine workspaces to support and assist caregivers.
Shift toward decentralized care services. Having decentralized care services in resident settings provides a personalized care experience while making it more efficient for care staff to carry out their tasks. Reimagining the traditional centralized nursing station provides options to break down support areas closer to the resident needing care.
Embrace new technologies and point of care design strategies. This makes caregiving more effective and enjoyable. With the right building technological infrastructure care givers can have resident records and care plans on their portable devices to assist the resident in any setting.
Utilize ergonomic design. Implementing innovative strategies for handling patients during personal and medical care using ergonomic design to help the well-being of the caregiver and enhance the quality of care provided. For example, both residents and caregivers can benefit from bathing and toilet facilities that have been designed based on successful assistive care research.
Consider employee retention in the design. Update employee areas and programs to improve employee retention. Redesigning staff breakrooms to encourage socialization can provide caregivers the opportunity to recharge outside of resident care areas.

Mirabella ASU

Jewish Homes
Focus on holistic wellness.
Modernize food service programs. By providing more choice and variety, the facility can better cater to individual dietary needs and preferences. Design food services areas to allow for cook to order delivery and allow residents to engage in food preparation.
Incorporate biophilic design strategies. Biophilic design features, such as natural lighting and materials, will enhance residents’ overall wellbeing. Biophilic design can encourage physical activity, facilitate socialization, and increase connection to the natural world.
Improve access to nature. Provide spaces and amenity areas that connect the indoors to the outdoors. Rooms that open to outdoor plazas, walking paths, and natural areas can offer residents the opportunity to observe wildlife, experience the changing of the seasons and foster a connection to nature.
Incorporate sustainability. Becoming a more sustainable community will benefit both the residents and staff. Use less energy from your utility and generate more power on site with the use of renewable energy sources like solar. Many projects can benefit from solar and other renewable energy sources to make the community more resilient in the long term.

Mirabella Portland

Aegis Overlake

Maryville Nursing Home, URC Dining
Wondering how to navigate California’s Office of Health Care Access and Information (HCAI)? Read more here.
Interested in meeting our dedicated team of senior renovations experts? Read more here.

Jason Erdahl
Principal, Director of Senior Communities
(503) 977-5235
How Lighting Can Influence Resident Health and Wellness in Senior Care Settings
Lighting plays an important role in a building’s architecture, as it can enhance a space, create an aesthetic, and draw attention to different elements. But in senior care settings, lighting plays an even bigger role. When used strategically, lighting can influence resident health and wellness, as well as safety.
The Role of Lighting in Senior Care Facility Design
AM Principal Chris Ebert explains that as we age, the way our eyes work changes. “When designing for seniors, designers and architects must account for the effects of aging on how a person perceives color, light intensity, the negative effects of glare, and other health-related concerns, all of which can be addressed with the right design,” says Ebert. “Whether it is natural sunlight or specialty indoor lighting, high-quality lighting is proven to have a positive impact on one’s health and wellness. For example, the National Library of Medicine cites that blue lighting can accelerate post-stress relaxation.”

Aegis Living Lake Union
How Lighting Can Address Health Concerns
“Seniors generally benefit from higher lighting levels, more uniformity, and less glare. Together, these create a safer environment than poorly lit homes, reducing the risk of falls, and minimizing the difficulty of reading medicine labels,” explains Ebert.
Since seniors are more sensitive to glare than younger individuals, designers can reduce that glare with window shades, light shields, and finishes that aren’t overly reflective. “It is also important to provide uniform lighting through careful selection and placement of indirect and shielded direct lighting,” he says.
Circadian lighting can also help improve sleep and reduce agitation and depression. This kind of lighting changes color throughout the day, mimicking the way that sunlight changes during the day. Ebert notes that circadian lighting has also been shown to be especially helpful for seniors with memory issues like Alzheimer’s disease.
Best Practices When Designing Lighting for Senior Care Facilities
When designing a senior care facility, Ebert emphasizes the importance of natural light to support resident health and wellbeing. He notes that it’s important to ensure that common areas, living areas, and staff work areas have ample access to natural light. “When practical, designers should have windows on 2 or 3 sides of a room,” he says. “The numerous health benefits of access to natural daylight are undeniable. Science has shown that natural light makes us sharper and happier during the day, provides us with better sleep at night, and helps us recover faster when we get sick. For memory care patients, circadian lighting helps to reinforce the body’s natural rhythms and can help reduce the evening agitation known as sundowning.”
But integrating natural light into a facility also needs to be done strategically. “Bringing daylight indoors in a thoughtful way requires a delicate balance of interdependent variables,” says Ebert. “Simply adding more windows to a building is not a fix-all solution. To properly daylight indoor spaces, designers must balance lighting control, glazing requirements, indoor climate controls, solar heat gain, external views, nighttime darkness, and many other factors.”
Read the full article on I Advance Senior Care.

By Chris Ebert, AIA, NCARB


















