Over the last several years, more demand in smaller markets has resulted in increased proposals for larger scale developments. These jurisdictions have not previously had to review projects that utilize code criteria that are unique to larger building types.
From the construction permitting point of view, bigger buildings have different codes, and those codes have different interpretations from city to city, and sometimes reviewer to reviewer.
Jurisdictions are experts at the familiar but can often be resistant to the new. Given the role that building officials play in safeguarding the health, safety, and welfare of their community, a conservative approach to new code criteria is a reasonably common practice.
Our experience in jurisdictions with more complex code usage can help clients understand the way others have successfully worked with designers to implement unfamiliar strategies in code compliance.
Our expertise in larger buildings in bigger markets can be valuable with code analysis and interpretation in smaller markets, both from the designer and reviewers’ points of view.
We have consistently seen that building official/fire marshal engagement prior to submittal is key. Meeting early and often minimizes unforeseen issues arising during plan check review. Our history of discussions/solutions from multiple jurisdictions allows for specific issues to be flagged and addressed with real-world applications that have been proven to be successful.
We have found that when discussing podium construction there are several key elements to consider within the wood-framed components that differ from applications that do not include a concrete podium. Here are a few key items to consider:
- Type III: A wood construction with two-hour rated exterior walls, from the inside and out.
When building height exceeds 70 ft., this construction type allows for building heights up to 85 ft., and requires non-combustible exterior wall construction, commonly achieved through the use of fire-retardant treated lumber. Cladding and its support elements must also be non-combustible above 40 ft. Critical considerations include close study of the highest occupiable floor level based on fire access set-up point. If the lowest point of fire access results in a dimension to the highest occupiable floor level that exceeds 75 ft., then high-rise criteria become applicable. Cost typically limits high-rise construction to projects which far exceed 75 ft. height. Designers must consider this cost impact, especially when contemplating occupied roof decks, which some jurisdictions will allow to exceed the 75 ft. height, while others will not.
Project Example – Hudson on Farmer (Farmer Arts), Tempe, AZ (Framing construction, completed building)
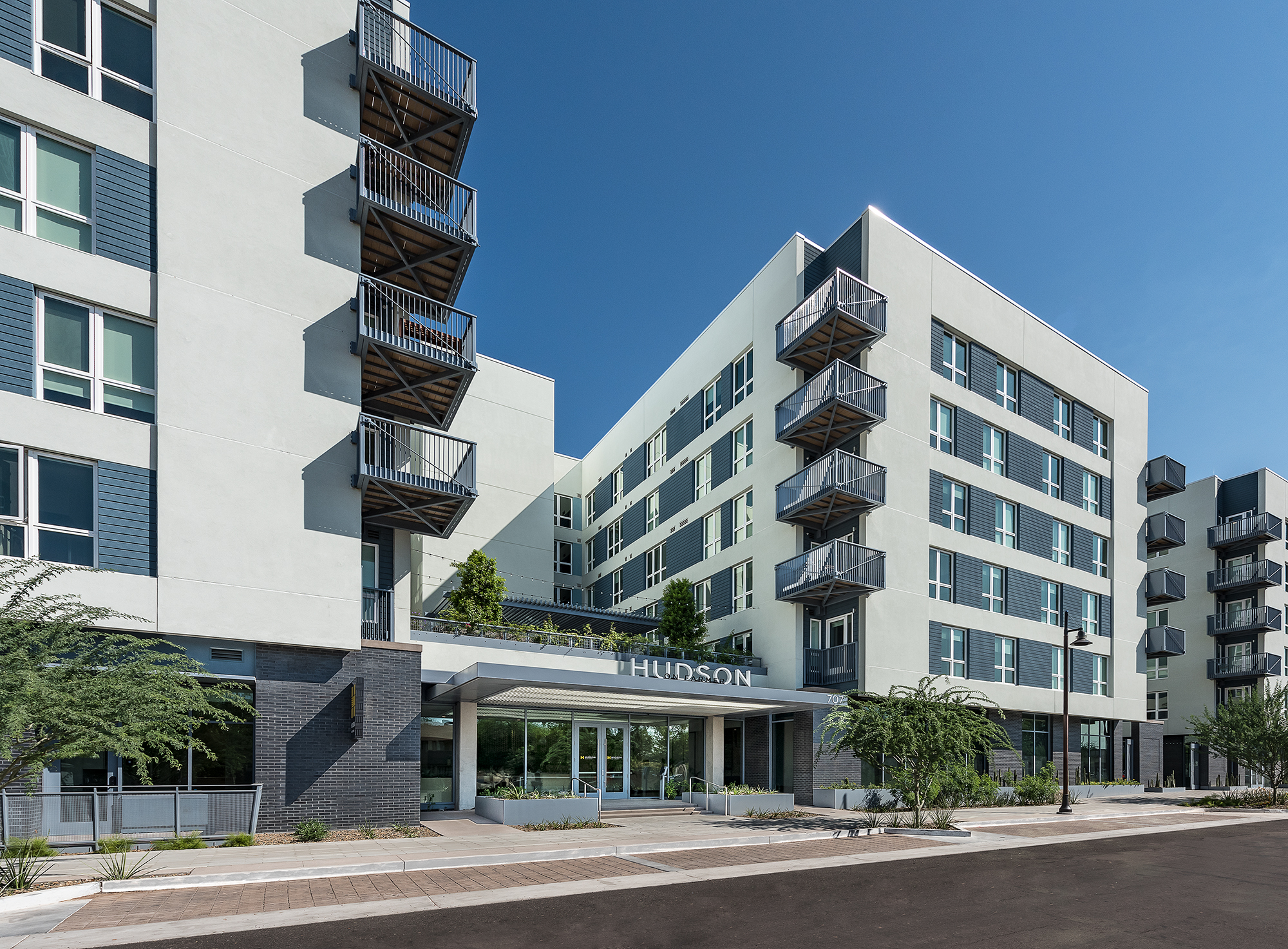


- Type V: A wood construction with one-hour rated exterior walls from the outside.
When construction does not exceed 70 ft. this construction type allows for reduced costs and more easily managed fire resistivity criteria. Building area is limited, and in many cases fire walls within the building are required to compartmentalize the structure. For multifamily buildings, corridors penetrate these walls requiring rated opening protection. Although these walls add cost, they provide an opportunity to reduce the number of stairwells when used as horizontal exits between building compartments. Designers must consider how, and when, to use the horizontal exit tool, ensuring that no more than half of the required exits from a floor level are provided by horizontal exits. Additionally, these opening assemblies can be provided via several options, including manufactured assemblies, and custom specified components. Designers must consider the comparative costs of the different approaches and the capacity of the project’s general contractor to manage the installation of the selected approach.
Project Example – Modera Northgate, Seattle, WA. (Final rendering, floor plan compartment diagram)

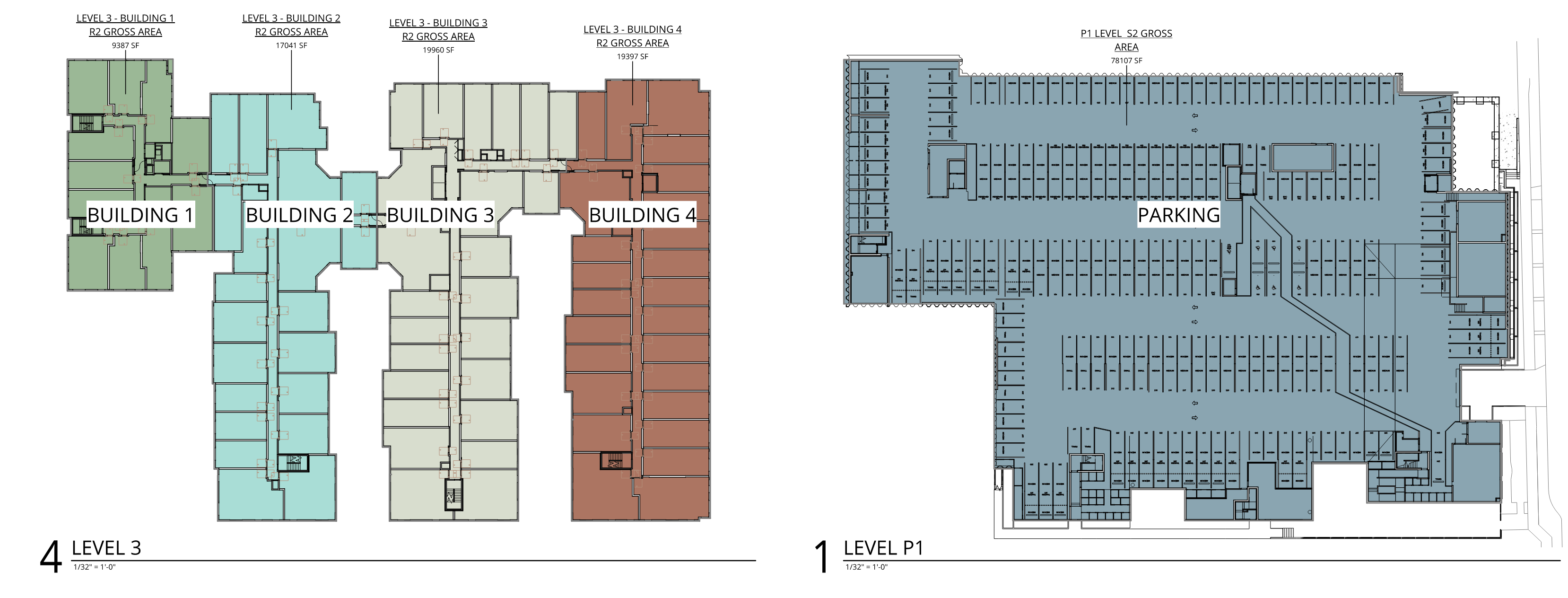
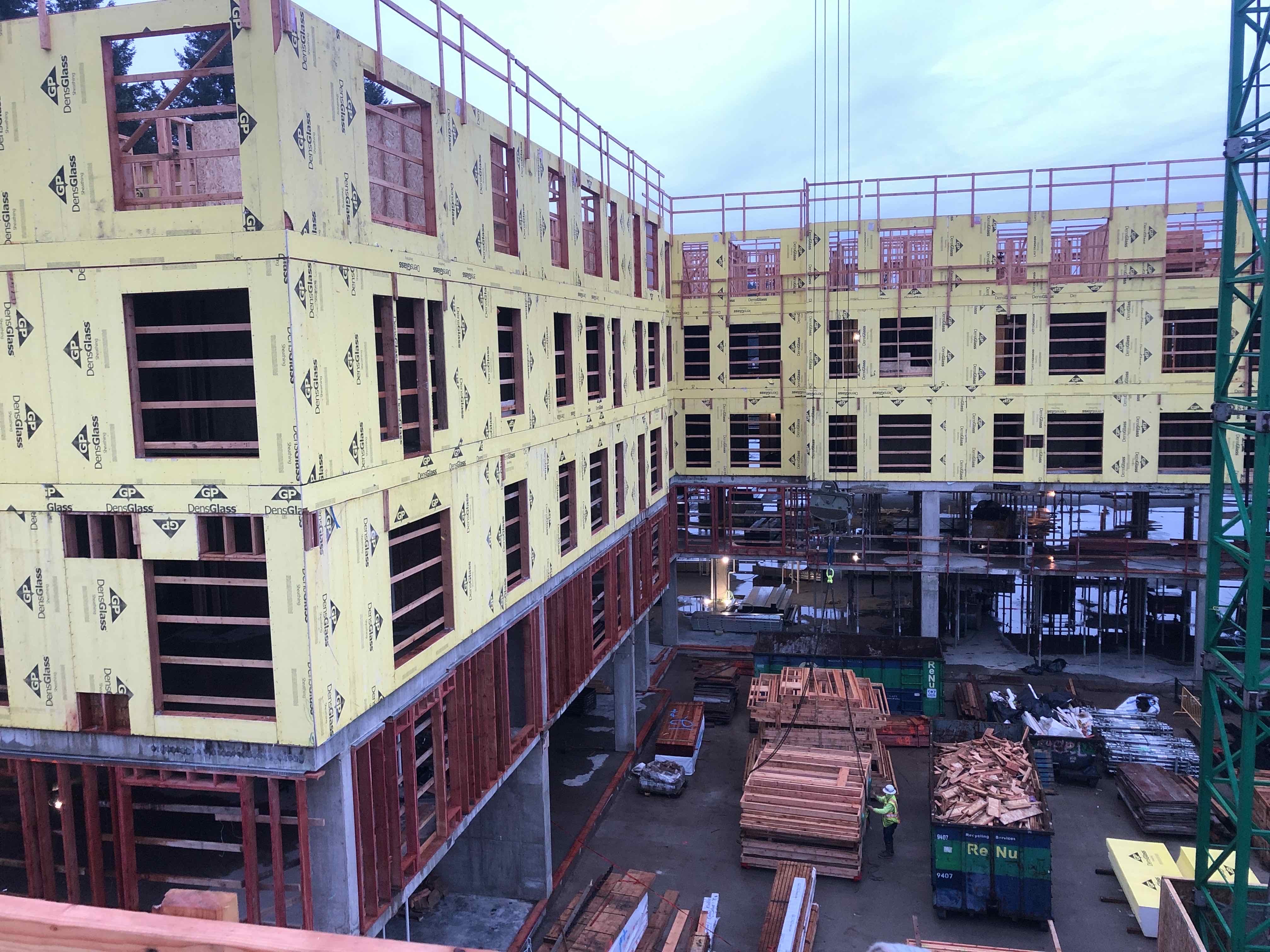
- Type I: Podium/basement non-combustible construction of one, two, or three levels can be provided as a podium for multiple stories of wood construction above.
The ability to allow for the wood frame construction type of the building above to penetrate the podium reduces costs when stairs are able to be built of wood. Exterior wall framing must be built of non-combustible framing, however, when using metal studs, exterior insulation is often required to meet energy code insulation values. Using fire-retardant treated lumber can be an effective tool in allowing for exterior sheathing and cladding planes to align across the podium level.
Project Example – Canopy (Shea Aurora) Phase II, Shoreline, WA (podium construction photo, final rendering)


There is no one-size-fits-all solution. However, being able to work from multiple points of view allows for specific concerns to be addressed, while looking to past successes for location-specific solutions.

by Don Sowieja, Principal AIA, NCARB