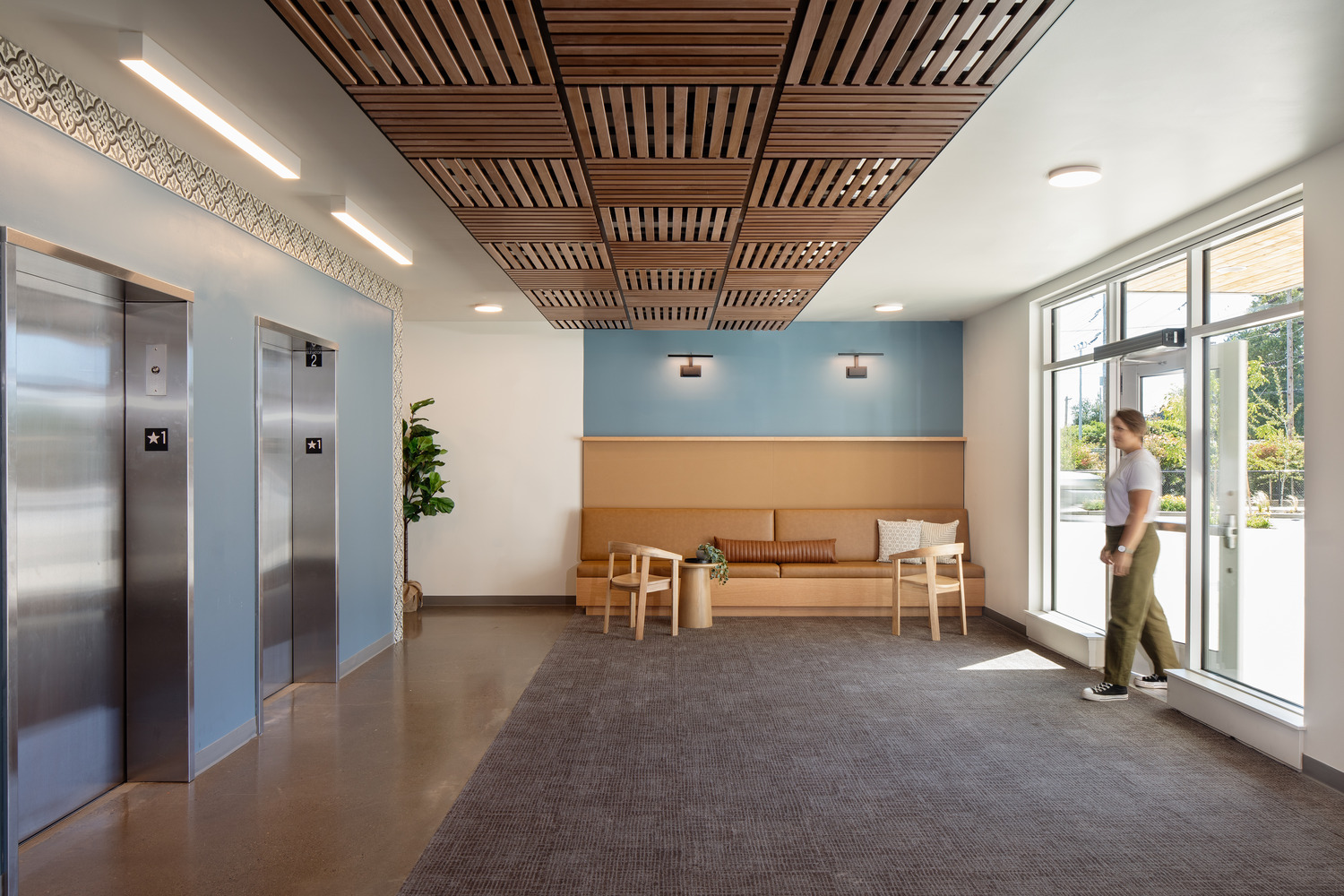
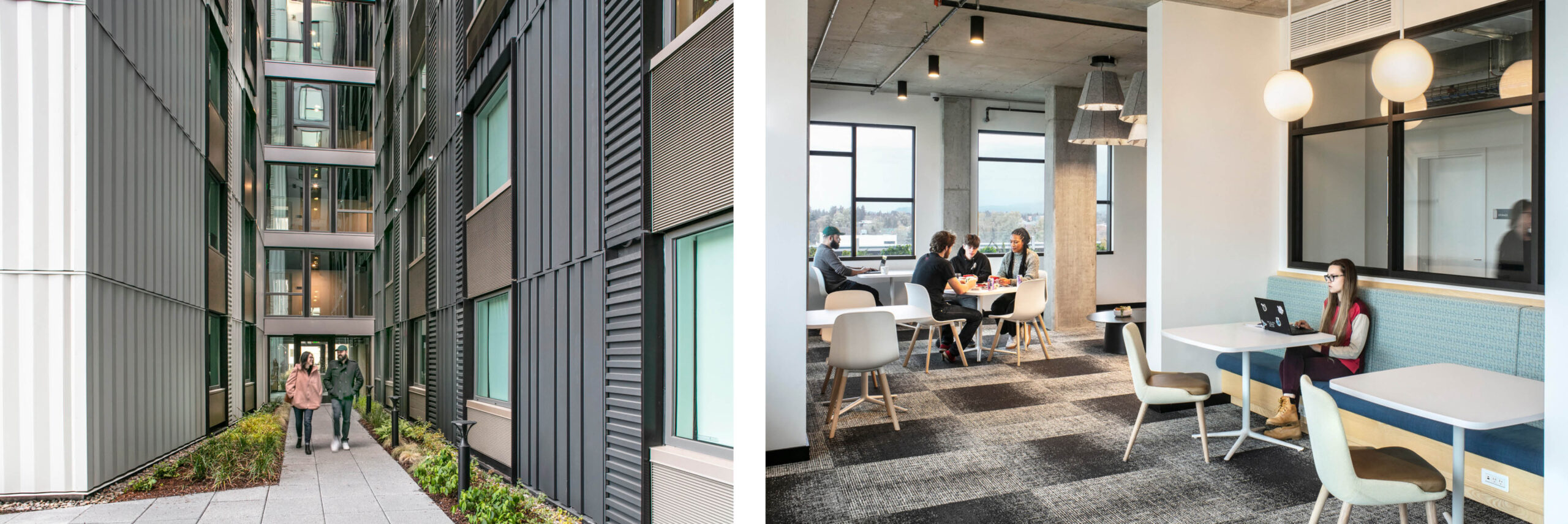
Named after the large, multigenerational mutual aid society created by Mexican and Texan farmworkers who migrated to Cornelius in the 1950s, Plaza Los Amigos honors the traditions of the past while supporting the development of new relationships.
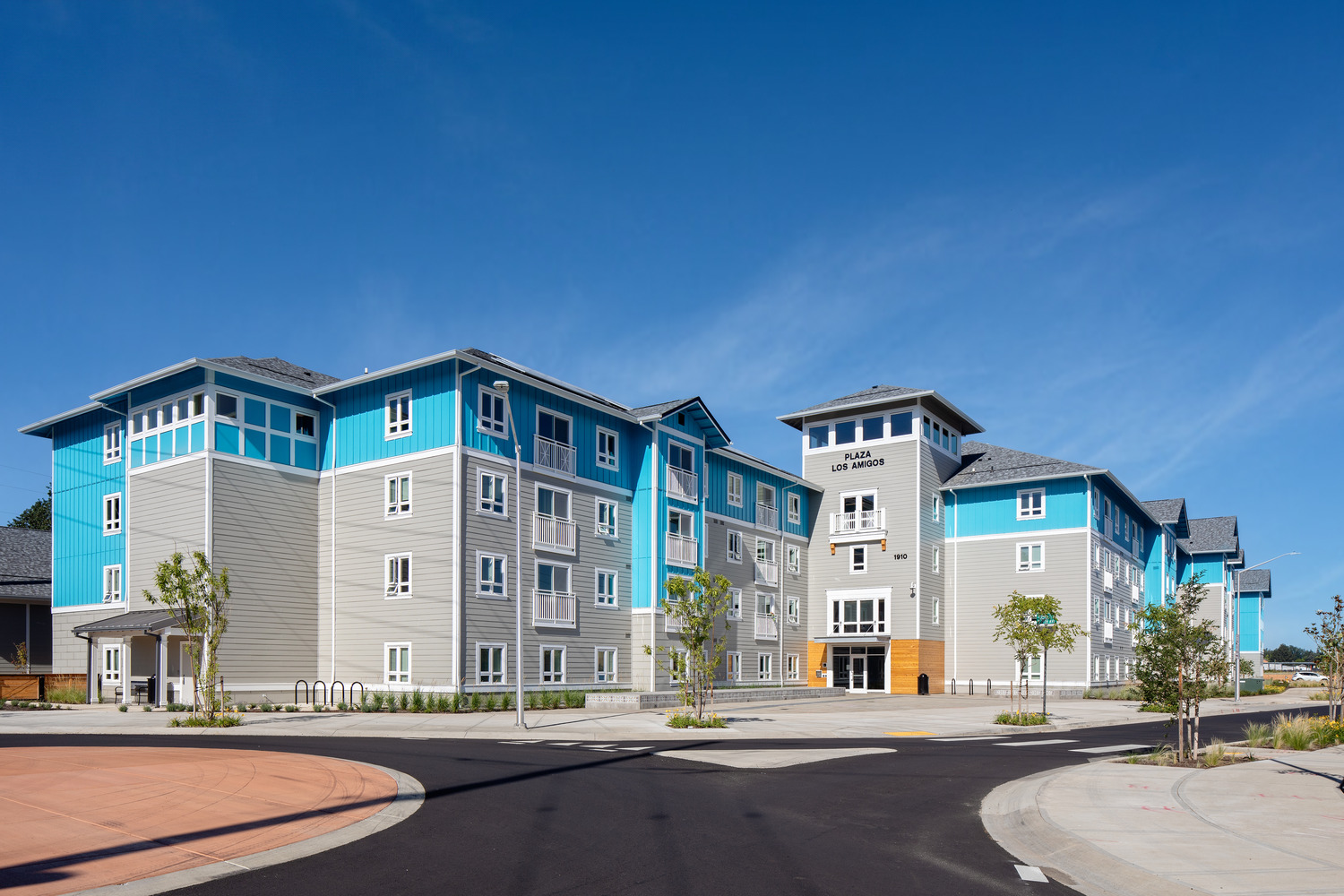

Opportunities to come together, celebrate, and support one another, much like the original Los Amigos group “Los Amigos Club” did, can be found throughout the property. Inside and out, community is emphasized through connected amenities and shared spaces, all designed with the traditions of the local Hispanic culture in mind.
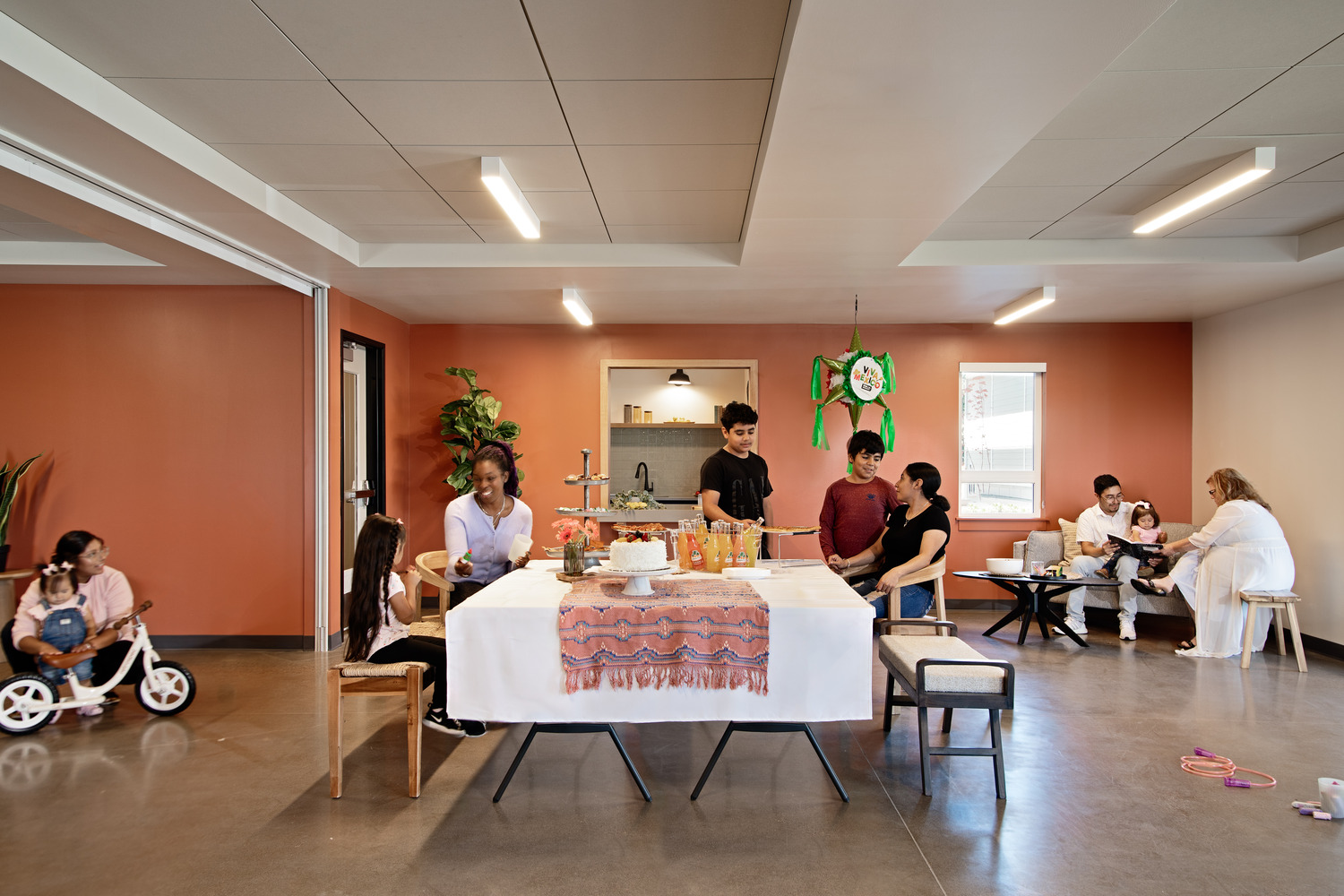

By embracing the heritage of Cornelius’ Hispanic demographic, the affordable, family-oriented housing complex seeks to strike a cohesive balance between reminders of home in Mexico and the aesthetics of the Pacific Northwest’s agricultural history.
Offering the promise of homemade food, a place to sleep, and a sense of belonging and support, the new Plaza Los Amigos is where strangers become friends, and friends become family.
Home on the Range
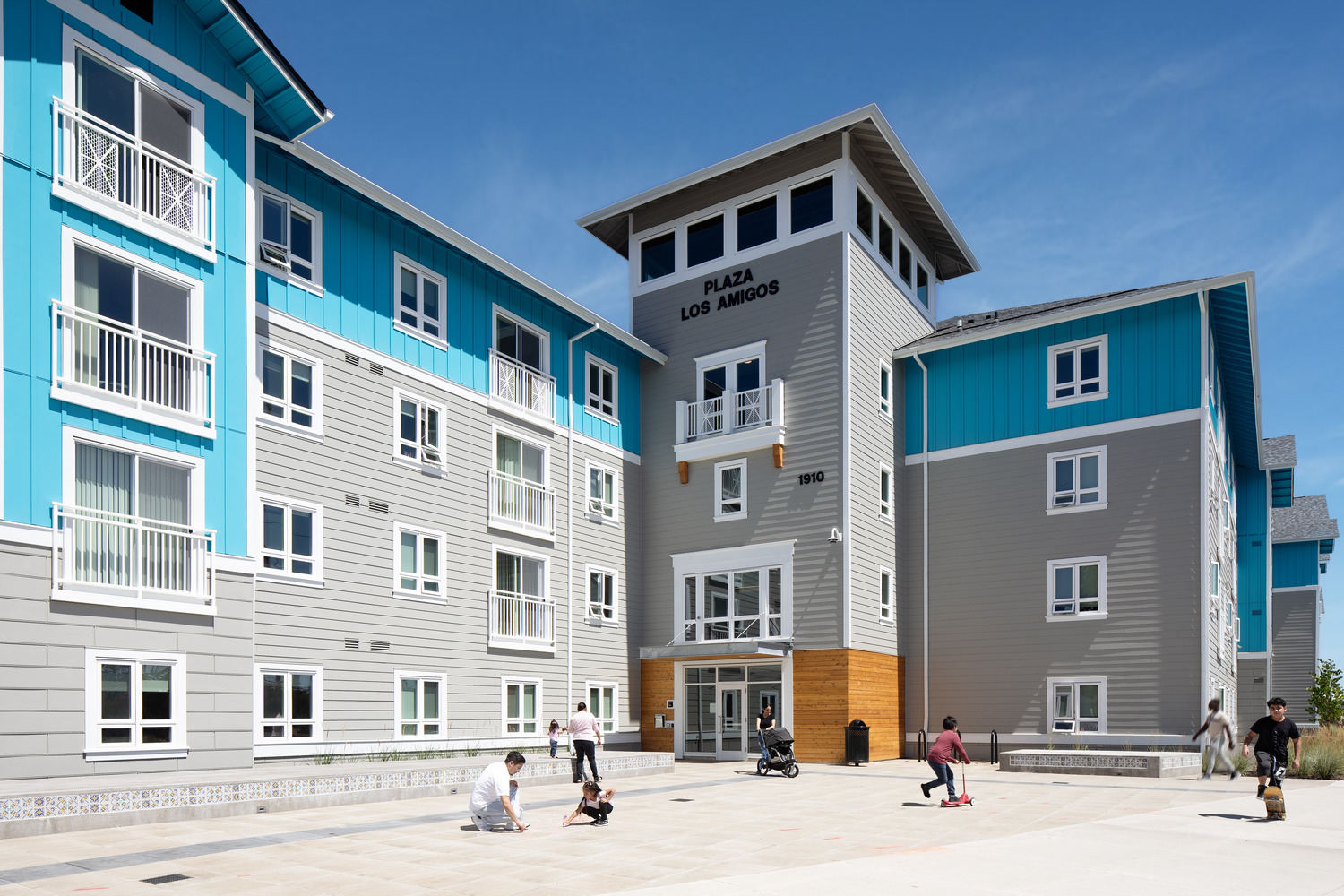

Inspired by the geographical location and the agricultural history of Cornelius, material choices traditionally tied to farmhouse aesthetics influence the design palette of Plaza Los Amigos, positioning the affordable housing complex as a spacious sanctuary of the new frontier.
Simple, yet hardy materials like lap and board and batten siding are paired with white trim and window frames, calling back to classical agricultural architecture and adding flashes of brilliance that stand apart from the rest of the structure’s grey-on-grey color scheme. The building is a zig-zag shape, permitting many connections between interior and exterior spaces and the residents that occupy them.
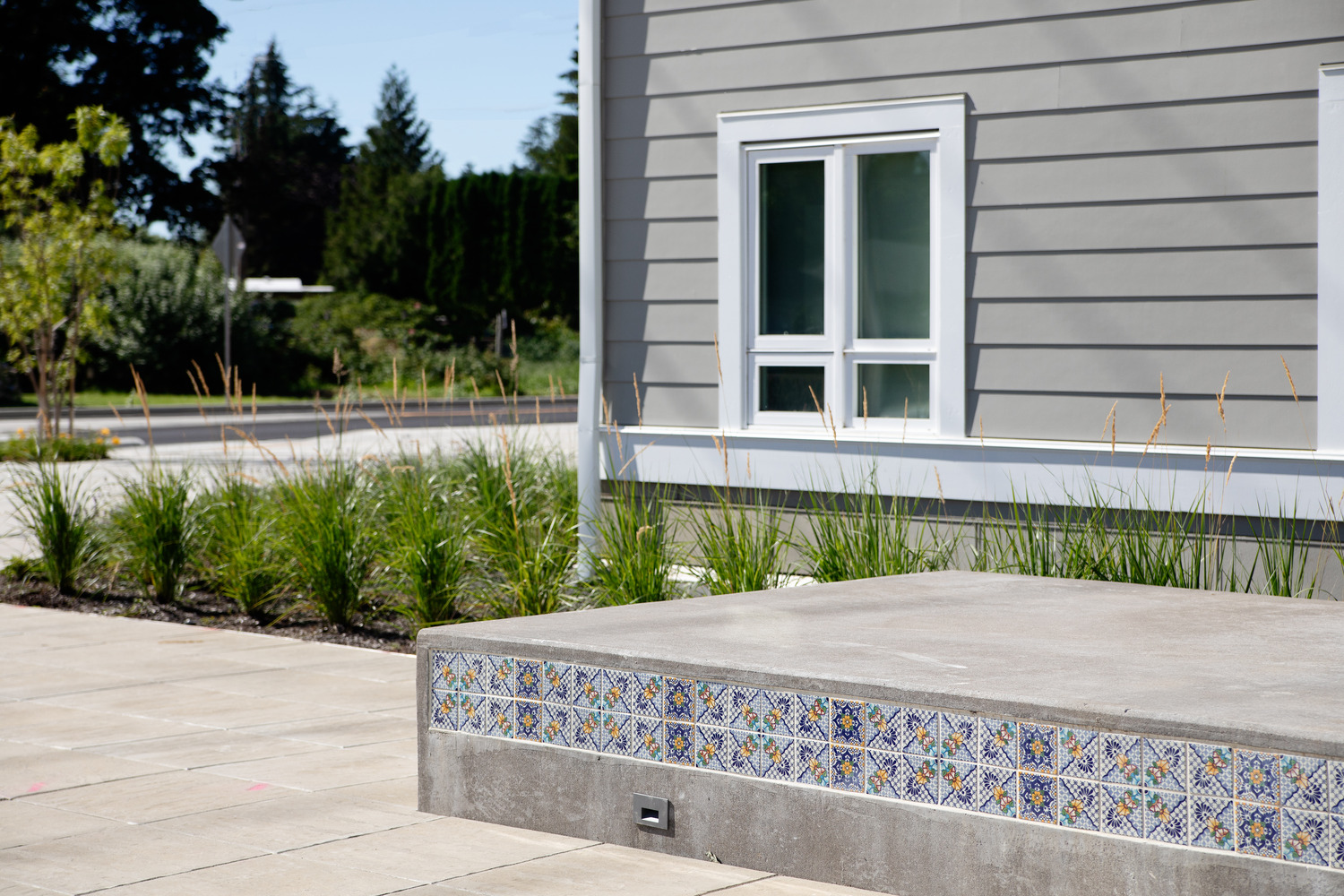

Saltillo tiles sourced from Mexico are used in planters and benches in the front courtyard of the site, bringing together the vibrant traditions of Hispanic culture and the regional, outdoorsy aesthetic of Oregon. The outdoor front plaza was a crucial element to the site, allowing residents to gather, host events, or enjoy the outdoors as they wait for a friend or rideshare to pick them up.
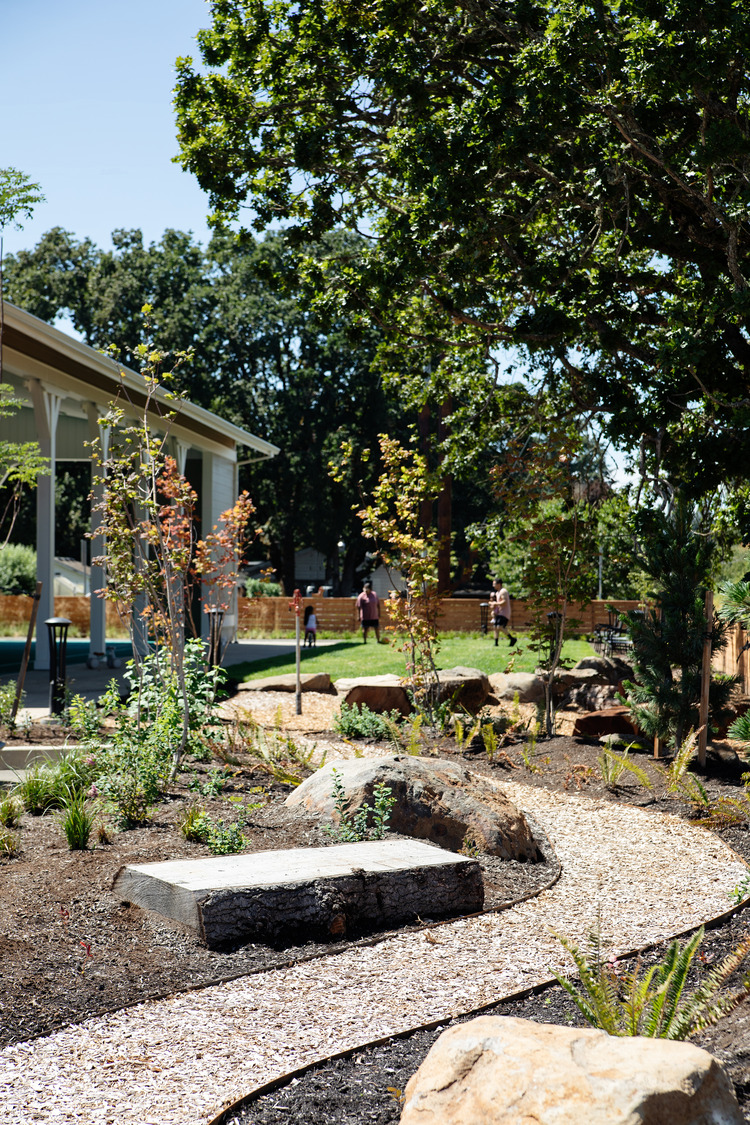

In the building’s back is an open space with a covered futsal court and greenery. Connecting to a park on the east of the site, both the front and back courtyards provide plenty of open space for use in get-togethers and other celebrations.
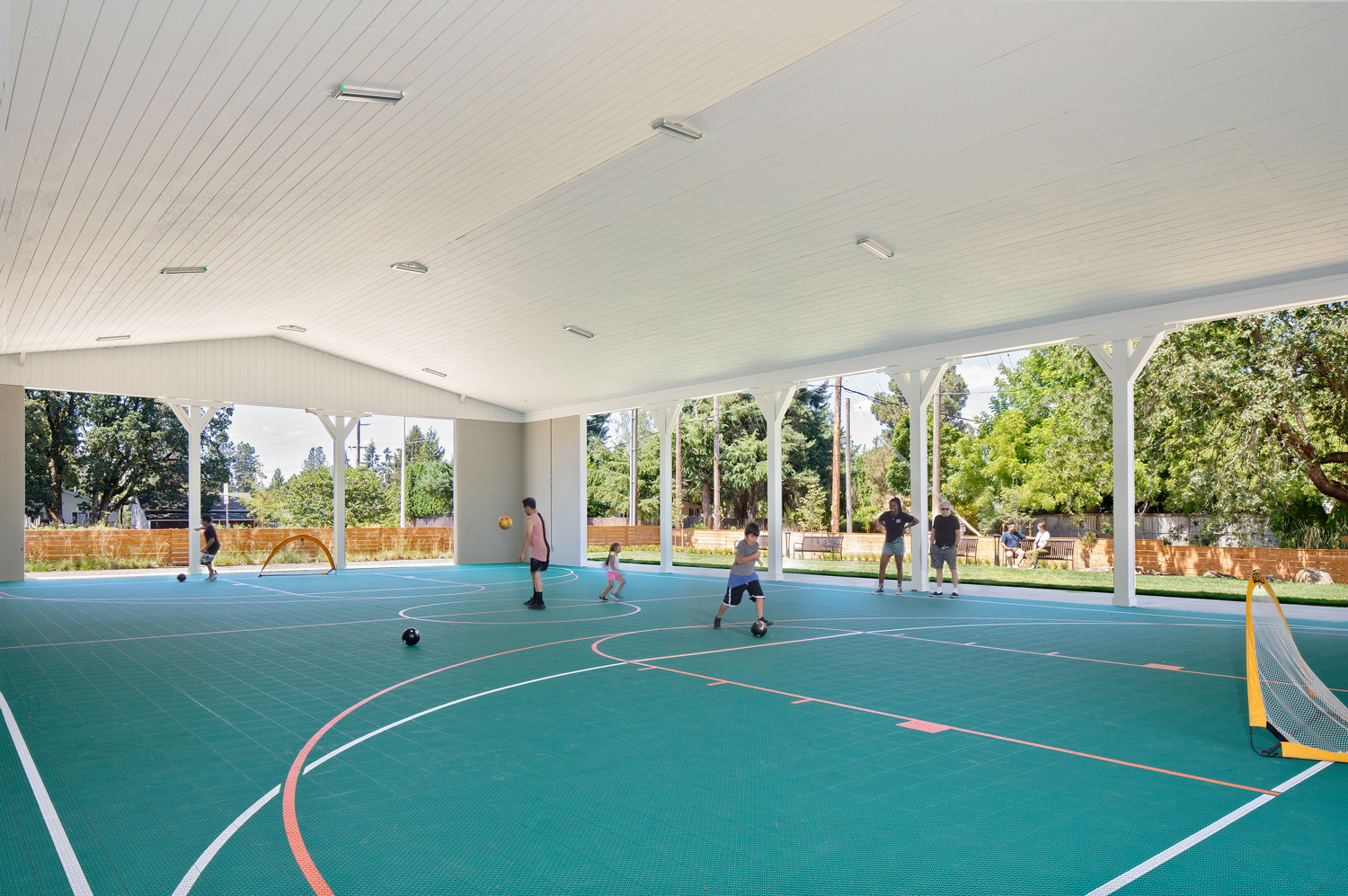

Where Families Flourish
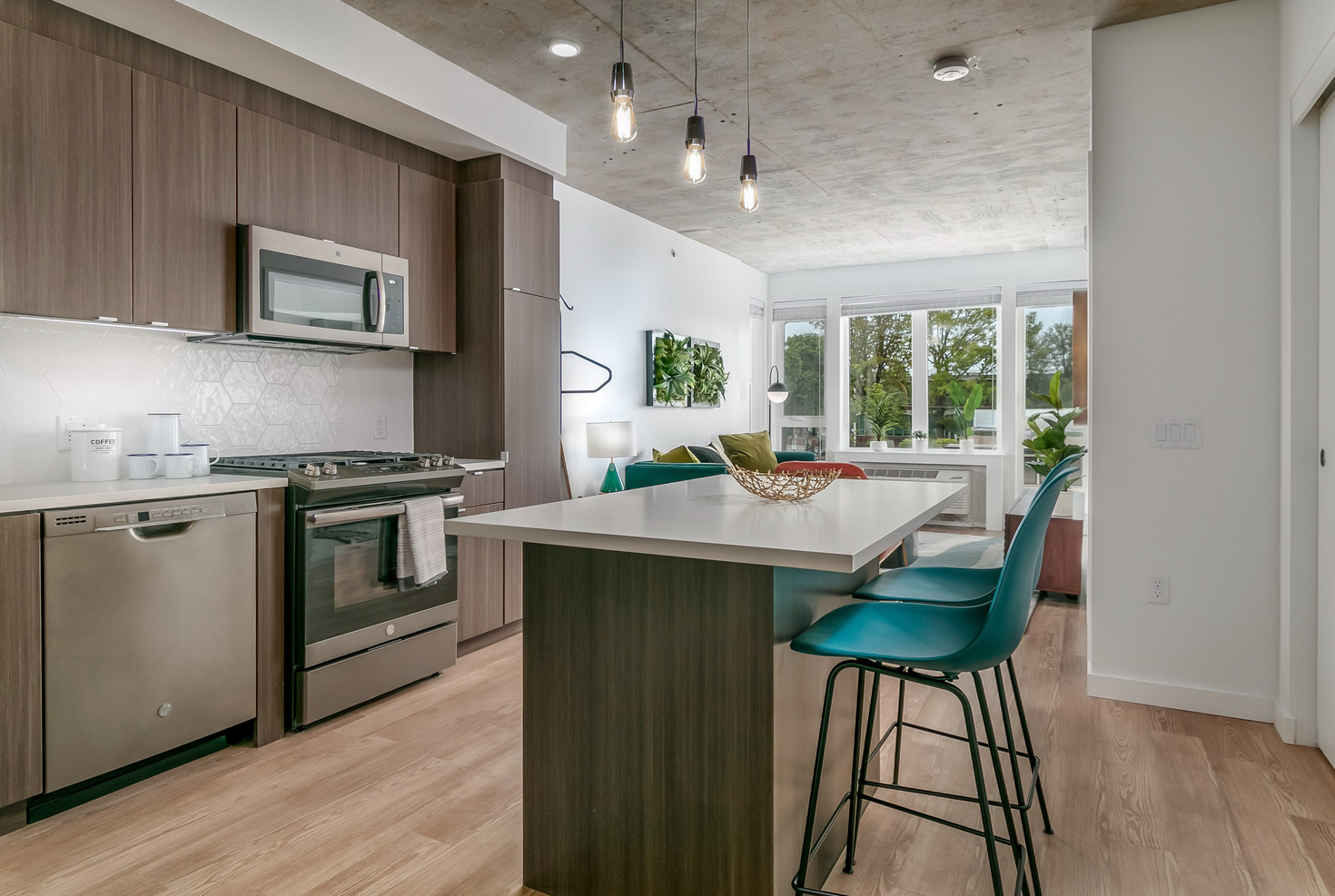
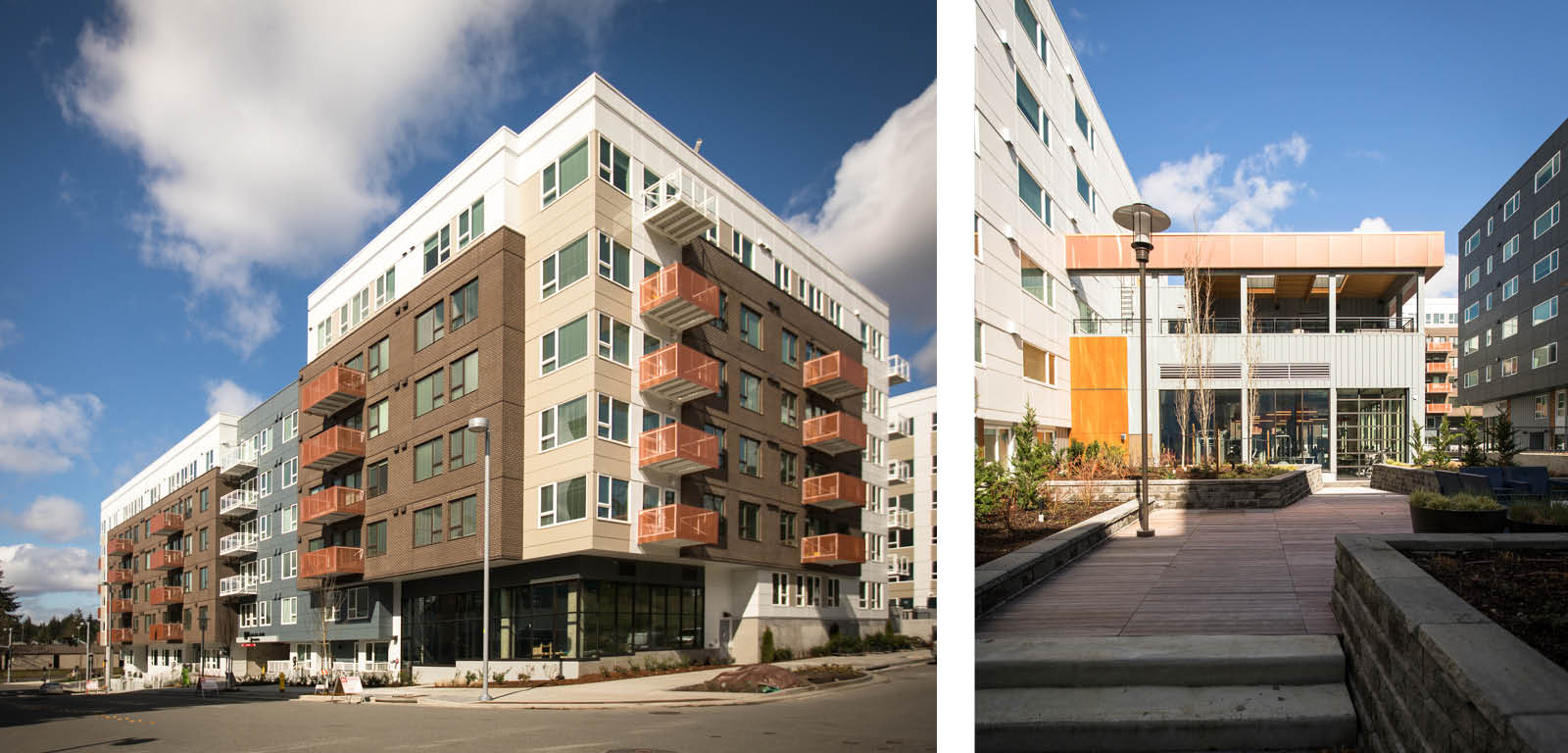
Comprised of 113 affordable 2- and 3-bedroom units, Plaza Los Amigos is designed as a home for families to flourish. An understanding that these units would be the backdrop for multiple generations to grow up and grow old in led to an emphasis on family-oriented elements throughout the individual units and shared spaces.
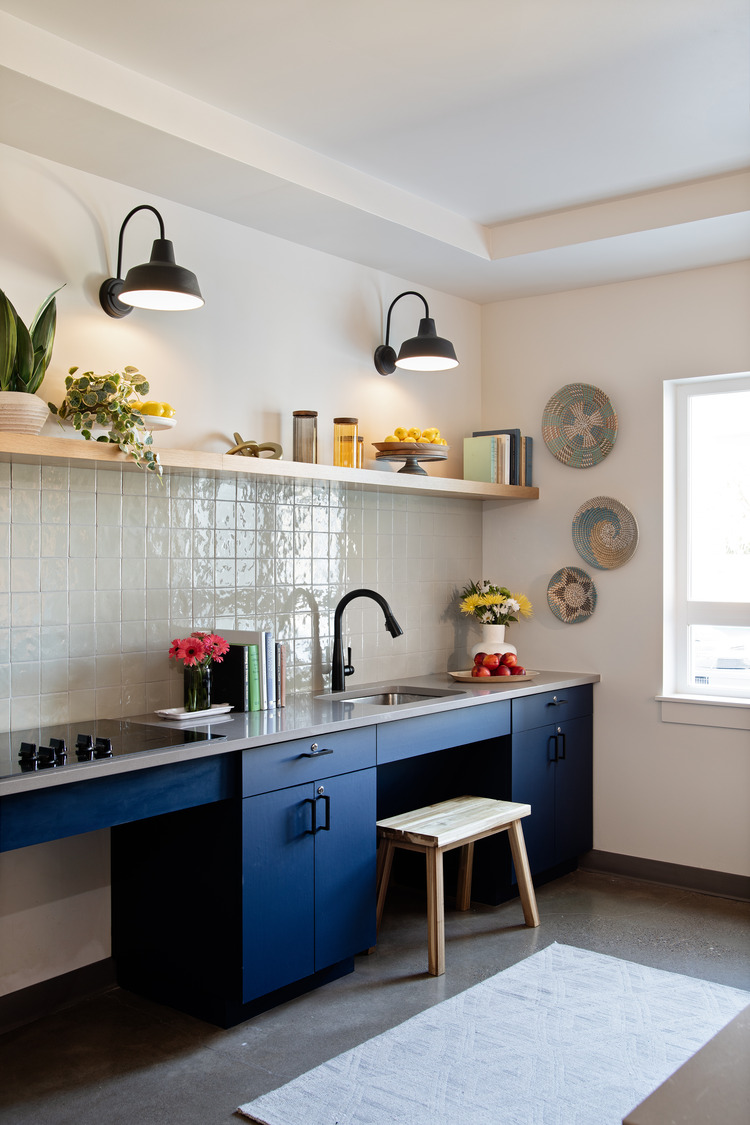

To support resident families through the challenges of raising kids, a unique decision was made to place residential kitchens along the exterior walls of units. This allows parents to keep an eye on their kids as they play outside in the plaza, while still being able to cook dinner or wash dishes.
Partnering with Sequoia Mental Health Services, the building offers culturally competent, accessible resources and support aimed at the safety, security, and well-being of residents. Sixteen individual residential units are designated to provide stability to unhoused community members.
Other forms of support are seen in the two lobby photo rails, which encourage residents to share and show off their accomplishments, whether they are good grades, a creative art project, a recent certification, or any other acknowledgement that they are proud of. A strong connection to the Dreamers resulted in this feature – Plaza Los Amigos wanted to highlight the dreams and achievements of its residents to encourage a more connected community.

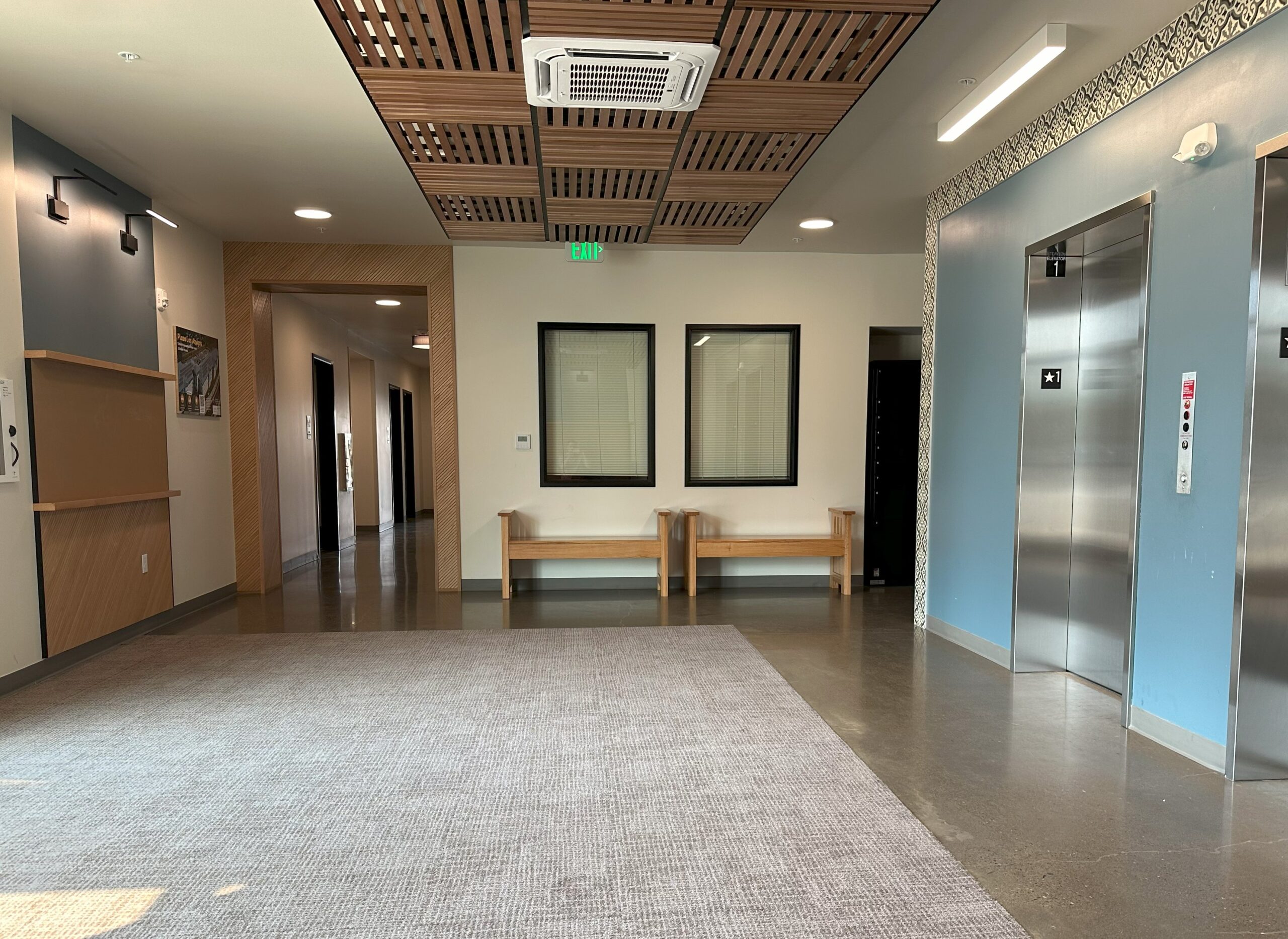
Spacious elevator lobbies on each floor – elevated by the patterns of colorful graphic tiles – serve as meeting points, overlooking the Plaza courtyard below and leading residents to shared amenities throughout the building. These amenities include laundry rooms on each floor, a community room and adjoining community kitchen, and an outdoor covered futsal court. The community kitchen includes a six-burner stoves, designed to help facilitate large celebrations and shared feasts that bring the community together as one.

As a special gift to Bienestar, one of the key architects on the project spent their own personal time transforming lumber from a oak tree on a nearby Bienestar site into two custom benches, to be utilized in the elevator lobby at the heart of the community. Engraved with a note explaining the collaboration between LMC Construction and Ankrom Moisan, the benches recognize and celebrate the significant work that Bienestar and Plaza Los Amigos do to provide affordable housing to those who need it in Washington County.
The Ins and Outs of Adaptive Reuse
What is Adaptive Reuse?
Adaptive Reuse Residential Conversions are projects that repurpose existing buildings for uses other than what the space was originally designed for.
Adaptive reuse offers developers the unique opportunity to save their investment, create and unparalleled story for end users, and make money by converting a disused or underutilized project into a one-of-a-kind residential space.

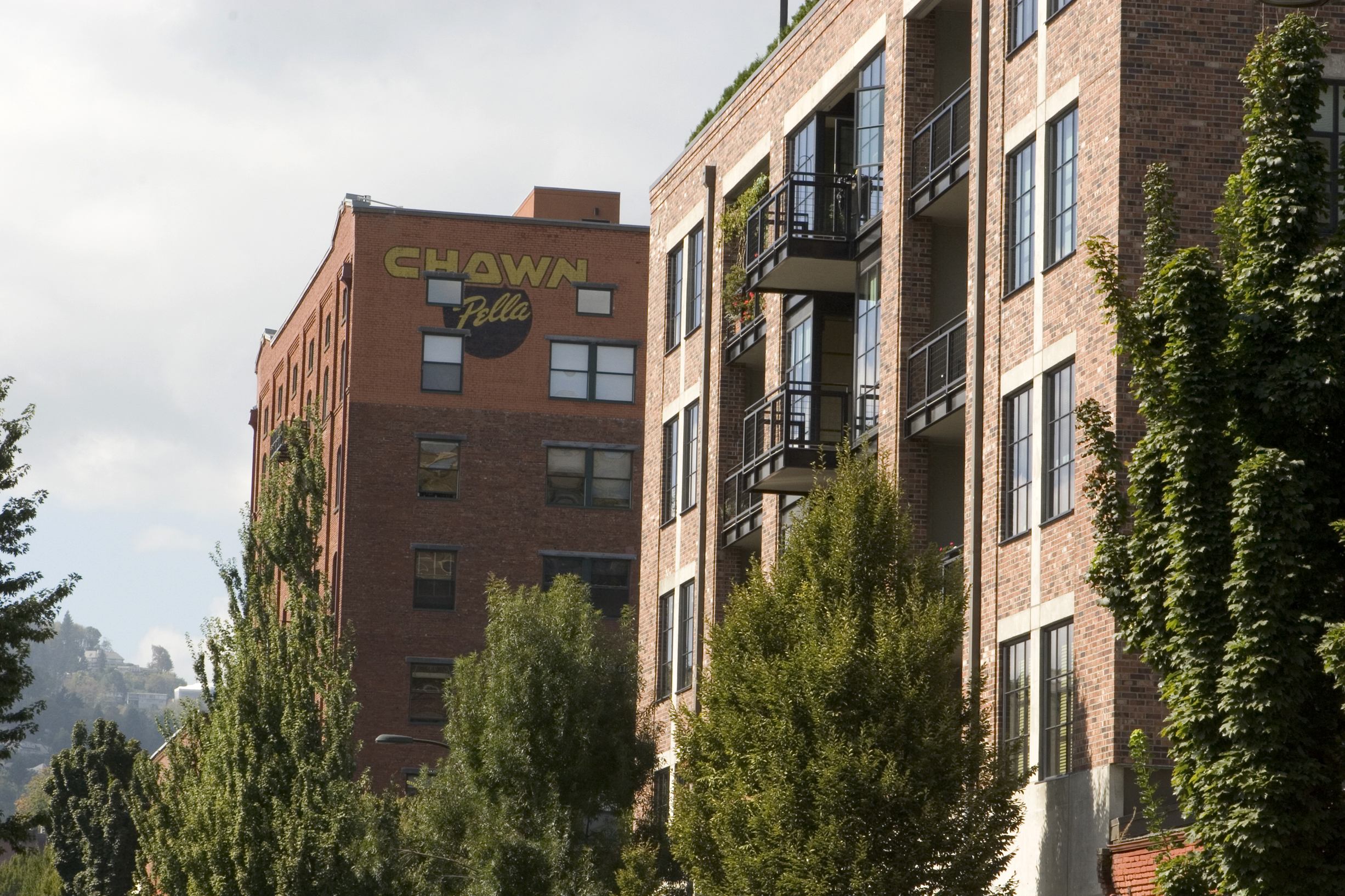
Chown Pella Lofts, an old factory warehouse converted into a multi-story residential condominium in Portland, OR’s Pearl District.
However, updating old buildings comes with layers of complexity.
Since 1994, Ankrom Moisan has been involved with adaptive reuse projects and housing conversions. The depth of our expertise means we have an intimate understanding of the limits and parameters of any given site – we know what it takes to transform an underperforming asset into a successful residential project.
Why Conversions?
There are many reasons to choose conversion over construction when considering how to revitalize old structures or adapt unused sites.
Rental Housing Demands
According to the National Association for Industrial and Office Parks (NAOIP), the United States needs to build 4.3 million more apartments by 2035 to meet the demand for rental housing. This includes 600,000 units (total) to fill the shortage from underbidding after the 2008 financial crisis. Adaptive reuse residential conversions are an affordable and effective way to create more housing and fulfill that need.
Desirable Neighborhoods
The way we see it, the success of our buildings, neighborhoods, and infrastructure is our legacy for decades to come. Areas with a diverse mix of older and newer buildings create neighborhoods with better economic performances than their more homogeneous counterparts. By preserving and protecting existing structures, conversions contribute positively to the health and desirability of the neighborhood, leading to a quicker tenant fill.
Being committed to the places we occupy, live in, and care about is another reason to embrace adaptive reuse residential conversion projects; they revive our cities. Reducing the number of buildings that sit empty in urban areas plays a major role in activating downtown districts.
Reduced Waste
Saving older, historic buildings also prevents materials from entering the waste stream and protects the tons of embodied carbon spent during the initial construction. AIA research has shown that building reuse avoids “50-75% of the embodied carbon emissions that would be generated by a new building.”
New Marketing Opportunities
Aside from these benefits to the community, adaptive reuse conversions present a way for developers to recover underutilized projects and break into top markets like affordable, market-rate, and student housing.
Construction Efficiencies
Compared to new buildings, residential conversion projects save time, money, and energy, since their designs are based on an existing structure. Adaptive reuse conversions also benefit from not having their percentage of glazing or amount of parking limited by current codes, since they’re already established.
One-of-a-Kind Design
We don’t believe in a magic formula or a linear “one-size-fits-all” approach to composition. Each site is a unique opportunity to establish a one-of-a-kind project identity that’s tied to its history and surroundings.
At the outset of any conversion, we analyze each individual site and tailor our process to align with the existing elements that make it unique. Working with what you have, our designs and deliverables – plans, units, systems narratives, pricing, and jurisdictional incentives – are custom-fit.
It’s our philosophy that you shouldn’t fight your existing structure to get a conversion made; if you can’t fix it, feature it.

Chown Pella Lofts.
Approaching each conversion opportunity with this mindset, we analyze the factors that set a site apart, and embrace those unique elements to ensure a residential conversion stands out. With this intricate and involved process, we’ve been able to get over 30 one-of-a-kind residential conversion projects under our belt.
Through these past experiences, we have identified six key characteristics that make a project a candidate for successful conversion, and six challenges that may crop up during the renovation process. To learn more about what attributes to look out for and what traits to be weary of when considering a residential conversion, read about our “Rule of Six” here.


By Jennifer Sobieraj Sanin, Design Director of Housing and Senior Principal, and Jack Cochran, Marketing Coordinator.
Residential Conversion Case Study
Converted from a Holiday Inn hotel to a residential apartment complex, 728 16th St. embraces its midcentury hotel past while providing a new take on residential housing. By utilizing strategic efficiencies within the renovation process, Ankrom Moisan’s adaptive reuse and renovations design team contained costs, expedited construction, and completed the project in a sustainable fashion.
The Challenge
Originally constructed in the 1970s, the site of 728 16th St. had seen better days. Years of water damage to the roof and walls meant the building’s enclosure needed updating. Additionally, because the structure was originally designed for traveling guests, rather than as permanent lodging, many of the rooms lacked the necessary amenities for residential living, such as kitchen appliances and other utilities like washers and dryers.
Adding these appliances to the space uncovered unique challenges around the inclusion of proper ducts and plumbing for those utilities.
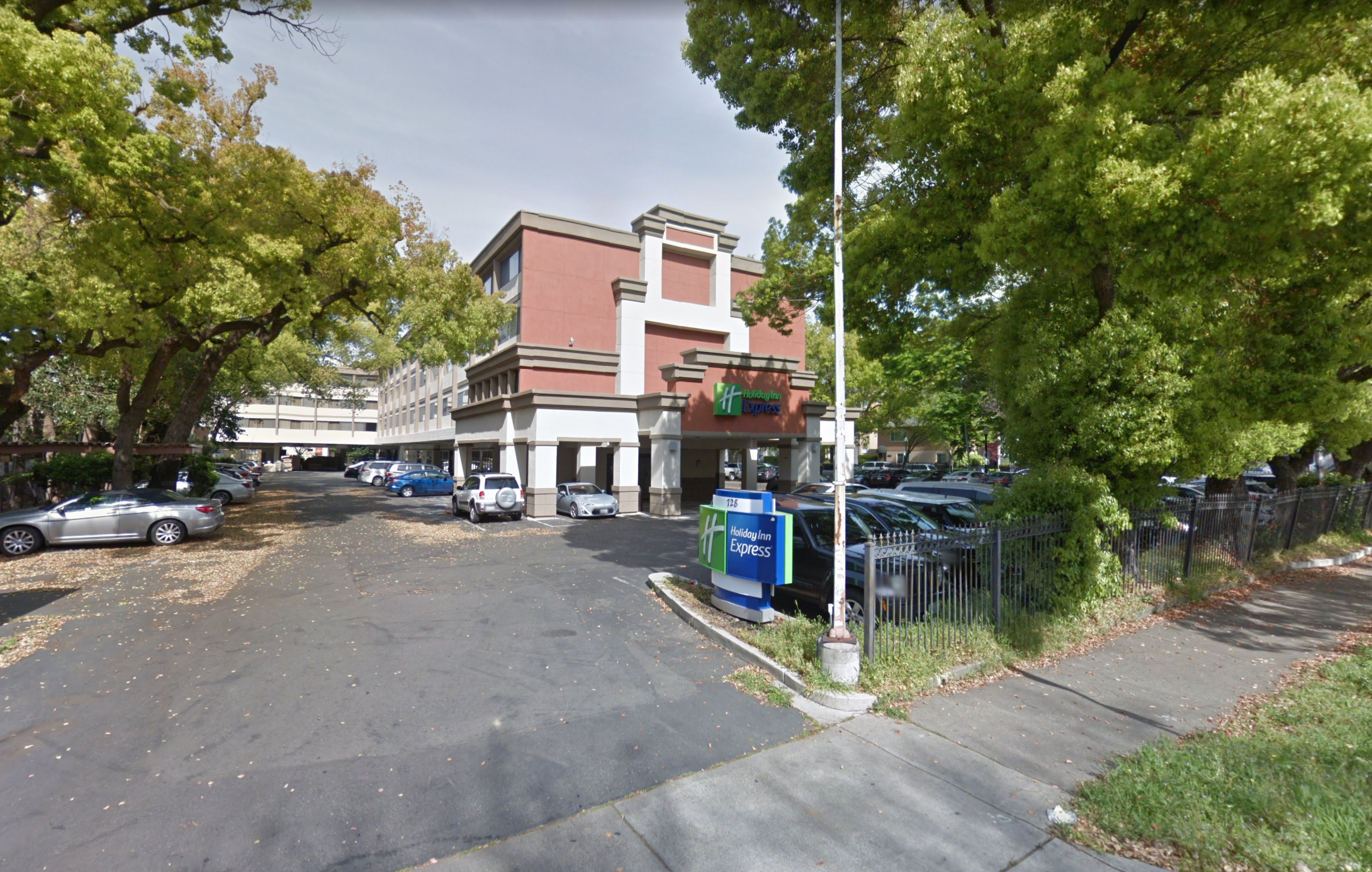

Before: 728 16th St. as a Holiday Inn
The Solution
Leveraging as much of the pre-existing space as possible resulted in the renovated 728 16th St. building’s unified design. Existing structure, utilities, and MEP infrastructure were optimized by the design team to maximize efficiencies and eliminate the need for a complete tear down. In this sense, the name of the game was understanding the parameters of the site and knowing how to work within those parameters to bring the design intent for the new building type to life.
Since the building’s enclosure was updated during the renovation, the design team was given the opportunity to reskin the building with a high performance rain screen system during the update, preventing any further water damage to the structure. This also allowed the team to shift the site’s layout and the location of amenities; the lobby itself was relocated, moved to a more central location of the site.
To increase the total number of units, portions of the existing hotel, such as the parking lot and food service kitchen were infilled and connected to the new lobby. Other existing hotel rooms were combined to create one or two-bedroom apartment units, with an emphasis on maintaining the pre-established bathroom layouts, since they contained plumbing fixtures and pipes that would be too difficult to relocate.
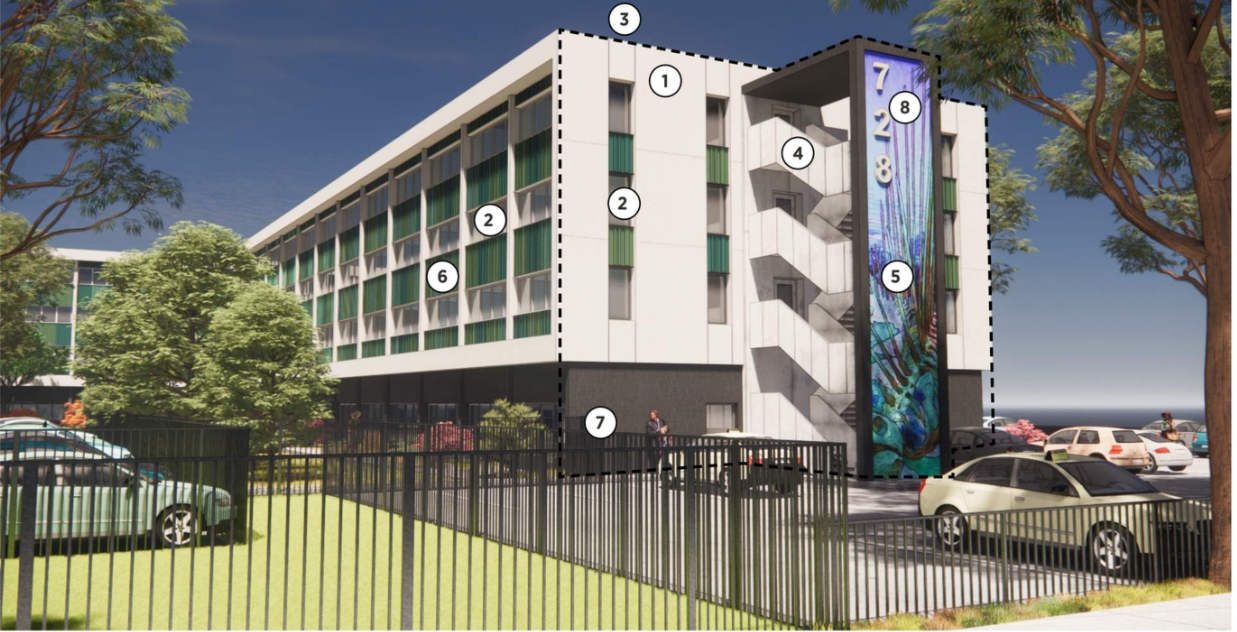

During: A rendering showing what 728 16th St. might look like as a residential housing complex.
Addressing the challenges that were uncovered by the lack of plumbing, pipes, and appliance ducts in the individual new and existing units, the renovations team made large-scale adjustments to the height of the ceilings, to accommodate those appliance ducts and plumbing pipes.
The Impact
By maintaining as much of the original structure as possible and eliminating the need for a tear down, 728 16th St.’s renovation created an expedited development process that ended up being more sustainable than a new build.
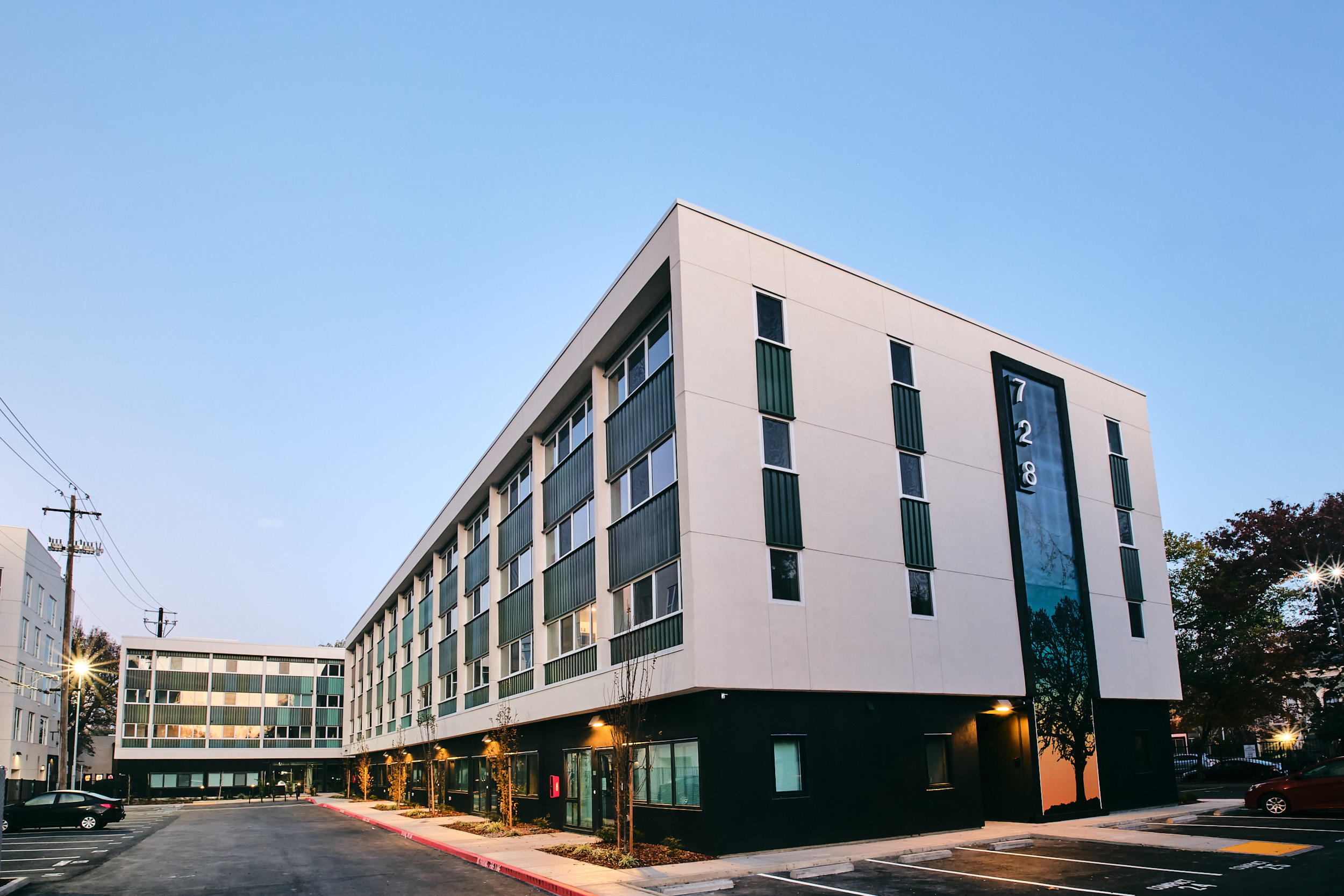

After: 728 16th St., converted from a Holiday Inn hotel to residential housing.
Embracing the existing structure, room layouts, and utilities of the Holiday Inn, Ankrom Moisan’s renovations team turned the underutilized hotel space into an affordable-by-design residential project in a desirable area. Shifting the layout and positioning of the site itself allowed 129 new units to be built, both increasing the amount of available housing in the area and diversifying the unit types within 728 16th St., as the original design was repetitive.
The fresh perspective on modern residential housing brought to life by the Ankrom Moisan adaptive reuse conversion team sets 728 16th St. apart as a place that remains competitive in new markets.
Overall, the building type conversion for this project was successful because the site exhibited at least two of the six key characteristics for effective renovations, otherwise known as the “Rule of Six.” Being situated in a walkable location and having at least a 12,000 square foot plate set 728 16th St. up for success, but a prospective adaptive reuse conversion truly only needs one of the six key characteristics to be a qualified candidate for successful conversion. Read more about the Rule of Six and how to tell if your site would make for a successful residential conversion here.
For guidance through the adaptive reuse process, contact Jennifer Sobieraj Sanin, Housing Studio Design Director and residential conversion expert.

By Jennifer Sobieraj Sanin, Housing Studio Design Director.
Contact: +1 (206)-576-1600 | jennifers@ankrommoisan.com
Should Your Building Become Housing? Critical Considerations for Adaptive Reuse
It’s the question on every developer’s mind right now. Is adaptive reuse feasible for my building? Cost-effective? What will a housing conversion project entail?
Since 1994, Ankrom Moisan has been involved with adaptive reuse projects and housing conversions. The depth of our expertise means we have an intimate understanding of the limits and parameters of any given site – we know what it takes to transform an underperforming asset into a successful residential project.
For customized guidance through the adaptive reuse evaluation process, contact Jennifer Sobieraj Sanin, Housing Studio Design Director and residential conversion expert.
The Rule of Six
While there is no magic formula or linear ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach to conversions, we have a framework that should be considered when approaching an adaptive reuse project. We call it “The Rule of Six.”
The Rule of Six outlines six key characteristics that make a project a candidate for successful conversion, and six challenges to be prepared for during the renovation process.
With this informed process, we’ve been able to get over 30 one-of-a-kind residential conversion projects under our belt.
The Six Key Characteristics for a Successful Conversion
Not every building is a good candidate for conversion. By evaluating multiple structure types and working closely with contractors on successful projects, we’ve identified six key characteristics that lead to the creation of successful, low-cost, conversions.
If a property has any of these traits – whether it’s one characteristic of all six – it might qualify as a candidate for a successful conversion.
- Class B or C Office
- 5-6 Levels, or 240′ Tall
- Envelope Operable Windows Preferred
- Walkable Location
- 12,000 Sq. Ft. Plate Minimum
- Depth to Core Not to Exceed 45′
To find out if a property makes for a good adaptive reuse project, consider conducting a feasibility study on the site.
Reach out to get started on your feasibility study today.
The Six Challenges to be Prepared For
West Coast conversions can be particularly challenging with their seismic requirements, energy codes, and jurisdictional challenges – your conversion team should be prepared for these hurdles. The solutions vary by project; contact us to see how we can solve your project’s challenges.
- Change of Use: It’s the reason we upgrade everything. The simple act of changing a building’s use from office to residential immediately triggers a ‘substantial alteration.’ This label starts all the other necessary upgrades.
- Seismic-structural Upgrades: Buildings on the West Coast must meet a certain code level to be deemed acceptable for the health, safety, and welfare of end-users. Often, this required level does not match the current code, meaning negotiations with the jurisdiction are necessary.
- Egress Stairs: Stair width is usually within the code demands for conversion candidates, but placement is what we need to evaluate. When converting to residential, it’s sometimes necessary to add a stair to the end of a corridor.
- Envelope Upgrades and Operable Windows: West Coast energy codes require negotiated upgrades with jurisdictions, as existing envelopes usually don’t meet the current codes’ energy and performance standards. Operable windows are a separate consideration. They are not needed for fresh air but are often desired by residents for their comfort.
- Systems and Services Upgrades: These upgrades often deal with mechanical and plumbing – checking main lines and infrastructure, decentralizing the system, and adding additional plumbing fixtures throughout the building to support residential housing uses.
- Rents and Financials: Determining how to compete with new build residential offerings is huge. At present, conversions cost about as much as a new build. Our job is to solve this dilemma through efficient and thoughtful design, but we need development partners to be on the same page as us, knowing where to focus to make it work.
At the outset of any conversion, we analyze each individual site and tailor our process to align with the existing elements that make it unique. Working with what you have, our designs and deliverables – plans, units, systems narratives, pricing, and jurisdictional incentives – are custom-fit.
To better understand if adaptive reuse is right for your building, get in touch with us. We can guide you through the feasibility study process.
To see how we’ve successfully converted other buildings into housing, take a look at our ‘retro residential conversion’ case study.

By Jennifer Sobieraj Sanin, Housing Studio Design Director.
Contact: +1 (206)-576-1600 | jennifers@ankrommoisan.com
New Code Increases Accessibility
Background
At Ankrom Moisan, we work hard to ensure an equal experience for all users of the spaces we design. We explore how to push beyond the expected with accessibility features on projects like Wynne Watts Commons, and we welcome updated codes and standards to address the needs of our community. As the 2021 Building Code takes effect in each jurisdiction, the embedded 2017 A117.1 Standard for Accessible and Usable Buildings and Facilities also takes effect. The new 2017 A117.1 provides significant updates to accessibility clearances based on a study of wheelchair users. The A117.1 is developed by the International Code Council (same authors as the International Building Code). Their challenge is to find the best design criteria for a wide range of abilities, from wheelchair users to standing persons with back problems to persons with low vision or hearing challenges. Ankrom Moisan has participated in their process as an “interested party” in one issue, kitchen outlets, and can attest to the countless hours that go into just one requirement.
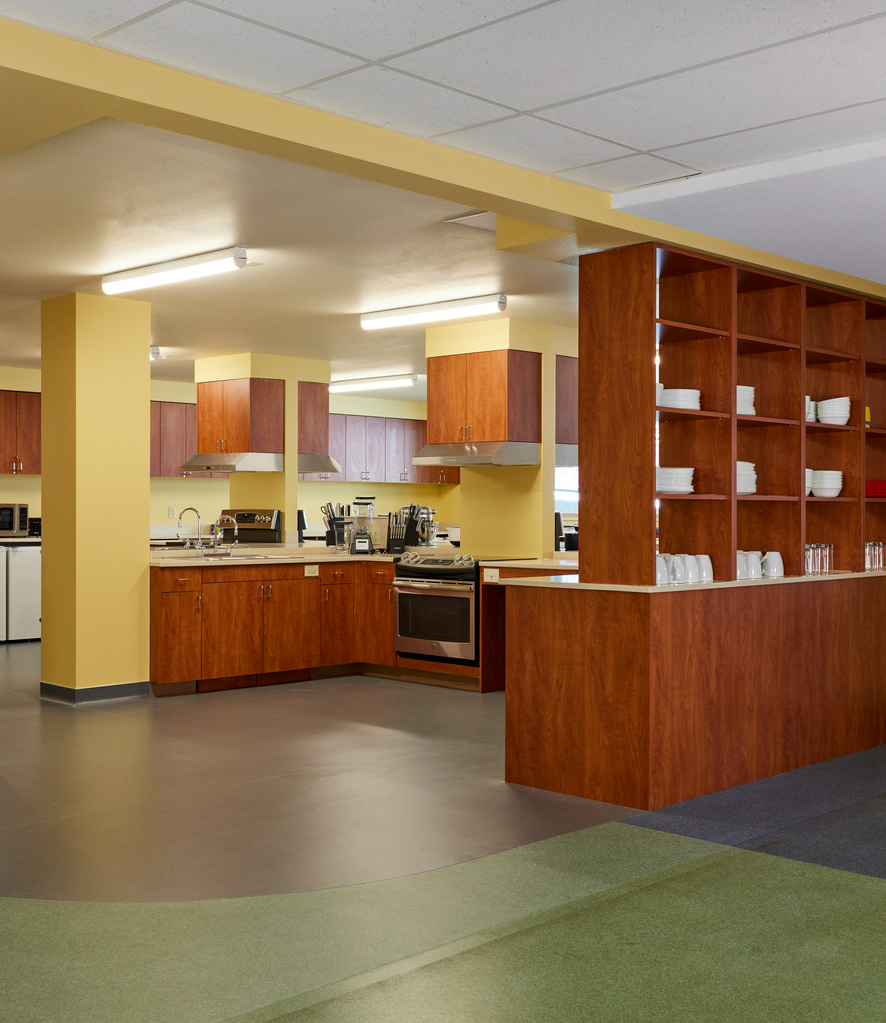 At the Ronald McDonald House expansion we wanted to make all families staying for short or long stays be able to use all the amenities, including the common kitchens.
At the Ronald McDonald House expansion we wanted to make all families staying for short or long stays be able to use all the amenities, including the common kitchens.
Changes
Overall impacts to projects by this change are modest, resulting in a few rooms being enlarged by a few inches. While the changes are minimal to buildings, they provide much higher levels of accessibility for impacted users. The most impactful updates are changes to the following requirements:
- In most cases, clear floor spaces grow from 30-inch by 48-inch to 30-inch by 52-inch.
- The turning circle that was a 60-inch “wedding cake” with knee and toe clearance all around is now a 67-inch cylinder with minimal knee and toe clearance.
When looking at a typical privately funded apartment building, the changes are minimal as long as they are understood at the start of the project. There are no changes to Type B units (except new exceptions for kitchens outlets were added), and for the Type A units, the kitchen, bathroom, and walk-in closet may grow a few inches. The trash chute access room will see the biggest change, growing up to 7” in both directions. All these changes are minor when incorporated into the initial design of the building but could be very tricky late in the design process.
There are still some unknowns; If there are Accessible units in a project, they will now require windows to be fully accessible. While the height and clear floor space requirements are easy to meet, we are still searching for a window style and manufacturer that can meet the requirements that windows are operable without tight grasping and less than 5 pounds of pressure to open and lock/unlock.
Our work isn’t done; kitchen outlets were simplified in the corners where a range and refrigerator protrude past the counter with this code cycle, but we must wait for the next A117.1 cycle for kitchen outlets to no longer dictate kitchen design. Ankrom Moisan submitted code changes that are now in effect in the 2022 Oregon Structural Specialty Code and submitted a proposal for the next version of A117.1 and can report that kitchen outlets will no longer drive design or require any special design or construction features in the next code cycle.
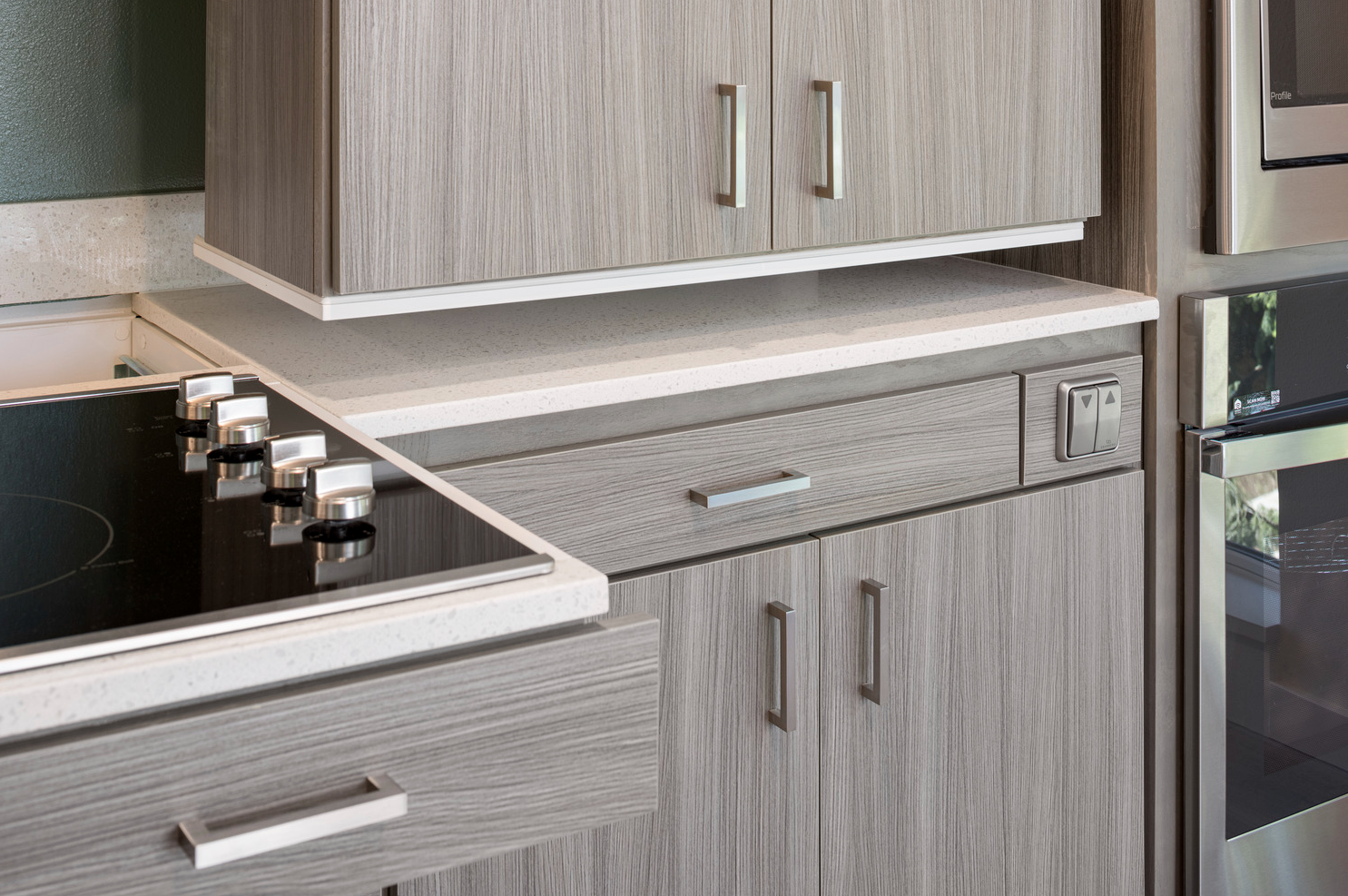 At the Wynne Watts Commons the team provided universal design residential units that included cooktops that pull out and upper cabinets lower with the controls shown in the cabinet front.
At the Wynne Watts Commons the team provided universal design residential units that included cooktops that pull out and upper cabinets lower with the controls shown in the cabinet front.
Added complexity with new code change
From a designer’s perspective, the requirements of accessibility have grown exceptionally complex. For example, under the new A117.1, there are now different size clearances for new and existing as well as Type A and Type B units, and the definition of “existing” in the A117.1 does not match the definition in the building code. This adds to the already confusing accessibility requirements that require us to reference multiple documents for any given item (building code with unique amendments by jurisdiction, Americans with Disabilities Act, Fair Housing Act, etc.). Coupled with different interpretations from different experts and code officials it is no wonder why accessibility requirements feel a bit daunting to us and our clients. As an example, California does not adopt the A117.1 but rather chooses to write its own Chapter 11 of the building code with its own unique scoping and technical criteria. And that is just accessibility, our Architects are juggling fire life safety, energy code, constructability, and our client’s budget all while creating great places where communities thrive.
As a firm, we had a challenge to overcome; the new accessibility requirements do not apply to all our projects at the same time. Depending on where they are in the permitting process and the jurisdiction they are in, every project must determine when, and if, they are required to flip to the new code. While most of our projects will be using the new code by early 2024, many will still be under the old code for years to come. We had to develop Revit resources for our project teams that could work for both codes at the same time. Our Accessibility experts partnered with our BIM team to develop a system meeting these goals and requirements:
- It had to be as simple and easy to use as possible for our project teams.
- It had to be blatantly obvious, by a quick glance within Revit, what codes were being shown on any given project.
- It had to provide all the options now allowed by the standards and guide teams to pick the applicable option.
Our solution to this challenge was rolled out to our project teams in September 2022 and provided over 500 updated Revit families.
Below is our graphic of the changes to the A117.1 that affect AM projects. The orange color helps all team members quickly identify the new families are being used.
We have found so many nuances in the accessibility codes that it can be hard to make generic statements. We would love to talk to you about your specific project or topic. Please reach out to Cara Godwin at carag@ankrommoisan.com to learn about accessibility for your project.
* Originally published October 6, 2022, updated 12/01/2023

by Cara Godwin, Senior Associate
Developers Are Setting Their Sights on Redmond, WA
Developers are setting their sights on Redmond, WA, and for good reason; the area is experiencing a rapid transformation resulting in unique development opportunities. Thanks to a comprehensive growth plan from the city, a strong employment base, increasing transportation options, and excellent recreational amenities, Redmond is a highly desirable location.
However, the opportunities in Redmond are not without obstacles. The challenging regulatory environment makes development in Redmond unpredictable for teams without prior experience. Complicated review processes and new zoning rules make familiarity with the proposed code changes essential to success.
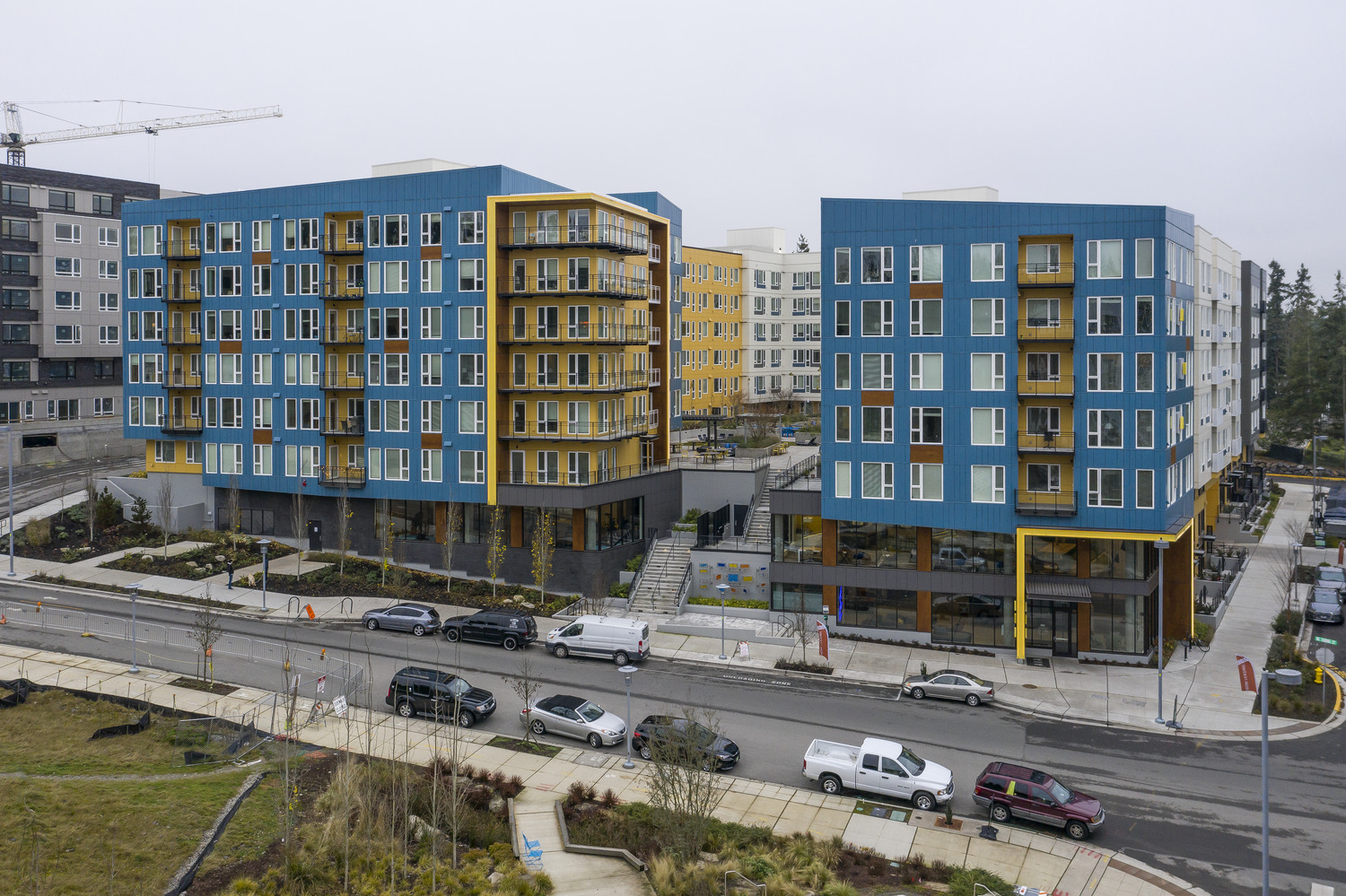

Avalon Esterra Park
The draw of Redmond.
Strong employment base. Home to campuses for Microsoft, Meta, and Nintendo, Redmond has strong employment in the tech sector and a high Average Median Income (AMI). As a result, rents are high (almost equivalent to Bellevue and Seattle) but the market is still less developed, and many low-density central sites remain.
Increased transportation and connectivity. With the East Link Light Rail stations nearing completion (expected to open in 2025), Redmond will soon be well connected to the rest of the region, making it a more desirable community to commute to and from.
High livability. Another draw to the area is the large—and growing—collection of urban amenities, including public parks and trails. Redmond is one of a small number of cities designated as a Bicycle Friendly Community—thanks to an extensive network of on-street bike lanes and off-street trails providing easy access to downtown, neighborhoods, and even to other cities. Nearing completion is the already-popular Redmond Central Connector Trail, a 3.9-mile trail corridor linking Redmond neighborhoods. Redmond is proving to be a highly livable location and is an increasingly popular alternative for Seattleites looking to escape the urban blight issues common in Seattle. There is currently a 3% lower vacancy rate in Redmond than in downtown Seattle or Tacoma: Redmond vacancy is on par with strong submarkets like Bellevue and Ballard.

Aloft & Element Hotels
Opportunities to keep an eye on.
Upzones. Redmond is currently working on updates to their comprehensive plan and is showing considerable upzones in the Overlake area and Downtown. Redmond’s growth targets are significant, and the city is actively creating opportunities for a substantial number of new households to be added to the area in the coming years.
Increased FAR. We are already seeing much higher height limits and Floor Area Ratio (FAR) proposed in Downtown and Overlake. Now is a good time to start studying sites in these upzoned areas.
Available land. Existing landowners are studying and planning for development with the upzones and some will be looking to sell entitlements and available land.
How our Redmond expertise can help.
Navigating incentives. The new code has many possible incentives for development, many add substantial costs or have implementation challenges that have not been resolved, and the tiered structure is difficult to understand. We can help you select incentives that are right for your needs.
Relationships. We have personal contacts with Redmond City staff and an established rapport. We are also connected with Geotech consultants, cultural resource consultants, land use attorneys, and various specialty consultants required to get a project approved in Redmond.
Experience with new code. We have studied the implications of new code, attending meetings, following the code changes, and providing comments on behalf of owners.
Our Redmond experience.
Entitlements:
We have significant recent experience in entitling sites throughout the city. A few examples:
- Avalon Esterra Park Blocks 4 and 7: 482 units: built
- Dual Brand Hotel Aloft/Element Hotel, 150/131 keys: built
- Avalon AVA, 386 units: built
- KGIP 16701 Cleveland, 125 units: in design
- Vega, 350 units: under construction
- Overlake East, 798 units: in design

Aloft & Element Hotels
Modifying entitlements:
We have recent experience modifying existing entitlements to suit new owners—troubled development properties are great opportunities.
Vega. This 350-unit development was modified from a prior SPE approval. Our client Alliance took over a previously entitled site that was not well designed for the market. We redesigned the development and modified the entitlement, cutting a year out of schedule from an entitlement that would have started from scratch.
Avalon Esterra Park. In 2011, as the current wave of development was just beginning, we were brought in to design Blocks 4 and 7 of what is now known as Esterra Park. Adjacent to the upcoming light rail station, this site is prominent, and our design work there became the precedent for an entirely new neighborhood. Our expertise helped inform the master developer and allowed them to successfully respond to market realities. We pivoted from a roughly equal mix of office and residential uses in the originally approved Esterra Park master plan to one that heavily favored residential development in the built Esterra Park. Our work on Esterra Park also helped set a materials precedent that has proved beneficial for the developer and the city. We worked closely with the owner, contractor, and suppliers to educate the city staff about the current cladding performance of fiber cement siding to give the city quality buildings at a price point that the developers could afford.

Esterra Park
Ground-up multifamily:
We have recent experience building multifamily in Redmond for multiple developers. A few examples:
- Vega, currently under construction
- Overlake East, Phase 1 and 2, projected start of construction, Q1 2025
- Three projects that are built with AvalonBay Communities

Overlake East
Feasibility studies:
We are familiar with the proposed upcoming upzones and have studied sites in detail with the new land use code which is not yet in effect and have had conversations with the city about adopting these standards early if applicable.
Master planning:
We have experience with the master-planning process required for large multi-building sites, which there are many opportunities for in the Redmond Overlake area. Our projects with AvalonBay were the first to test the newly adopted master plan for the Overlake Hospital site. Overlake East is three phase project with first two phases mixed use multifamily, third phase optional multifamily or office building, 798 units in total.
Want to know more? Get in touch with us:

David Kelley, Executive Vice President, AIA, NCARB, LEED AP

JP Emery, Principal, NCARB, MBA

Joe Tucker, Principal, AIA, NCARB
New Seattle Development Design Review Exemptions
The City Council has amended the land use code to make two important changes to the design review program aimed at encouraging additional low-income housing. The first change permanently exempts low-income housing projects from the Design Review program. The second change provides a new Design Review exemption for projects that meet Mandatory Housing Affordability (MHA) requirements by providing units on site via the Performance Option under the Land Use Code. Projects that opt into the Performance Option can skip MUP and Design Review and proceed directly to Building Permit where land use code compliance will be evaluated concurrently with other review subjects.
Expediated Timelines:
Bypassing Design Review and MUP milestones could yield significant time and cost saving on project delivery.
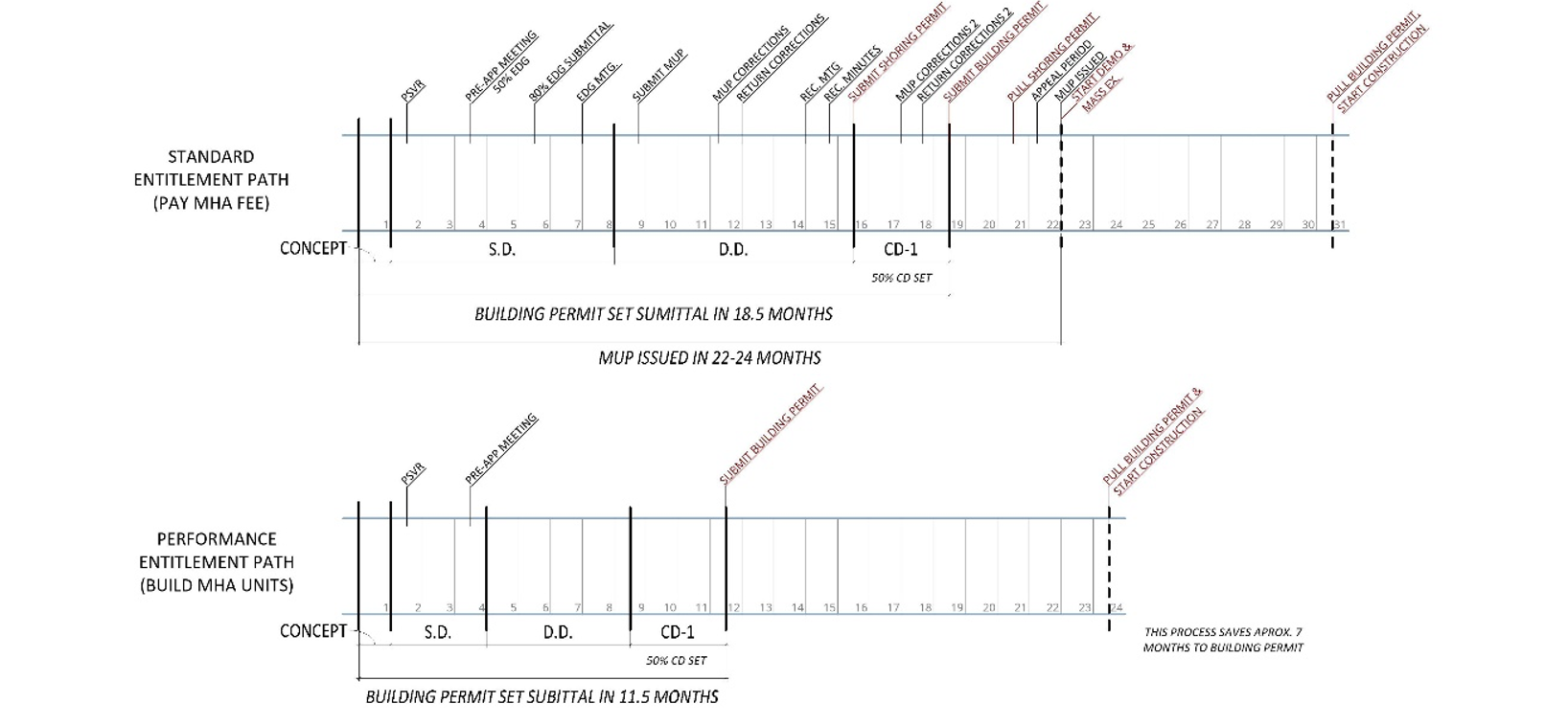
Schedule comparisons showing how fast the entitlements process can be if MHA units are provided instead of the ‘payment in lieu.’
Calculating the Number of Affordable Housing Units Required to avoid Design Review:
If a project contains commercial space, the area dedicated to affordable units required to satisfy the Performance Option is calculated as a percentage of the overall applicable area in commercial use. If a project contains residential space, the required number of affordable units is calculated as a percentage of the total number of dwelling units in the project. Developments that contain both commercial and residential space will use a combination of both calculation methods.
Performance Amount for Commercial Development:
The net unit area of affordable housing required to comply with Performance Option is outlined in Tables A&B for SMC 23.58B.050. The required square footage set-aside for affordable units varies respectively by zone, MHA suffix (M/M1/M2), and performance area intensity as noted in Map A for SMC 23.58C.050. For most zones, the area of affordable housing required ranges between 5-9% of the applicable commercial floor area.
Performance Amount for Residential Development:
The number of affordable housing units required to comply with Performance Option is outlined in Tables A&B for SMC 23.58C.050. The required percentage set-aside similarly varies respectively by zone, MHA suffix (M/M1/M2), and performance area intensity as noted in Map A for SMC 23.58C.050. For most zones, the number of affordable housing units required ranges between 5-11% of the total number of units to be developed in each structure.
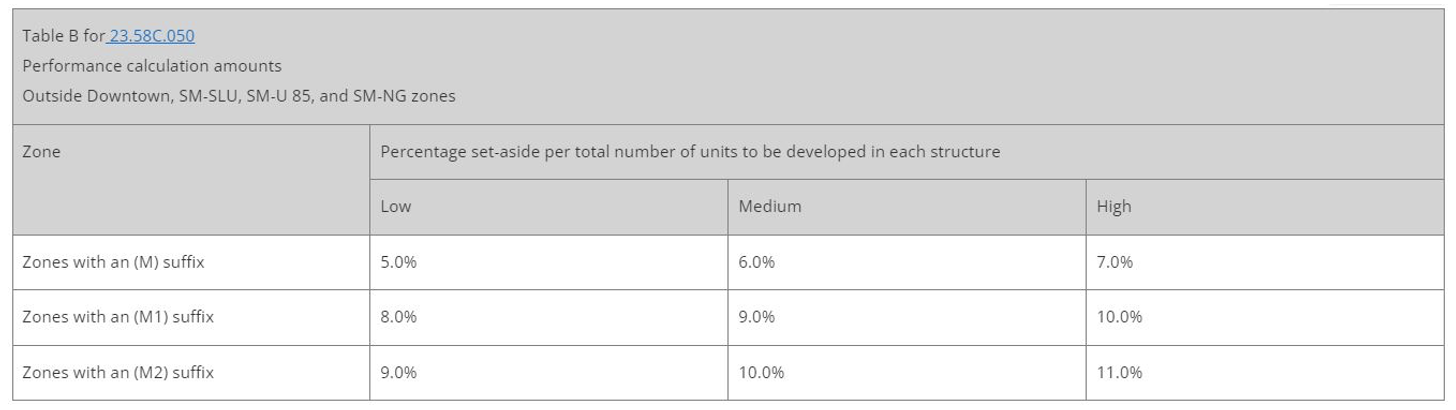
Table from the Seattle municipal code indicating how many units need to be affordable for a project to be exempt from development design review.
Performance Standards for Qualifying Affordable Units:
Duration: Units provided to comply with the Performance Option must remain affordable for 75 years from the date of certificate of occupancy.
Distribution & Comparability: Units provided to satisfy the Performance Option must be generally distributed throughout the structure and be comparable to other units in terms of: Type of dwelling unit such as live-work unit or congregate residence sleeping room; Number and size of bedrooms and bathrooms; Net unit area; Access to amenity areas; Functionality; and Lease term.
Eligibility: Household eligibility varies with unit size and rental date.
At initial occupancy (lease-up), units with a net area of 400 sf or less are eligible to households with incomes up to 40% of AMI. Units with a net area greater than 400 sf are eligible to households with incomes up to 60% of AMI.
Thereafter at annual certification, units with a net area of 400 sf or less are eligible to households with incomes up to 60% of AMI. Units with a net area greater than 400 sf are eligible to households with incomes up to 80% of AMI.
Public Subsidy: Affordable housing units provided to satisfy the requirements of the Performance Option may NOT be used to earn public subsidy such as through the Multifamily Housing Property Tax Exemption (MFTE Program).
Rent Levels: Monthly rents for units with a net area of 400 sf or less, shall not exceed 30% of 40% of AMI. Monthly rents for units with a net area greater than 400 sf, shall not exceed 30% of 60% of AMI. “Monthly rent” must include a utility allowance for heat, gas, electricity, water, sewer, and refuse collection, as well as any recurring fees that are required as a condition of tenancy.
Annual Certification, Third Party Verification: Every year an owner of the rental unit must obtain from each tenant a certification of household size and income. Owners of rental units shall attempt to obtain third party verification whenever possible to substantiate income at each certification, which shall include contacting the individual income source(s) supplied by the household. If written or oral third-party documentation is not available, the owner may accept original documents (pay stubs, W-2, etc.) At the discretion of the Director of Housing, the owner may accept tenant self-certifications after the initial income verification and first annual recertification. The owner shall maintain all certifications and documentation obtained on file for at least six years after they are obtained.
Reporting: Once a year the owner of the rental unit shall submit a written report to the Director of Housing, verified upon oath, demonstrating compliance with Chapter 23.58C. The written report shall state: the occupancy and vacancy of each rental unit, the monthly rent charged for the unit, and the income and size of the household occupying the unit. The Director of Housing may require other documentation to ensure compliance including documentation of rents, copies of tenant certifications, documentation supporting determinations of tenant income including employer’s verification or check stubs, and other documentation necessary to track program outcomes and the demographics of households served. The owner of the rental unit shall pay the Office of Housing an annual fee of $150 per rental unit for the purposes of monitoring compliance with the requirements.


By Jennifer Sobieraj Sanin, Managing Design Principal, and Michael Lama, Project Designer
Getting a Parent’s Perspective on Student Housing
2023 has been a big year for Matt Janssen. With his youngest leaving for college, it was the first year both of his kids were out of the house. What’s more, they both moved into student housing projects that Ankrom Moisan designed.
Matt, a Design Principal at AM, recently sat down and talked to us about what it was like to view these projects from a fresh, and intimate, perspective—as a parent of a resident.
Q: Over the summer you moved your son into Union on Broadway. What was that experience like?
A: Walking into an Ankrom Moisan project I’ve worked on is always special, but this visit was especially meaningful. As we entered Union on Broadway, I remember we gave each other anxious looks. Here he was, a University of Oregon freshman who had just been given a job on the Duck football team and was now moving out of the house to live alone for the first time in his life. He was nervous. I was even more nervous.
Union on Broadway
Q: What were you thinking then?
A: I recall thinking about all the aspects of the design that I hoped he would get to enjoy. As we walked through the amenity space on the twelfth floor, I wondered if he had brought a swimsuit to use the hot tub after his long days at Autzen Stadium. As I watched him get settled in his new studio apartment, I noticed his anxiety quickly being replaced by excitement, and I knew this was the perfect place for him to begin his next chapter.
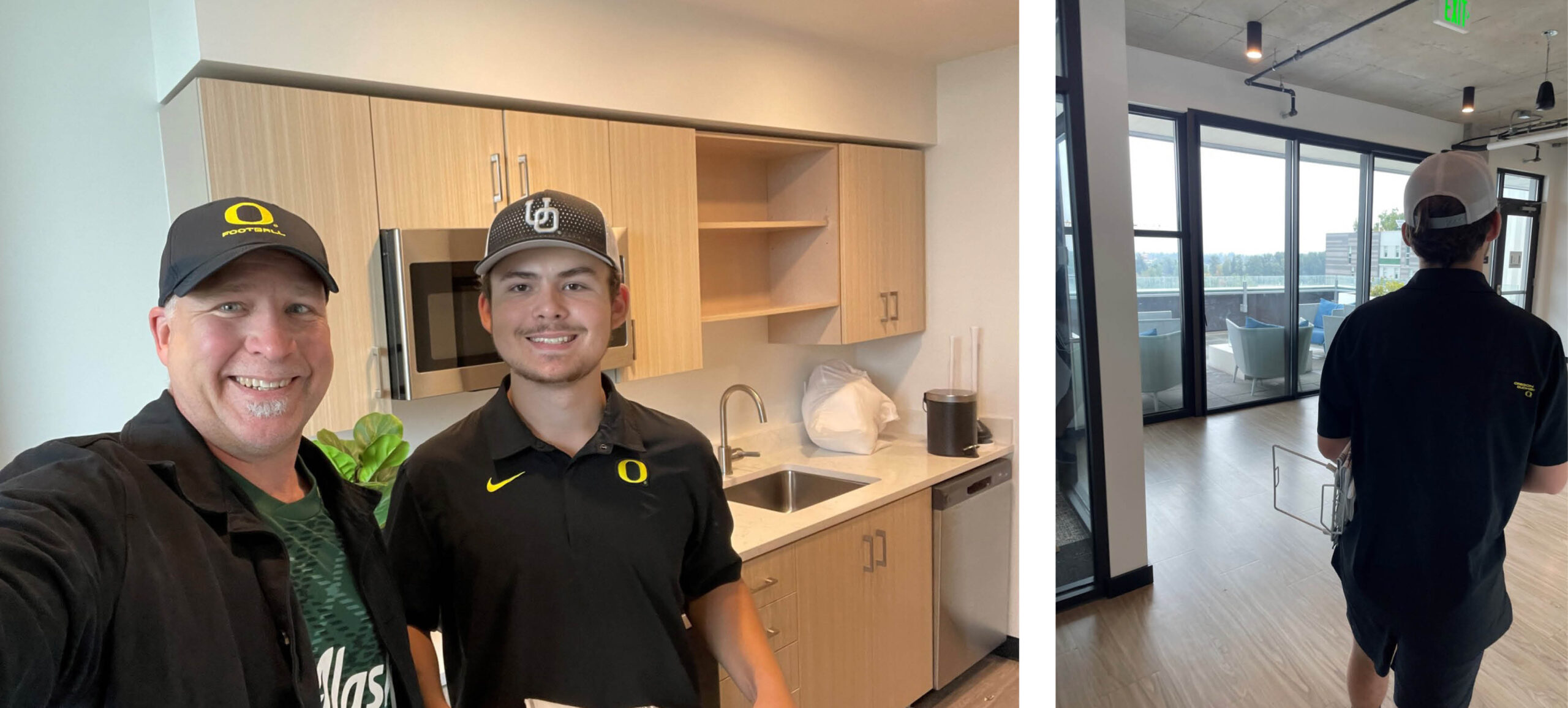

Matt and his son at Union on Broadway
Q: And just a few months later your eldest moved into The Standard at Seattle. That was a significant project for you, wasn’t it?
A: Yes. I started designing The Standard at Seattle, the largest project of my architectural career, in the fall of 2018. A new client, Landmark Properties, had asked AM to design a comprehensive student housing community in Seattle’s U-District, next to the University of Washington. It was a really exciting opportunity.
Q: What was it like to not only see it completed but to also get to move one of your children into the community?
A: Almost exactly five years after starting the project, I got to walk through the heart of the project—an urban mid-block pedestrian corridor that weaves between the twin 25-story towers—with my eldest. That was a special moment. I had seen that view of the project so many times before, but only through virtual reality glasses in our office.
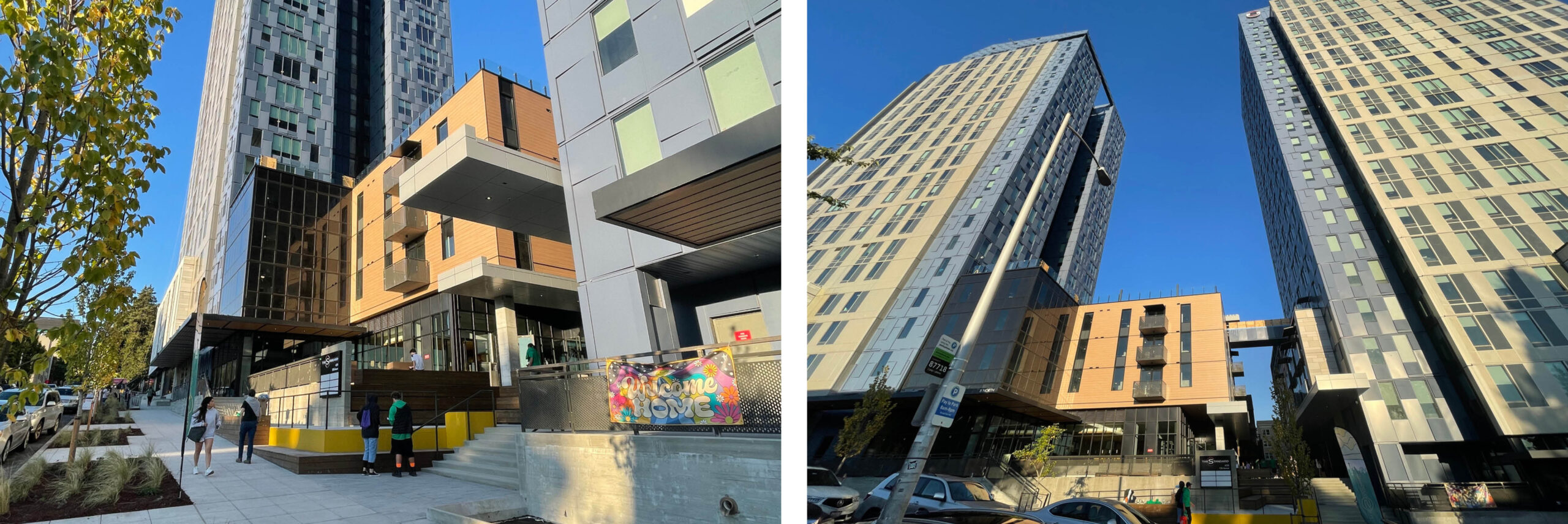

The Standard at Seattle
This is their last year at the University of Washington and their first time living off campus. A myriad of people helped us get everything up to the apartment and I remember after they left we all just looked at each other. “This place is incredible!” That made me smile and feel good that this was going to be the perfect ending to a wonderful University of Washington experience.
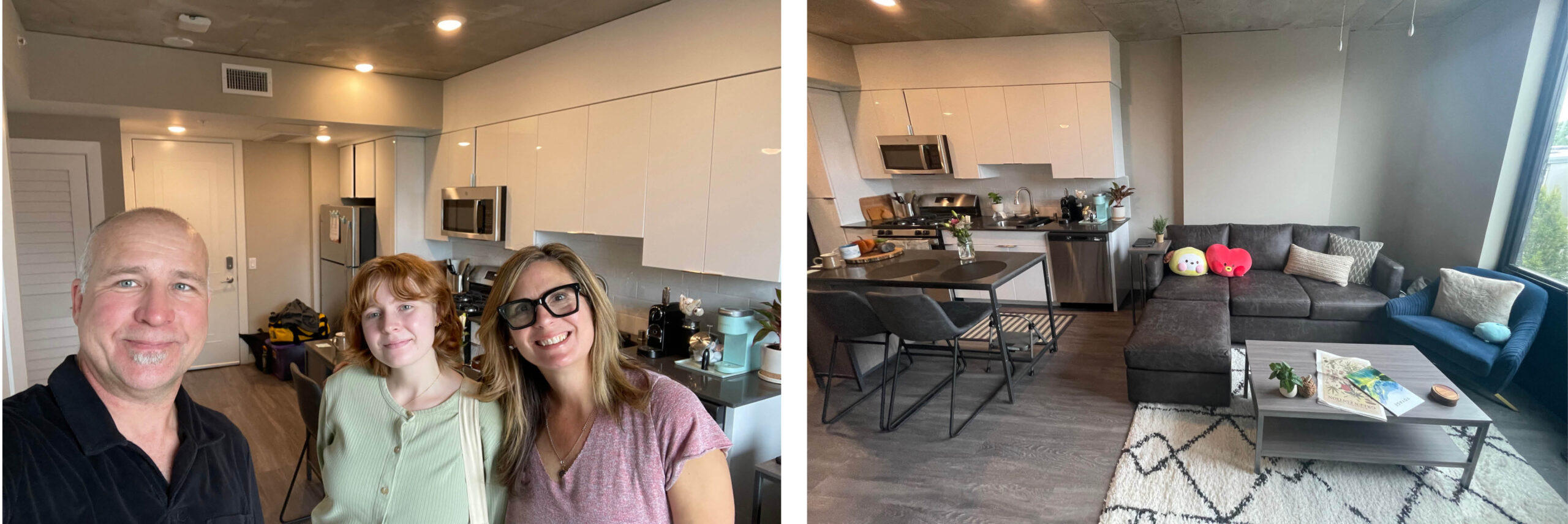

Matt and his family at The Standard at Seattle

By Matt Janssen, Design Principal
Creating Active Environments within Senior Living Communities
Creating senior living communities with more “active adult” opportunities for residents to engage in is a smart and viable option for many communities. This design concept helps motivate seniors to become more independent and active, encourages socialization among residents, and offers conveniences to staff members at facilities with ongoing staff shortages.
Interested in learning about our design solutions for active communities? Read the full article, written by Jason Erdahl, Principal and Director of Senior Communities at Ankrom Moisan, on Seniors Housing Business. Or continue reading here for a brief summary.
Connection through nature and socialization
The idea of incorporating active environments into assisted living properties is heavily inspired by lifestyle, learning and wellness amenities. When designing these spaces, it is important to offer a variety of choices and to incorporate areas that encourage socialization, connection and spaces that improve one’s well-being. Some of these areas include cafes, theaters and arts and crafts rooms, as well as health and wellness centers with exercise rooms, aerobics spaces and swimming pools. When creating these active environments for seniors, it is also important to incorporate elements of nature. For example, biophilic elements help support physical and mental wellness with access to the outdoors, natural light, fresh air and materials that are found locally with healthy qualities.

Strategically locate amenities
The location of these amenities also helps play a role in promoting an active lifestyle for seniors. A popular design choice many architects and designers integrate within senior living are hubs. These hubs create a centralized grouping of amenities to foster socialization and activity while creating convenience and easy access for residents. The hubs typically contain all the amenities within one area including food services, entertainment, and health and wellness programs.
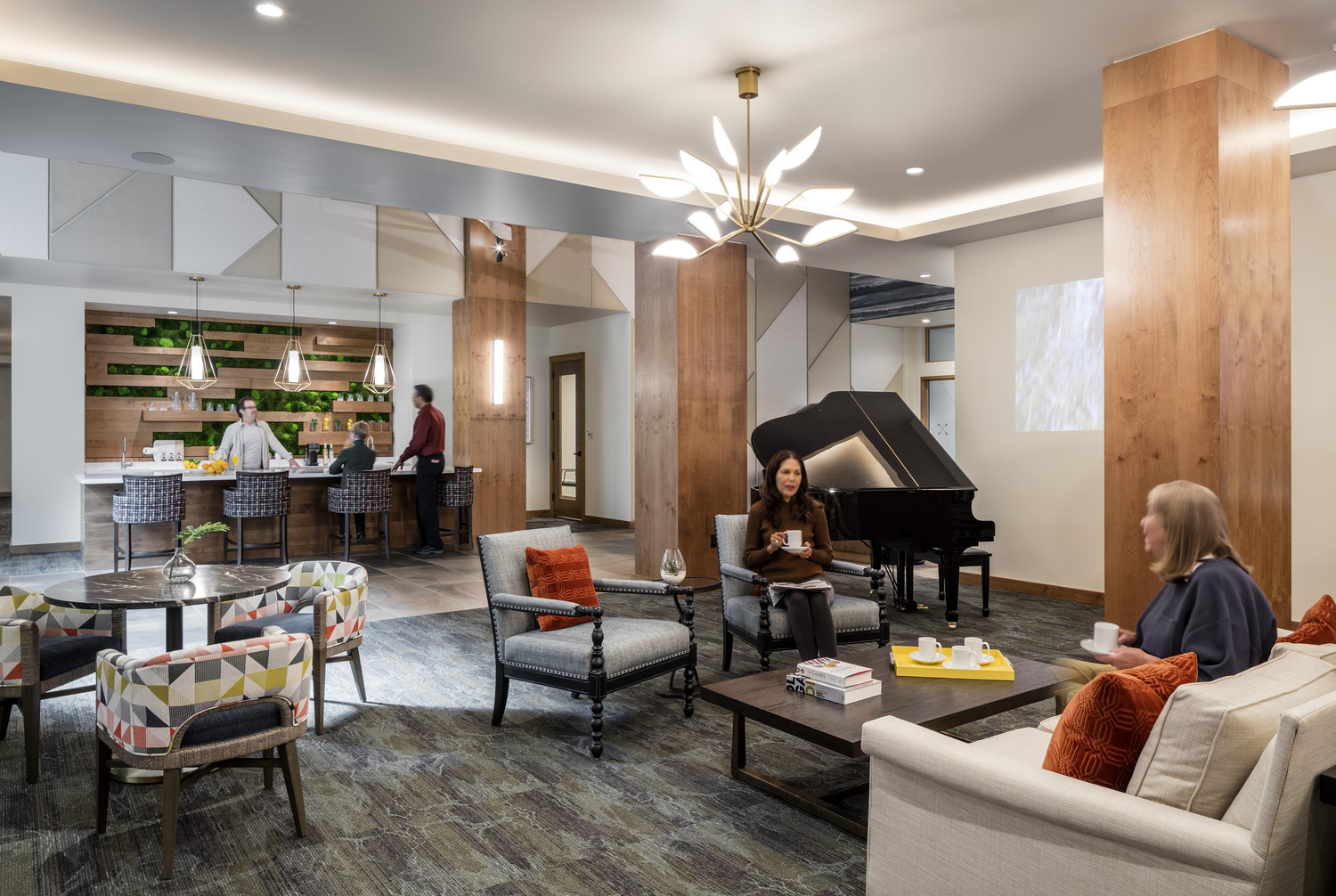

Be adaptable and versatile
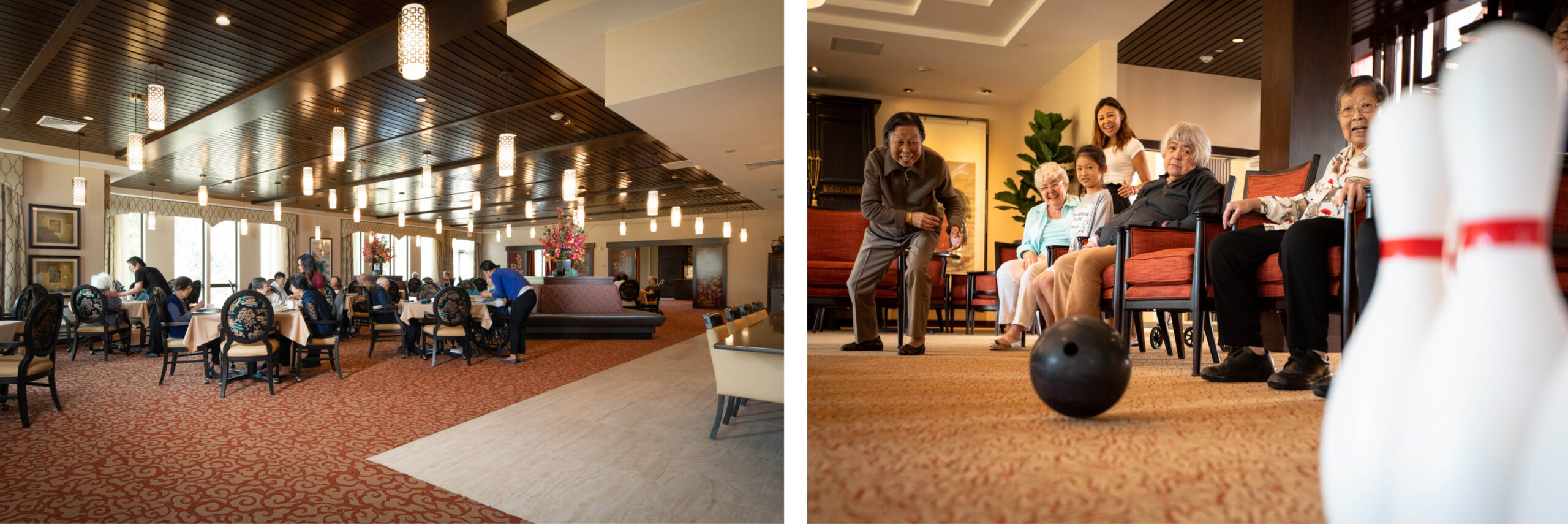
In low-acuity care settings, architects and designers must take into account that these spaces are designed for those who are aging. Therefore, creating spaces that are flexible, adaptable and allow for diversity in capability is paramount.
Specifically, when designing activity and amenity spaces, flexibility is key as many buildings do not have the space to accommodate all of the activities that might be beneficial for the residents. Providing common spaces for amenities that can change and adapt throughout the day allows staff and residents to have more fulfilling experiences. For example, a common room can host yoga classes in the morning and then bingo that afternoon.

Build tech-savvy spaces
Technology plays a huge role in senior living design and in encouraging residents to be more active. We are designing buildings with technology infrastructures, with both wired and wireless technologies, to accommodate the increase in device usage. Smart-home technologies and building automation for fixtures, appliances and systems allow residents to not only be more connected and engage in more fitness activities but feel safer with tech devices that monitor their health.
Read the full article on Seniors Housing Business >

By Jason Erdahl, Principal and Director of Senior Communities
The Art of Efficiency
Popularized because of their connection to nature and relative abundance of space, garden-style apartments are lower density, low-rise housing complexes that are typified by their green, garden-like surroundings. Through Ankrom Moisan’s experience designing high-quality low-density communities, we’ve found that successful garden-style design is all about striking a balance. There’s an art to creating a community that is highly livable and authentic, yet also efficient and economical. Based upon our expertise with this style of housing, here are our dos and don’ts for creating successful low-density garden-style communities.
Do capitalize on site assets.
Site plans are everything when it comes to designing unique low-density housing. Before any buildings are designed, take note of site features such as topography, open space, noteworthy views, and existing natural resources such as bodies of water or mature trees. Designing a site plan around these features elevates the design of a garden-style apartment community to be authentic to its location, setting the place apart as a destination with its own identity. For example, at Deveraux Glen the site plan intentionally takes advantage of the surrounding green space by orienting the buildings to maximize views. This is apparent in the irregular perimeter, shown below.
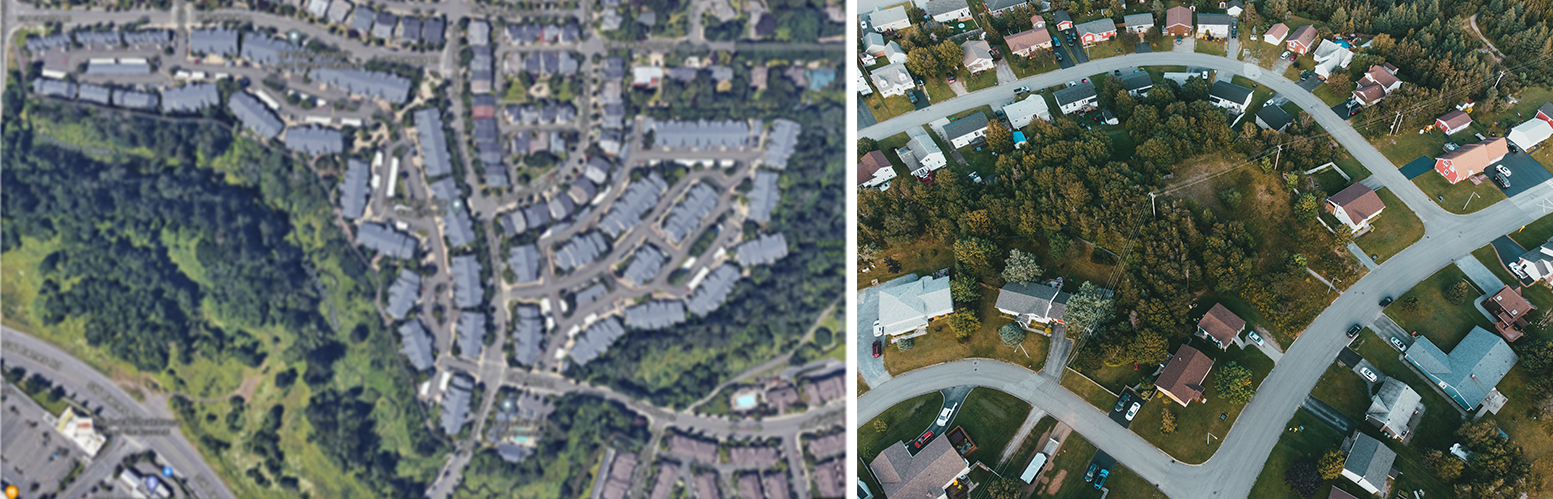

Deveraux Glen site plan | Aerial of a neighborhood by Erik Maclean
Do balance the parking.
While parking yield is important, preserving the character of the place is also essential for success. This requires finding a careful balance. Because available parking ratio ultimately determines home yield, and not allowable density, parking drives (pun intended) everything. Efficient footprints like parking must be designed first, with buildings fitting into the site afterwards and conforming to the lot’s parameters based on the home plan. However, that does not mean the parking lot has to be the focal point for a site’s layout. Remember: nobody wants to live in a parking lot. A certain degree of intentionality is required to design a desirable community that has a sense of place and doesn’t just feel like an asphalt lot.
North Ogden masterplan | Garden-style development photo by Maahid
Don’t neglect landscaping.
Use greenery to break up the humdrum of asphalt. Whenever possible, a space of 15 feet between parking and ground-level homes is ideal for garden-style, as it budgets 5 feet for the pedestrian sidewalk and 10 full feet for landscaping. There should also be landscaping between head-in parking stalls. 5 feet is the minimum amount of space recommended, but again, having more room for trees to be planted both screens the car park from above, and improves the quality of the space at ground level. Utilizing landscaping in this way improves the apartment’s sightlines and views for both the ground-floor homes that look towards the parking lot and the upper-story homes looking down on it. While covered parking may improve the visual landscape of a community, taking it a step further with green roofs or alternated landscaping does much more for both the environment and residents. The ultimate goal in garden-style design is to create a place that is as livable as possible to drive absorption, retention, and rent rates.

Club at the Park | Parking lot at The 206
Do consider walkability.
Since garden-style home doors are exterior-facing, the outdoor experience must be carefully considered. Distances between frequently visited areas need to take walkability into account. Remote parking may allow for an increase in home yield but result in a reduction in rent rate. Designers should be very intentional with how far residents will have to walk to get from their cars to their front door, and vice versa. Parking allocation studies need to be done to assign parking stalls to certain buildings and determine whether or not distances and available parking options realistically work. Trash enclosures, too, need to be within a reasonable distance from residential homes and located along a route accessible to trash collection vehicles for removal. By putting forethought into residents’ travel patterns, designers can create a highly livable place.

Meridian Gardens rendering | Kitts Corner rendering
Do enhance ground-level homes.
Ground level living is perhaps the most important design consideration for low density garden-style apartments. There are a handful of ways to enhance first-floor ground-level homes, the most effective being the inclusion of a stoop at the entrance. Stoops help create a sense of defensible space, and resident identity. Ground level homes also benefit from street elements. Streets are characterized by parallel parking and sidewalks, whereas parking lots are based on 90-degree parking, which means that light from cars in parking lots are angled directly into ground-level windows and the amount of land dedicated to the car is the greatest. Ground-level homes often receive the short end of the stick, so giving those homes extra thought can go a long way for improving the resident experience.

Stoops at The Villas at Amberglen West | Ground-level porches at The Arbory
Don’t underestimate the importance of identity.
Develop an encompassing identity for the entire community through a central amenity. As the heart of the place, the amenity building reinforces the character of the site. Surrounding spaces should support that identity through the quality and character of their architecture and interior design. Don’t shortchange design fees here; It’s better to spend up on the club house and economize elsewhere than to forgo the identity established by a central amenity.
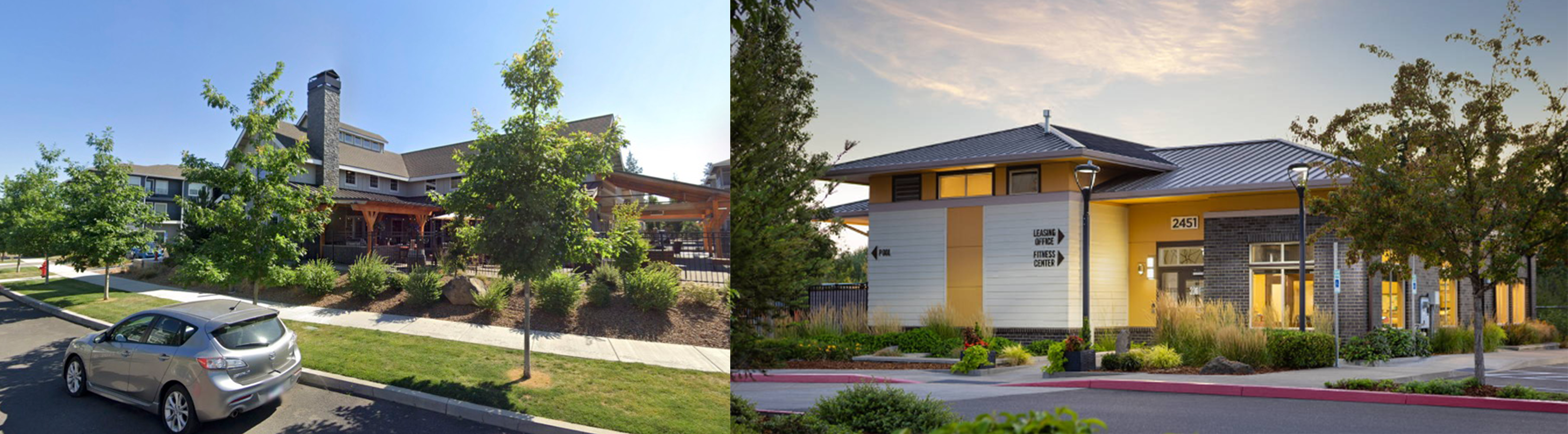

Clubhouse at Seasons Apartments and Farmington Reserve | Clubhouse at The 206
These guidelines are only a brief overview of some of the key principles to creating successful garden-style communities. There is a tremendous level of consideration of the specifics of a site when translating these principles into a successful design. What it all essentially comes down to is hiring an architect who understands these design principles and how to apply them to create efficient, high-quality communities. And of course, having beautifully maintained greenery doesn’t hurt, either.

By Don Sowieja, Principal-in-Charge
















